Lecture 25 - UF Physics
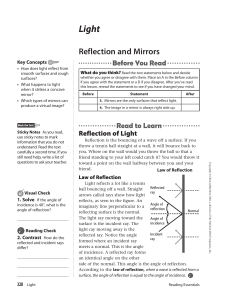
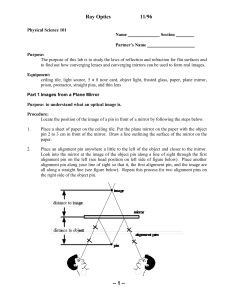
... 4. Ray Diagrams • A ray diagram can be used to determine the position and size of an image. • They are graphical constructions which tell the overall nature of the image. • They can also be used to check the parameters calculated from the mirror and magnification ...
... 4. Ray Diagrams • A ray diagram can be used to determine the position and size of an image. • They are graphical constructions which tell the overall nature of the image. • They can also be used to check the parameters calculated from the mirror and magnification ...
ppt
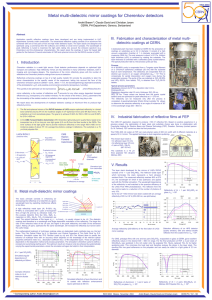
... Application specific reflective coatings have been developed and are being implemented in LHC experiments currently under construction. The broad-band reflective coating consists of an aluminum film combined with one or two pairs of low and high index dielectric layers. The layer stacks are designed ...
... Application specific reflective coatings have been developed and are being implemented in LHC experiments currently under construction. The broad-band reflective coating consists of an aluminum film combined with one or two pairs of low and high index dielectric layers. The layer stacks are designed ...
VeeMAX UV-Visible Variable Angle Specular Reflectance Accessory
... help define accuracy of the coating procedure and the performance of coated materials. Whether your coating is: • an anti-reflective coating on eyeglasses or binocular lenses • a UV mirror on a cockpit window • a solar reflective window for sky-scrapers • a metal first surface mirror for research la ...
... help define accuracy of the coating procedure and the performance of coated materials. Whether your coating is: • an anti-reflective coating on eyeglasses or binocular lenses • a UV mirror on a cockpit window • a solar reflective window for sky-scrapers • a metal first surface mirror for research la ...
Mirror

A mirror is an object that reflects light in such a way that, for incident light in some range of wavelengths, the reflected light preserves many or most of the detailed physical characteristics of the original light. This is different from other light-reflecting objects that do not preserve much of the original wave signal other than color and diffuse reflected light.The most familiar type of mirror is the plane mirror, which has a flat screen surface. Curved mirrors are also used, to produce magnified or diminished images or focus light or simply distort the reflected image.Mirrors are commonly used for personal grooming or admiring oneself (in which case the archaic term looking-glass is sometimes still used), decoration, and architecture. Mirrors are also used in scientific apparatus such as telescopes and lasers, cameras, and industrial machinery. Most mirrors are designed for visible light; however, mirrors designed for other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are also used.