Document
... The molecular barcodes constitute 20-bp sequences that are unique to each deletion and allow the identification of each deletion strain within a pool of many strains •Advantage: The comprehensive collection of null mutants can be screened for a specific phenotype. •Disadvantage: First, mutations in es ...
... The molecular barcodes constitute 20-bp sequences that are unique to each deletion and allow the identification of each deletion strain within a pool of many strains •Advantage: The comprehensive collection of null mutants can be screened for a specific phenotype. •Disadvantage: First, mutations in es ...
$doc.title
... is the gene product of the ntrC gene. Moreover, it is not just the NtrC (NRI) that is required, because NRI has to be activated into NRI -phosphate by becoming phosphorylated. NRI is a DNA binding protein which, when phosphorylated binds to specific sequences of DNA and confers initiation activity o ...
... is the gene product of the ntrC gene. Moreover, it is not just the NtrC (NRI) that is required, because NRI has to be activated into NRI -phosphate by becoming phosphorylated. NRI is a DNA binding protein which, when phosphorylated binds to specific sequences of DNA and confers initiation activity o ...
practice exam 3_answer key
... 13. During which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope re-form? a. anaphase b. metaphase c. prophase d. telophase e. none of the above 14. The creation of genetically identical offspring by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg, is called a. asexual reproduction b. sexual ...
... 13. During which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope re-form? a. anaphase b. metaphase c. prophase d. telophase e. none of the above 14. The creation of genetically identical offspring by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg, is called a. asexual reproduction b. sexual ...
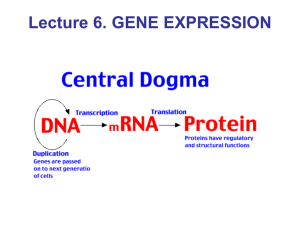
Transcription & translation
... What stops transcription? A sequence of bases on the DNA that cause the RNA polymerase and mRNA strand to be released—remember mRNA has to be modified before it can leave the nucleus! ...
... What stops transcription? A sequence of bases on the DNA that cause the RNA polymerase and mRNA strand to be released—remember mRNA has to be modified before it can leave the nucleus! ...
Control of Gene Expression
... cows, mice, goats, and a variety of other mammals. At this point in time, human embryos created by SCNT have not developed past the 8 cell stage. (and it raises serious ethical questions) ...
... cows, mice, goats, and a variety of other mammals. At this point in time, human embryos created by SCNT have not developed past the 8 cell stage. (and it raises serious ethical questions) ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA
... • Initiation of RNA synthesis occurs only at promoters – Usually starts at GTP or ATP – New RNA strand base pairs temporarily with DNA template to form DNA/RNA template – DNA must unwind then rewind – Template strand – Nontemplate strand or coding strand ...
... • Initiation of RNA synthesis occurs only at promoters – Usually starts at GTP or ATP – New RNA strand base pairs temporarily with DNA template to form DNA/RNA template – DNA must unwind then rewind – Template strand – Nontemplate strand or coding strand ...
Document
... SignalSRP cleaving detaches enzyme and polypeptide cuts off signal synthesis peptide. resumes. ...
... SignalSRP cleaving detaches enzyme and polypeptide cuts off signal synthesis peptide. resumes. ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... • Long understood that eukaryote genes composed of short exons separated by long introns • Introns transcribed to RNA that is spliced out before proteins produced • Now know splicing for a gene-containing locus can be done in multiple ways – Individual exons left out of final product – Only portions ...
... • Long understood that eukaryote genes composed of short exons separated by long introns • Introns transcribed to RNA that is spliced out before proteins produced • Now know splicing for a gene-containing locus can be done in multiple ways – Individual exons left out of final product – Only portions ...
Transcription - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... finds the beginning of a protein recipe called the promotor - promotor = a series of nucleotides that indicate the start of a protein recipe The RNA polymerase opens the DNA molecule at the promotor ...
... finds the beginning of a protein recipe called the promotor - promotor = a series of nucleotides that indicate the start of a protein recipe The RNA polymerase opens the DNA molecule at the promotor ...
Expression profiling reveals off
... gene regulations in common (data not shown), but the vast majority of the transcript expression patterns were siRNA-specific rather than target-specific. The number and identity of altered transcripts did not correspond to the ability of the siRNA to silence the target gene. Target mRNA levels were ...
... gene regulations in common (data not shown), but the vast majority of the transcript expression patterns were siRNA-specific rather than target-specific. The number and identity of altered transcripts did not correspond to the ability of the siRNA to silence the target gene. Target mRNA levels were ...
Slide 1
... 3 important stages in protein synthesis: • The coding by triplets of bases to produce mRNA (Transcription) • The linking of mRNA to tRNA at ribosomes (Translation) ...
... 3 important stages in protein synthesis: • The coding by triplets of bases to produce mRNA (Transcription) • The linking of mRNA to tRNA at ribosomes (Translation) ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Takes places in the nucleus of the cell The process by which the information from DNA is transferred to RNA. DNA uncoils and unzips. • The exposed DNA bases are matched up with RNA bases in the nucleus to form mRNA. ...
... • Takes places in the nucleus of the cell The process by which the information from DNA is transferred to RNA. DNA uncoils and unzips. • The exposed DNA bases are matched up with RNA bases in the nucleus to form mRNA. ...
Power point
... gene expression by making a region of DNA either more or less able to bind the transcription machinery • Associated with most eukaryotic genes are multiple control elements, segments of noncoding DNA that serve as binding sites for transcription factors that help regulate transcription • Control ele ...
... gene expression by making a region of DNA either more or less able to bind the transcription machinery • Associated with most eukaryotic genes are multiple control elements, segments of noncoding DNA that serve as binding sites for transcription factors that help regulate transcription • Control ele ...
Chapter 25 RNA Metabolism
... energy-expensive pathway leading to protein synthesis, an ideal target for regulating gene expression. The RNA polymerase binds to each promoter in very different efficiency. Protein factors binding to DNA sequences close or distant to the promoters can promote (activator) or repress (repressor) ...
... energy-expensive pathway leading to protein synthesis, an ideal target for regulating gene expression. The RNA polymerase binds to each promoter in very different efficiency. Protein factors binding to DNA sequences close or distant to the promoters can promote (activator) or repress (repressor) ...
1) Definition of the gene
... (maternal and paternal): this protein is made from the PDH gene on each chromosome. As a general rule, both copies of each gene in your DNA are active (unless one copy is defective). If you have one good copy, usually it’s OK. ...
... (maternal and paternal): this protein is made from the PDH gene on each chromosome. As a general rule, both copies of each gene in your DNA are active (unless one copy is defective). If you have one good copy, usually it’s OK. ...
3 macromolecules no pics pdf
... • Over time, this molecule began to differentiate and compete much the same way the early RNA molecules did • Some DNA molecules utilized the tRNA molecules to create strands of amino acids that it could use to become more specialized • Others utilized lipids to form strong outer barriers that were ...
... • Over time, this molecule began to differentiate and compete much the same way the early RNA molecules did • Some DNA molecules utilized the tRNA molecules to create strands of amino acids that it could use to become more specialized • Others utilized lipids to form strong outer barriers that were ...
Document
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
o"', ,jl w - 'J'
... Arrays - stacks- Queues - List. Database Management System :- Characteristics of DBMS- advantages of DBMS over file processing - Actors on the scenedatabase models- structure of DBMS. Introduction to MSEXCEL- use of worksheet to enter data, edit data, copy data, move data. Use of in-built statistica ...
... Arrays - stacks- Queues - List. Database Management System :- Characteristics of DBMS- advantages of DBMS over file processing - Actors on the scenedatabase models- structure of DBMS. Introduction to MSEXCEL- use of worksheet to enter data, edit data, copy data, move data. Use of in-built statistica ...