2001
... b. They are not transcribed c. They are not translated d. They could eventually be lost from the genome bydeletion or other mechanism. e. They could evolve into new geneswith different functions Regardingnucleosome structure, which of the following statements is correct? A. Nucleosomesare spherical ...
... b. They are not transcribed c. They are not translated d. They could eventually be lost from the genome bydeletion or other mechanism. e. They could evolve into new geneswith different functions Regardingnucleosome structure, which of the following statements is correct? A. Nucleosomesare spherical ...
Biobowl3_students
... DNA replication requires the enzyme ______ to synthesize an RNA primer, the enzyme ______ to unwind the double helix, and the enzyme ______ to connect Okazaki fragments ...
... DNA replication requires the enzyme ______ to synthesize an RNA primer, the enzyme ______ to unwind the double helix, and the enzyme ______ to connect Okazaki fragments ...
Gene Mutations and Cancer Part 2
... genes throughout a person’s life. However, some environmental factors, such as smoking, increase the risk of abnormal DNA methylation patterns. Tumour suppressor genes are usually switched on to slow down cell division. If parts of a tumour suppressor gene become heavily methylated, the gene is de-a ...
... genes throughout a person’s life. However, some environmental factors, such as smoking, increase the risk of abnormal DNA methylation patterns. Tumour suppressor genes are usually switched on to slow down cell division. If parts of a tumour suppressor gene become heavily methylated, the gene is de-a ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... Morgan and white eyed vs. wild type fruit flies, mutant phenotype, sex-linked genes, examples like hemophilia, sex-influenced trait, nondisjunction, aneuploidy, translocation, Down Syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, metafemale, XYY syndrome Ch. 20 DNA Technology genetic engineering, re ...
... Morgan and white eyed vs. wild type fruit flies, mutant phenotype, sex-linked genes, examples like hemophilia, sex-influenced trait, nondisjunction, aneuploidy, translocation, Down Syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, metafemale, XYY syndrome Ch. 20 DNA Technology genetic engineering, re ...
UNIT 4 PART 2 APPLIED GENETICS
... Acids are separated by running them through an electrified gel. • Restriction Enzymes are used to cut the DNA into different size pieces. • The large pieces move slowly, while the small pieces move quickly. • This is sometimes called DNA ...
... Acids are separated by running them through an electrified gel. • Restriction Enzymes are used to cut the DNA into different size pieces. • The large pieces move slowly, while the small pieces move quickly. • This is sometimes called DNA ...
dna microinjection
... • the super- ovulated females are mated and killed • the fertilized eggs are flushed from their oviducts • microinjection of the fertilized eggs ...
... • the super- ovulated females are mated and killed • the fertilized eggs are flushed from their oviducts • microinjection of the fertilized eggs ...
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
... A linker histone helps to pull nucleosomes together into the 30-nm fiber ...
... A linker histone helps to pull nucleosomes together into the 30-nm fiber ...
DNA structure and replication Three key features needed for any
... the pairs of bases holding the chains together. The vertical line marks the fibre axis. …………….It ...
... the pairs of bases holding the chains together. The vertical line marks the fibre axis. …………….It ...
Statistical Applications in Biology and Genetics
... Overview of quantitative research area related to genetics Sample project I: Bayesian Regression Analysis with application to Microarray studies Sample project II: BHTA algorithm for complex traits ...
... Overview of quantitative research area related to genetics Sample project I: Bayesian Regression Analysis with application to Microarray studies Sample project II: BHTA algorithm for complex traits ...
Homeostasis
... Genetic Mutations and how they arise Sex Linked Traits and Multiple Alleles Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Trisomy and Monosomy Karyotyping Determining Blood Types in Punnett Squares Structure of DNA and RNA Nucleotides – three main parts Nitrogen-Containing Bases – four different types Purine ...
... Genetic Mutations and how they arise Sex Linked Traits and Multiple Alleles Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Trisomy and Monosomy Karyotyping Determining Blood Types in Punnett Squares Structure of DNA and RNA Nucleotides – three main parts Nitrogen-Containing Bases – four different types Purine ...
Can environmental factors acting on an organism cause inherited
... One of the well known epigenetic signal is DNA methylation which tags cytosine with a methyl group. It is generally associated with silencing gene expression because active genes are usually unmethylated. Another important epigenetic mechanism is chromatin remodelling. Chromatins are densely packed ...
... One of the well known epigenetic signal is DNA methylation which tags cytosine with a methyl group. It is generally associated with silencing gene expression because active genes are usually unmethylated. Another important epigenetic mechanism is chromatin remodelling. Chromatins are densely packed ...
IMPLICATIONS OF ANTHROPGENY FOR MEDICINE AND
... particular gene. Recombination: Exchanges between chromosomes that causes independent inheritance of alleles. Sequence: The linear order of the building blocks, which encodes individual form and function. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Single nucleotide differences (e.g. A vs. T). Transcrip ...
... particular gene. Recombination: Exchanges between chromosomes that causes independent inheritance of alleles. Sequence: The linear order of the building blocks, which encodes individual form and function. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Single nucleotide differences (e.g. A vs. T). Transcrip ...
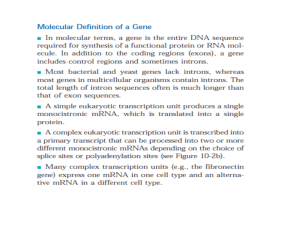
Expressing Genetic Information
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
Unit 10 Biotechnology review guide 2014
... called ____________________________________. 13. What is the name used to describe the offspring from a cross between two varieties of plants in an attempt to create a new plant variety with traits from both parents? _______________ 14. The method whereby developing pure lines, breeders preserve des ...
... called ____________________________________. 13. What is the name used to describe the offspring from a cross between two varieties of plants in an attempt to create a new plant variety with traits from both parents? _______________ 14. The method whereby developing pure lines, breeders preserve des ...
Study Guide for LS
... - DNA is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. - In a DNA strand, the rungs (the part you step on) of the “ladder” are made of nucleotide bases. - In a DNA strand, the sides of the “ladder” are made of alternating sugar and phosphate ...
... - DNA is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. - In a DNA strand, the rungs (the part you step on) of the “ladder” are made of nucleotide bases. - In a DNA strand, the sides of the “ladder” are made of alternating sugar and phosphate ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... • In some cases, DNA binding domain and activating domains are even carried on separate polypeptides, and form a complex on DNA. • Herpes virus activator VP16 interacts with the Oct1 DNA-binding protein found in cells infected by this virus. ...
... • In some cases, DNA binding domain and activating domains are even carried on separate polypeptides, and form a complex on DNA. • Herpes virus activator VP16 interacts with the Oct1 DNA-binding protein found in cells infected by this virus. ...
forensics - bayo2pisay
... that is repeated in a head-to-tail manner at a specific chromosomal locus interspersed in genome Number of repeated units vary per human Loci – VNTR’s One VNTR – 17 bp, repeated 70 to 450 times Total: 1190 to 7650 base pairs ...
... that is repeated in a head-to-tail manner at a specific chromosomal locus interspersed in genome Number of repeated units vary per human Loci – VNTR’s One VNTR – 17 bp, repeated 70 to 450 times Total: 1190 to 7650 base pairs ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 12. What did Morgan and his students show that is important to modern genetics? Genes control Biochemical Events 13. What organism did Beadle and Tatum use for their experiments? 14. What did Beadle and Tatum do to this organisms to produce genetic changes? 15. What changes did this process cause to ...
... 12. What did Morgan and his students show that is important to modern genetics? Genes control Biochemical Events 13. What organism did Beadle and Tatum use for their experiments? 14. What did Beadle and Tatum do to this organisms to produce genetic changes? 15. What changes did this process cause to ...
DNA- Experiments and People
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
DNA People - Biology Junction
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
Dioxyribose Nucleic Acid
... – Amino acids make proteins in your body. • There are only 20 amino acids. ...
... – Amino acids make proteins in your body. • There are only 20 amino acids. ...
Genetic Technology 13.1 and 13.2 notes
... • The cross of an individual with unknown genotype with an individual of known genotype (ideally recessive). • Purpose: to help determine which organisms will have the greatest chances of passing on desired traits. ...
... • The cross of an individual with unknown genotype with an individual of known genotype (ideally recessive). • Purpose: to help determine which organisms will have the greatest chances of passing on desired traits. ...
mc2 Chromatin - WordPress.com
... DNA bending can affect transcription and site-specific recombination ...
... DNA bending can affect transcription and site-specific recombination ...
Gene Technology
... Other DNA Technologies • Probe – short DNA or RNA strand with attached radioactive or fluorescent materials to “tag” specific sequences. – Nucleotide sequences are complementary to the gene of interest • Southern blot – used to indicate certain fragments that hybridized with a probe. ...
... Other DNA Technologies • Probe – short DNA or RNA strand with attached radioactive or fluorescent materials to “tag” specific sequences. – Nucleotide sequences are complementary to the gene of interest • Southern blot – used to indicate certain fragments that hybridized with a probe. ...