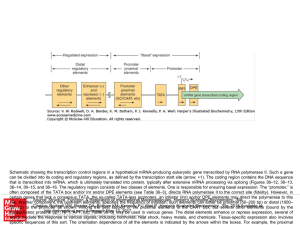
RNA polymerase
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 nucleotides; complementary to an mRNA codon. ...
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 nucleotides; complementary to an mRNA codon. ...
Cracking the PPR code: predicting and manipulating protein/RNA
... and everyone in the Barkan Lab ...
... and everyone in the Barkan Lab ...
Introduction to Molecular Biology
... Consist of thousands of DNA probes corresponding to different genes arranged as an array. Each probe (sometimes consisting of a short sequences of synthetic DNA) is complementary to a different mRNA (or cDNA) mRNA isolated from a tissue or cell type is converted to fluoroscently labeled mRNA or cDNA ...
... Consist of thousands of DNA probes corresponding to different genes arranged as an array. Each probe (sometimes consisting of a short sequences of synthetic DNA) is complementary to a different mRNA (or cDNA) mRNA isolated from a tissue or cell type is converted to fluoroscently labeled mRNA or cDNA ...
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES
... mRNA must be exported from the nucleus before it can be translated. This means that other factors being equal, protein synthesis in a prokaryote can be faster than in a eukaryote. It also means that the primary mRNA transcript can be processed before it is exported from the nucleus, with translation ...
... mRNA must be exported from the nucleus before it can be translated. This means that other factors being equal, protein synthesis in a prokaryote can be faster than in a eukaryote. It also means that the primary mRNA transcript can be processed before it is exported from the nucleus, with translation ...
2nd lesson Medical students Medical Biology
... information into RNA is known as transcription (TC), with the further conversion into protein being termed translation (TL). This concept of information flow is known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation ...
... information into RNA is known as transcription (TC), with the further conversion into protein being termed translation (TL). This concept of information flow is known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation ...
2nd lesson Medical students Medical Biology
... information into RNA is known as transcription (TC), with the further conversion into protein being termed translation (TL). This concept of information flow is known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation ...
... information into RNA is known as transcription (TC), with the further conversion into protein being termed translation (TL). This concept of information flow is known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation ...
Gene to protein
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
Ch 1617 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
Document
... And an intermediate phenotype is seen. At the molecular level, both functional and non-functional proteins are present. This is more like codominance. ...
... And an intermediate phenotype is seen. At the molecular level, both functional and non-functional proteins are present. This is more like codominance. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... And an intermediate phenotype is seen. At the molecular level, both functional and non-functional proteins are present. This is more like codominance. ...
... And an intermediate phenotype is seen. At the molecular level, both functional and non-functional proteins are present. This is more like codominance. ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... group, deoxyribose (a sugar with 5 carbon atoms) and a nitrogenous base. Alternating phosphate groups and sugars form the skeleton of the ...
... group, deoxyribose (a sugar with 5 carbon atoms) and a nitrogenous base. Alternating phosphate groups and sugars form the skeleton of the ...
DNA - hdueck
... Long single strand of RNA that has the coded complement from the DNA. Can fold back to form H-bonds with itself Brings the code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, specifically to ribosomes. ...
... Long single strand of RNA that has the coded complement from the DNA. Can fold back to form H-bonds with itself Brings the code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, specifically to ribosomes. ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... shown here and the codon chart in Figure 17.4 (page 313) in Biology, 7th edition to answer the next questions. Original template strand of DNA: 3 TAC GCA AGC AAT ACC GAC GAA 5 a. If this DNA strand produces an mRNA, what is the sequence of the mRNA? ________________________________________________ ...
... shown here and the codon chart in Figure 17.4 (page 313) in Biology, 7th edition to answer the next questions. Original template strand of DNA: 3 TAC GCA AGC AAT ACC GAC GAA 5 a. If this DNA strand produces an mRNA, what is the sequence of the mRNA? ________________________________________________ ...
scientists and philosophers find that gene has a multitude of meanings
... autoimmune disease, for example, or my hair, which looks like the fibers left behind on the rim of an aspirin bottle after the cotton ball has been removed, only wispier. Now it turns out that genes, per se, are simply too feeble to accept responsibility for much of anything. By the traditional defi ...
... autoimmune disease, for example, or my hair, which looks like the fibers left behind on the rim of an aspirin bottle after the cotton ball has been removed, only wispier. Now it turns out that genes, per se, are simply too feeble to accept responsibility for much of anything. By the traditional defi ...
Lecture_5
... What is gene expression? • The amount of RNA produced from a gene. • Level of RNA produced from a gene is controlled by: – Transcription – Degradation ...
... What is gene expression? • The amount of RNA produced from a gene. • Level of RNA produced from a gene is controlled by: – Transcription – Degradation ...
Transcription
... protein. *this occurs in a RIBOSOME* Figure 10.11A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... protein. *this occurs in a RIBOSOME* Figure 10.11A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 4 Cellular Metabolism
... where protein synthesis will occur. They lie across the __ribosome_ and wait for the ___transfer RNA to bring in the appropriate amino acids. The correct amino acids will be lined up because the tRNA bases are arranged in _anti-codons_ that are complementary to the __cocons_ of the bases of the mRNA ...
... where protein synthesis will occur. They lie across the __ribosome_ and wait for the ___transfer RNA to bring in the appropriate amino acids. The correct amino acids will be lined up because the tRNA bases are arranged in _anti-codons_ that are complementary to the __cocons_ of the bases of the mRNA ...
Section 7.2: Transcription: DNA
... 6. DNA Replication and Transcription DNA replication Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA polymerase 7. Answers may vary. Sample an ...
... 6. DNA Replication and Transcription DNA replication Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA polymerase 7. Answers may vary. Sample an ...
Applications of RNA minimum free energy computations
... sequences, which are processed from a stem-loop precursor by Dicer (Tuschl, 2003; Lim et al., 2003) – see Figure 1, which depicts the predicted secondary structure for C. elegans let-7 precursor RNA. MicroRNA is (approximately) the reverse complement of a portion of transcribed mRNA and has been sho ...
... sequences, which are processed from a stem-loop precursor by Dicer (Tuschl, 2003; Lim et al., 2003) – see Figure 1, which depicts the predicted secondary structure for C. elegans let-7 precursor RNA. MicroRNA is (approximately) the reverse complement of a portion of transcribed mRNA and has been sho ...
Poster
... RNA polymerase II is essential to life in cells. Found in the nucleus of a cell, this molecule is a multi‐subunit protein. RNA Pol II makes messenger RNA (mRNA) copies of genes. This process is called transcription and is the first step in protein synthesis. Genes are made of DNA and contain t ...
... RNA polymerase II is essential to life in cells. Found in the nucleus of a cell, this molecule is a multi‐subunit protein. RNA Pol II makes messenger RNA (mRNA) copies of genes. This process is called transcription and is the first step in protein synthesis. Genes are made of DNA and contain t ...
File
... a. the ribosomes moves nucleotides along the mRNA in the b. relocates the initial to the site and ejects it from the ribosome c. repositions the growing polypeptide chain to the site and exposes the next codon on the mRNA at the site ...
... a. the ribosomes moves nucleotides along the mRNA in the b. relocates the initial to the site and ejects it from the ribosome c. repositions the growing polypeptide chain to the site and exposes the next codon on the mRNA at the site ...
DNA sequences at the beginning of genes—at least in
... how they flag a small set of genes for transcription midblastula transition," says Kai Chen, PhD, a former graduate student in Zeitlinger's lab and the before that, holds important information about normal development and disease in animals and in study's first author. "We expected to see widespread ...
... how they flag a small set of genes for transcription midblastula transition," says Kai Chen, PhD, a former graduate student in Zeitlinger's lab and the before that, holds important information about normal development and disease in animals and in study's first author. "We expected to see widespread ...
RNA Polymerase II analysis in Drosophila Melanogaster
... The principle is that DNA-binding proteins in cells are cross-linked to the DNA that they are binding. By using a specific antibody, we can immunoprecipitate the protein–DNA complex. After the crosslinking, the cells are bursted and the DNA is broken into pieces by sonication. The DNA is purified wi ...
... The principle is that DNA-binding proteins in cells are cross-linked to the DNA that they are binding. By using a specific antibody, we can immunoprecipitate the protein–DNA complex. After the crosslinking, the cells are bursted and the DNA is broken into pieces by sonication. The DNA is purified wi ...