PowerPoint version
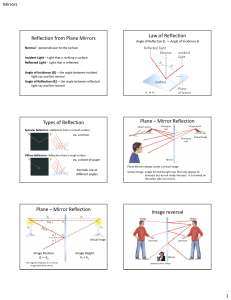
... different places at different depths and different times. This results in a mostly blurred image, which is why rough, grainy surfaces do not reflect images well. ...
... different places at different depths and different times. This results in a mostly blurred image, which is why rough, grainy surfaces do not reflect images well. ...
lecture23
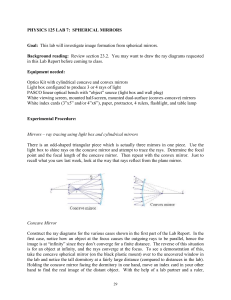
... its magnification for an object 10 m from the mirror. The ray diagram looks like the one on the previous slide, but with the object much further away (difficult to draw). ...
... its magnification for an object 10 m from the mirror. The ray diagram looks like the one on the previous slide, but with the object much further away (difficult to draw). ...
RAY OPTICS notes
... The image is real if the rays actually converge to the point; it is virtual if the rays do not actually meet but appear to diverge from the point when produced backwards. ...
... The image is real if the rays actually converge to the point; it is virtual if the rays do not actually meet but appear to diverge from the point when produced backwards. ...
PPT
... • Focal point is at half the curvatuire radius: f= r/2 . •Rays parallel to the axis, reflect through the focal point. • Rays hitting the mirror after going to the focal point, emerge parallel. • Rays going through the center of curvature, reflect back on themselves. ...
... • Focal point is at half the curvatuire radius: f= r/2 . •Rays parallel to the axis, reflect through the focal point. • Rays hitting the mirror after going to the focal point, emerge parallel. • Rays going through the center of curvature, reflect back on themselves. ...
Physics 161 Lecture 26 Mirrors and Lenses December 6, 2016
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
Mirror

A mirror is an object that reflects light in such a way that, for incident light in some range of wavelengths, the reflected light preserves many or most of the detailed physical characteristics of the original light. This is different from other light-reflecting objects that do not preserve much of the original wave signal other than color and diffuse reflected light.The most familiar type of mirror is the plane mirror, which has a flat screen surface. Curved mirrors are also used, to produce magnified or diminished images or focus light or simply distort the reflected image.Mirrors are commonly used for personal grooming or admiring oneself (in which case the archaic term looking-glass is sometimes still used), decoration, and architecture. Mirrors are also used in scientific apparatus such as telescopes and lasers, cameras, and industrial machinery. Most mirrors are designed for visible light; however, mirrors designed for other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are also used.