BACTERIAL GENETICS
... storage site where the gene is not expressed to an active site where transcription and translation occur. The insertion of a new gene into the active site in a sequential repeated programmed manner is the source of the consistent antigenic variation. These movements have the effect of allowing the ...
... storage site where the gene is not expressed to an active site where transcription and translation occur. The insertion of a new gene into the active site in a sequential repeated programmed manner is the source of the consistent antigenic variation. These movements have the effect of allowing the ...
E1. A trait of pneumococci is the ability to synthesize a capsule
... C. 32P and 35S were chosen as radioisotopes to label the phages because phosphorous is found in nucleic acids, while sulfur is found only in proteins. D. There are multiple reasons why less than 100% of the phage protein is removed from the bacterial cells during the shearing process. Perhaps the sh ...
... C. 32P and 35S were chosen as radioisotopes to label the phages because phosphorous is found in nucleic acids, while sulfur is found only in proteins. D. There are multiple reasons why less than 100% of the phage protein is removed from the bacterial cells during the shearing process. Perhaps the sh ...
Beginning to crack the code of `junk DNA`
... Kazazian, 71, has no plans to slow down. He is investigating whether this type of self-replicating junk DNA holds more power over human illness than has previously been imagined. It might influence our risk for cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other common conditions. "The one thing that drew ...
... Kazazian, 71, has no plans to slow down. He is investigating whether this type of self-replicating junk DNA holds more power over human illness than has previously been imagined. It might influence our risk for cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other common conditions. "The one thing that drew ...
7. Recombinant DNA Vectors
... plasmids--analyzing small DNA regions, expressing genes in cell viruses--cloning larger regions (lambda virus), gene therapy (adenovirus) artificial chromosome vectors (BACs, PACs, YACs)--cloning chromosomal regions b. Conventional E. coli plasmid cloning vectors typically have: origin of replicatio ...
... plasmids--analyzing small DNA regions, expressing genes in cell viruses--cloning larger regions (lambda virus), gene therapy (adenovirus) artificial chromosome vectors (BACs, PACs, YACs)--cloning chromosomal regions b. Conventional E. coli plasmid cloning vectors typically have: origin of replicatio ...
DNA RNA structure
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
Fruit Salad—Hold the DNA, Please
... All the genetic information for a living organism is contained in its DNA, which is housed in the nucleus of its cells. DNA is made up of nucleotides and a sugar phosphate backbone that bond together in a double-helix form. It is a very long molecule made of millions of nucleotides. Between two indi ...
... All the genetic information for a living organism is contained in its DNA, which is housed in the nucleus of its cells. DNA is made up of nucleotides and a sugar phosphate backbone that bond together in a double-helix form. It is a very long molecule made of millions of nucleotides. Between two indi ...
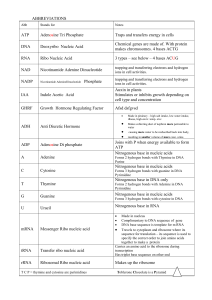
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
News Release
... While Eddie clearly has many ancestors, if we want to trace a family line back through the generations, there are two ancestral lineages that we can learn much more about than the others, that of the father’s father’s father and the mother’s mother’s mother and so on back in time. The fatherline is ...
... While Eddie clearly has many ancestors, if we want to trace a family line back through the generations, there are two ancestral lineages that we can learn much more about than the others, that of the father’s father’s father and the mother’s mother’s mother and so on back in time. The fatherline is ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... Peptide bonds link amino acids together There are 20 essential amino acids found in all living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
... Peptide bonds link amino acids together There are 20 essential amino acids found in all living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
Nucleic Acids - Informational Polymers
... 4. We can use DNA and proteins as tape measures of evolution • Genes (DNA) and their products (proteins) document the hereditary background of an ...
... 4. We can use DNA and proteins as tape measures of evolution • Genes (DNA) and their products (proteins) document the hereditary background of an ...
Chapter08_MBP1022H
... bacterial genome • engineered to contain only sequences needed to function as a DNA cloning vector: • a bacterial origin of replication (ori) • an antibiotic resistance gene (eg. B-lactamase confers resistance to ampicillin (amp)) • one or more unique restriction enzyme cutting sites which can be us ...
... bacterial genome • engineered to contain only sequences needed to function as a DNA cloning vector: • a bacterial origin of replication (ori) • an antibiotic resistance gene (eg. B-lactamase confers resistance to ampicillin (amp)) • one or more unique restriction enzyme cutting sites which can be us ...
Molecular Genetics Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... b. fusion into circular forms known as e. fusion with other newly transcribed plasmids. mRNA. c. linkage to histone molecules. All of the following are directly involved in translation except a. mRNA. b. tRNA. c. ribosomes. d. DNA. The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From thi ...
... b. fusion into circular forms known as e. fusion with other newly transcribed plasmids. mRNA. c. linkage to histone molecules. All of the following are directly involved in translation except a. mRNA. b. tRNA. c. ribosomes. d. DNA. The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From thi ...
PPT Version - OMICS International
... in the last 23 years. Currently, he is a Professor of Pathology and Director of High Throughput Genome Center at University of Pittsburgh. • In the last 13 years, Dr. Luo has been largely focusing on genetic and molecular mechanism of human prostate and hepatocellular carcinomas. In this period, his ...
... in the last 23 years. Currently, he is a Professor of Pathology and Director of High Throughput Genome Center at University of Pittsburgh. • In the last 13 years, Dr. Luo has been largely focusing on genetic and molecular mechanism of human prostate and hepatocellular carcinomas. In this period, his ...
Section 3 - DNA Sequencing
... • These are pieces of DNA within genes, which are transcribed but then spliced out of the RNA before it is translated. • They make it much harder to find genes, since finding open reading frames is not enough, you also need to find where introns and exons start and end. ...
... • These are pieces of DNA within genes, which are transcribed but then spliced out of the RNA before it is translated. • They make it much harder to find genes, since finding open reading frames is not enough, you also need to find where introns and exons start and end. ...
Review Questions
... DNA, the recipe for making proteins, never leaves the nucleus (nucleoid region in bacteria). Yet all the protein-making machinery is located out in the cytoplasm. So how does the information get to the cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a c ...
... DNA, the recipe for making proteins, never leaves the nucleus (nucleoid region in bacteria). Yet all the protein-making machinery is located out in the cytoplasm. So how does the information get to the cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a c ...
Forensic DNA Fingerprinting Kit - Bio-Rad
... Level 1 questions are simple to adapt and do not add extra days to the running of this laboratory. An example of how to organize and execute a Level 1 question is given below. Level 2 questions may add a few days onto the lab and may require some additional materials to answer. Level 3 questions are ...
... Level 1 questions are simple to adapt and do not add extra days to the running of this laboratory. An example of how to organize and execute a Level 1 question is given below. Level 2 questions may add a few days onto the lab and may require some additional materials to answer. Level 3 questions are ...
Integrated Programme Sec 2 SBGE, LSS Biology Module Topic
... o All animals and plants of the same species have the same number of chromosomes A human cell contains 23 pairs (2n=46) of chromosomes o Except in the sex cells (n=23) B. Chromosomes-Genes-DNA Chromosomes Chromatin is a nuclear material that contains the genetic code. Heterochromatin : condens ...
... o All animals and plants of the same species have the same number of chromosomes A human cell contains 23 pairs (2n=46) of chromosomes o Except in the sex cells (n=23) B. Chromosomes-Genes-DNA Chromosomes Chromatin is a nuclear material that contains the genetic code. Heterochromatin : condens ...
Evidence that a Safe Dose of Mutagen Does Not Exist
... 1. The physical principle of molecular mass action dictates that even the best DNA repair system in the most healthy person can not detect and repair all premutational lesions prior to DNA replication. Assuming it were true, many people are "repair compromised" because of their genotype or due to th ...
... 1. The physical principle of molecular mass action dictates that even the best DNA repair system in the most healthy person can not detect and repair all premutational lesions prior to DNA replication. Assuming it were true, many people are "repair compromised" because of their genotype or due to th ...
DNA_fingerprinting
... these repeats vary from individual to individual. These are the polymorphisms targeted by DNA fingerprinting. E.g. there is a region of DNA just beyond the insulin gene on chromosome 11, consisting of 7 to 40 repeats, depending on the individual. E.g. TCATTCATTCATTCATTCAT is a short tandem repeat (S ...
... these repeats vary from individual to individual. These are the polymorphisms targeted by DNA fingerprinting. E.g. there is a region of DNA just beyond the insulin gene on chromosome 11, consisting of 7 to 40 repeats, depending on the individual. E.g. TCATTCATTCATTCATTCAT is a short tandem repeat (S ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
... Each DNA strand is made of combinations of four chemical units, called nucleotide bases, which comprise the genetic "alphabet." The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Bases on opposite strands pair specifically: A’s always pair with T’s, and C’s always pair with G’s. ...
... Each DNA strand is made of combinations of four chemical units, called nucleotide bases, which comprise the genetic "alphabet." The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Bases on opposite strands pair specifically: A’s always pair with T’s, and C’s always pair with G’s. ...
genetics review package
... gene is inserted, foreign protein can be made 7. Explain what restriction enzymes are and why they are important. Restriction enzymes cut at palindromes and leave sticky ends behind. They are important because they recognize only specific sites and allow us to remove specific genes. The ...
... gene is inserted, foreign protein can be made 7. Explain what restriction enzymes are and why they are important. Restriction enzymes cut at palindromes and leave sticky ends behind. They are important because they recognize only specific sites and allow us to remove specific genes. The ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
... Each DNA strand is made of combinations of four chemical units, called nucleotide bases, which comprise the genetic "alphabet." The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Bases on opposite strands pair specifically: A’s always pair with T’s, and C’s always pair with G’s. ...
... Each DNA strand is made of combinations of four chemical units, called nucleotide bases, which comprise the genetic "alphabet." The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Bases on opposite strands pair specifically: A’s always pair with T’s, and C’s always pair with G’s. ...