Biology Chapters 8 and 9 Test Review
... G2—the phase in which the cell prepares to divide. Mitosis Phase—the phase with prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. [See below] o Mitosis Prophase—where the cell’s nuclear membrane breaks down and nuclear material condenses together as the Centrosome [in plants] or Centriole [in anima ...
... G2—the phase in which the cell prepares to divide. Mitosis Phase—the phase with prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. [See below] o Mitosis Prophase—where the cell’s nuclear membrane breaks down and nuclear material condenses together as the Centrosome [in plants] or Centriole [in anima ...
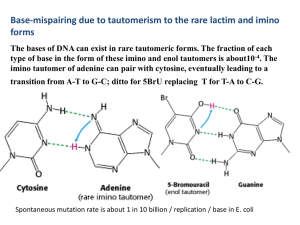
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... Nitrous acid (HNO2) hydrolyzes amino groups on bases via diazotization. Adenine is deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It is likely that mutations in DNA repair genes will lead to the accumulati ...
... Nitrous acid (HNO2) hydrolyzes amino groups on bases via diazotization. Adenine is deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It is likely that mutations in DNA repair genes will lead to the accumulati ...
Policy for sample drop-off and storage in the DNA Analysis Facility
... If the lab has grown to the point where a second box is needed we are happy to provide another, but not if the box is full because no one is removing old samples. Fragment Analysis: Samples for Fragment Analysis are to be placed on the top shelf of the “Fragment Analysis” refrigerator located in 305 ...
... If the lab has grown to the point where a second box is needed we are happy to provide another, but not if the box is full because no one is removing old samples. Fragment Analysis: Samples for Fragment Analysis are to be placed on the top shelf of the “Fragment Analysis” refrigerator located in 305 ...
The 3`termini of transcripts originating from genes
... a procaryotic division of organisms, which, on the basis of 16S rRNA cataloguing has been considered a seperate kingdom beside the eubacteria and the eucaryotes. This view has been substantiated by numerous investigations showing many different traits which are typical for archaebacteria (see (1) fo ...
... a procaryotic division of organisms, which, on the basis of 16S rRNA cataloguing has been considered a seperate kingdom beside the eubacteria and the eucaryotes. This view has been substantiated by numerous investigations showing many different traits which are typical for archaebacteria (see (1) fo ...
Aspekte der Thermodynamik in der Strukturbiologie Einführung in
... • Predicting elements of secondary structure (Ch. 6, 11) • Predicting the domain organization of proteins (Ch. 6, 7, 9, 11) • Visualizing protein structures in 3D (Ch. 11) • Predicting a protein’s 3D structure from its sequence (Ch. 11) • Finding all proteins that share a similar sequence (Ch. 7) • ...
... • Predicting elements of secondary structure (Ch. 6, 11) • Predicting the domain organization of proteins (Ch. 6, 7, 9, 11) • Visualizing protein structures in 3D (Ch. 11) • Predicting a protein’s 3D structure from its sequence (Ch. 11) • Finding all proteins that share a similar sequence (Ch. 7) • ...
CH18_Regulation of Gene Expression Powerpoint
... • Only a small fraction of DNA codes for proteins, and a very small fraction of the non-protein-coding DNA consists of genes for RNA such as rRNA and tRNA • A significant amount of the genome may be transcribed into noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) • Noncoding RNAs regulate gene expression at two points: mRN ...
... • Only a small fraction of DNA codes for proteins, and a very small fraction of the non-protein-coding DNA consists of genes for RNA such as rRNA and tRNA • A significant amount of the genome may be transcribed into noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) • Noncoding RNAs regulate gene expression at two points: mRN ...
o How is covariation used in RNA structure
... f. ____ Protein interactions are not required for the functions of most proteins. g. ____ An exon is a segment of a eukaryotic gene that does not encode protein. h. ____ In eukaryotes, one gene can sometimes encode several proteins. i. ____ Transcription factors are proteins that often bind specific ...
... f. ____ Protein interactions are not required for the functions of most proteins. g. ____ An exon is a segment of a eukaryotic gene that does not encode protein. h. ____ In eukaryotes, one gene can sometimes encode several proteins. i. ____ Transcription factors are proteins that often bind specific ...
Introduction to
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Small subunit- Binds to a mRNA molecule and reads its genetic codes- 30S P site- Donates the amino acid used to form the polypeptide chain A site- The amino acid located here accepts the released amino acid from the P site. It also accepts the next tRNA from the cytoplasm Compare structure of DNA to ...
... Small subunit- Binds to a mRNA molecule and reads its genetic codes- 30S P site- Donates the amino acid used to form the polypeptide chain A site- The amino acid located here accepts the released amino acid from the P site. It also accepts the next tRNA from the cytoplasm Compare structure of DNA to ...
Doc S1.
... designed following kit instruction. Each primer is dissolved to a final concentration of 100 pmol/µl (10X primer). For and rev primers are then mixed to a final concentration of 10 pmol/µl (Q-PCR primer mix). 10X primers and primer mix are stored at -20°C.Three types of primer pairs are used for pre ...
... designed following kit instruction. Each primer is dissolved to a final concentration of 100 pmol/µl (10X primer). For and rev primers are then mixed to a final concentration of 10 pmol/µl (Q-PCR primer mix). 10X primers and primer mix are stored at -20°C.Three types of primer pairs are used for pre ...
Chapter 1
... The difference between DNA and RNA is in the group at the 2’position of the sugar. DNA has a deoxyribose sugar (2’–H); RNA has a ribose sugar (2’–OH). A nucleotide consists of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group on either the 5’or 3’position of the ...
... The difference between DNA and RNA is in the group at the 2’position of the sugar. DNA has a deoxyribose sugar (2’–H); RNA has a ribose sugar (2’–OH). A nucleotide consists of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group on either the 5’or 3’position of the ...
生物化學基本概念
... converting genetic information from genes into the amino acid sequences of proteins. The three universal types of RNA include transfer () RNA (tRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Messenger (訊息) RNA acts to carry genetic sequence information between DNA and ribosomes, directing pro ...
... converting genetic information from genes into the amino acid sequences of proteins. The three universal types of RNA include transfer () RNA (tRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Messenger (訊息) RNA acts to carry genetic sequence information between DNA and ribosomes, directing pro ...
Introduction to Molecular Genetics
... DNA polymerases read the template and match the complementary base ...
... DNA polymerases read the template and match the complementary base ...
Notes
... RNA polymerase and the polymerase dissociates from the template DNA. Once released, an RNA polymerase is free to transcribe a new gene. Regulation of transcription Environmental changes induce changes in gene expression. Regulation of transcription initiation is the most common form of gene control ...
... RNA polymerase and the polymerase dissociates from the template DNA. Once released, an RNA polymerase is free to transcribe a new gene. Regulation of transcription Environmental changes induce changes in gene expression. Regulation of transcription initiation is the most common form of gene control ...
File
... • Initiation - The tRNA carrying an amino acid comes into P-site and bonds by base pairing its anti-codon with the mRNA start codon (what is the start codon?) • Elongation – The second tRNA then comes into A-site and bonds to codon of mRNA – The two amino acids joined with peptide bond • Termination ...
... • Initiation - The tRNA carrying an amino acid comes into P-site and bonds by base pairing its anti-codon with the mRNA start codon (what is the start codon?) • Elongation – The second tRNA then comes into A-site and bonds to codon of mRNA – The two amino acids joined with peptide bond • Termination ...
Transcription in Bacteria
... During initial transcription, RNA polymerase produces and releases short RNA transcripts of less then ten ribonucleotides (abortive synthesis) before escaping the promoter (promotor clearance). It is not clear why RNA polymerase must undergo this period of abortive initiation before achieving escape ...
... During initial transcription, RNA polymerase produces and releases short RNA transcripts of less then ten ribonucleotides (abortive synthesis) before escaping the promoter (promotor clearance). It is not clear why RNA polymerase must undergo this period of abortive initiation before achieving escape ...
Name: Biochemistry 465 Hour exam II Spring 2006
... A) associates with the promoter before binding core enzyme. B) combines with the core enzyme to confer specific binding to a promoter. C) is inseparable from the core enzyme. D) is required for termination of an RNA chain. E) will catalyze synthesis of RNA from both DNA template strands in the absen ...
... A) associates with the promoter before binding core enzyme. B) combines with the core enzyme to confer specific binding to a promoter. C) is inseparable from the core enzyme. D) is required for termination of an RNA chain. E) will catalyze synthesis of RNA from both DNA template strands in the absen ...
DNA RNA PSyn notes
... 4. Given the following nitrogen base sequence in a molecule of DNA: AATCGTTCGTTAGCGCCA (this is obviously only one side of the DNA molecule) answer the following: a. what would the other side of the DNA strand look like? b. what would a transcribed mRNA strand look like? c. how many amino acids woul ...
... 4. Given the following nitrogen base sequence in a molecule of DNA: AATCGTTCGTTAGCGCCA (this is obviously only one side of the DNA molecule) answer the following: a. what would the other side of the DNA strand look like? b. what would a transcribed mRNA strand look like? c. how many amino acids woul ...