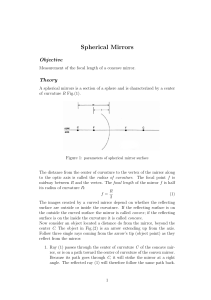
System for observing interference phenomenon: In the previous
... In this geometry, the reflected ray 1, travels an extra optical path, a compensating plate G2 of same thickness as plate G1 ) is inserted in the path of ray 2 such that G2 is parallel to G1 . This introduces the same optical path in glass medium for ray 2 as ray 1 travels in plate G1 (therefore is c ...
... In this geometry, the reflected ray 1, travels an extra optical path, a compensating plate G2 of same thickness as plate G1 ) is inserted in the path of ray 2 such that G2 is parallel to G1 . This introduces the same optical path in glass medium for ray 2 as ray 1 travels in plate G1 (therefore is c ...
supplemental_material
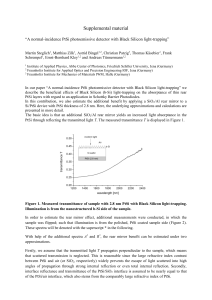
... In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination is from the polished, PtSi coated sample side (Figure 2). These spectra will be denoted with the superscript * in the following. With help of the additional sp ...
... In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination is from the polished, PtSi coated sample side (Figure 2). These spectra will be denoted with the superscript * in the following. With help of the additional sp ...
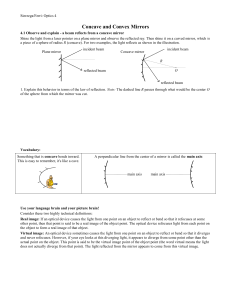
Concave and Convex Mirrors
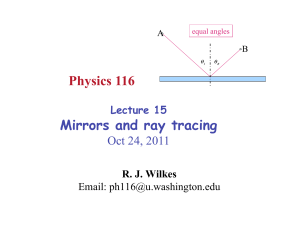
... Virtual image: An optical device sometimes causes the light from one point on an object to reflect or bend so that it diverges and never refocuses. However, if your eye looks at this diverging light, it appears to diverge from some point other than the actual point on the object. This point is said ...
... Virtual image: An optical device sometimes causes the light from one point on an object to reflect or bend so that it diverges and never refocuses. However, if your eye looks at this diverging light, it appears to diverge from some point other than the actual point on the object. This point is said ...
Mirror

A mirror is an object that reflects light in such a way that, for incident light in some range of wavelengths, the reflected light preserves many or most of the detailed physical characteristics of the original light. This is different from other light-reflecting objects that do not preserve much of the original wave signal other than color and diffuse reflected light.The most familiar type of mirror is the plane mirror, which has a flat screen surface. Curved mirrors are also used, to produce magnified or diminished images or focus light or simply distort the reflected image.Mirrors are commonly used for personal grooming or admiring oneself (in which case the archaic term looking-glass is sometimes still used), decoration, and architecture. Mirrors are also used in scientific apparatus such as telescopes and lasers, cameras, and industrial machinery. Most mirrors are designed for visible light; however, mirrors designed for other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are also used.