Genes Expression or Genes and How They Work: Transcription
... transcription, a set of proteins called ___________________ must first assemble on the promoter. The assembly process begins _________________ from the transcription start site, where proteins called ____________________ bind to a short TATA sequence in the promoter. Other basal factor proteins then ...
... transcription, a set of proteins called ___________________ must first assemble on the promoter. The assembly process begins _________________ from the transcription start site, where proteins called ____________________ bind to a short TATA sequence in the promoter. Other basal factor proteins then ...
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... particular way. For example, a plasma cell expresses continuously the genes for the antibody it synthesizes. Some are expressed only as conditions around and in the cell change. For example, the arrival of a hormone may turn on (or off) certain genes in that cell. ...
... particular way. For example, a plasma cell expresses continuously the genes for the antibody it synthesizes. Some are expressed only as conditions around and in the cell change. For example, the arrival of a hormone may turn on (or off) certain genes in that cell. ...
Document
... complex as ssRNAs and initiate destruction of all cellular RNAs that share homology to the dsRNA. RNAi has been incredibly useful to researchers because it can be used to reduce the expression of genes that are tough to mutate. TFIID is a complex of proteins within the basal/general transcriptional ...
... complex as ssRNAs and initiate destruction of all cellular RNAs that share homology to the dsRNA. RNAi has been incredibly useful to researchers because it can be used to reduce the expression of genes that are tough to mutate. TFIID is a complex of proteins within the basal/general transcriptional ...
bio_ch08
... – Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
... – Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
8.4 Transcription KEY CONCEPT Transcription converts a gene into a single-stranded RNA molecule.
... – Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
... – Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
8.4 Transcription
... – Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
... – Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
SoonChunHyang University: SoonChunHyang Institute of Medi
... topics in Molecular Biology in depth. This course primarily deals with nucleic acids and proteins and how these molecules interact within the cell to promote proper growth, division, and development. Especially this course will emphasize the molecular mechanisms of DNA replication, repair, transcrip ...
... topics in Molecular Biology in depth. This course primarily deals with nucleic acids and proteins and how these molecules interact within the cell to promote proper growth, division, and development. Especially this course will emphasize the molecular mechanisms of DNA replication, repair, transcrip ...
Unit 4 - University of Colorado Boulder
... expression (What steps are similar? What extra steps do we see in eukaryotes?). 12. List functions that are performed by various RNA molecules during the steps involved in transcription and translation. 13. Recognize the many steps of gene expression in which complementary base pairs play a key role ...
... expression (What steps are similar? What extra steps do we see in eukaryotes?). 12. List functions that are performed by various RNA molecules during the steps involved in transcription and translation. 13. Recognize the many steps of gene expression in which complementary base pairs play a key role ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... a. They tend to be weaker and smaller than diploid plants. b. They tend to be bigger and stronger than diploid plants. c. They tend to be weaker, but bigger than diploid plants. d. They tend to be smaller, but stronger than diploid plants ...
... a. They tend to be weaker and smaller than diploid plants. b. They tend to be bigger and stronger than diploid plants. c. They tend to be weaker, but bigger than diploid plants. d. They tend to be smaller, but stronger than diploid plants ...
2001
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------For each of the followingmultiple choice questions, choose the most appropriateanswer. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Formation of Z-DNA is favored by a. ...
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------For each of the followingmultiple choice questions, choose the most appropriateanswer. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Formation of Z-DNA is favored by a. ...
File
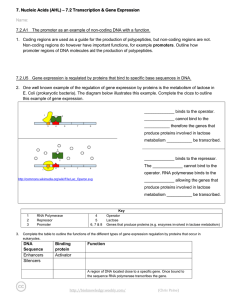
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
Molecular Genetics
... • mRNA Protein (facilitated by tRNA) • Happens in a ribosome, in the cytoplasm • Has three stages: (1)Initiation (2)Elongation (3)Termination ...
... • mRNA Protein (facilitated by tRNA) • Happens in a ribosome, in the cytoplasm • Has three stages: (1)Initiation (2)Elongation (3)Termination ...
Cell Signaling - Lectures For UG-5
... phosphorylation of the LRP coreceptor by GSK3 and another and another kinase, and thus allows subsequent binding of Axin. 2. This disrupts the Axin-APC-GSK3B-catenin complex, preventing phosphorylation of B-catenin by GSK3 which leads accumulation of B-catenin in the cell. 3. After translocation to ...
... phosphorylation of the LRP coreceptor by GSK3 and another and another kinase, and thus allows subsequent binding of Axin. 2. This disrupts the Axin-APC-GSK3B-catenin complex, preventing phosphorylation of B-catenin by GSK3 which leads accumulation of B-catenin in the cell. 3. After translocation to ...
Practice Exam- KEY - mvhs
... should eb the same (no introns were cut out). However, if the RNA is shorter than the DNA then you could conclude that it went through some post-translational modifications after transcription. 10. a) OUTER b) Most of the amino acids in this section are either polar or charged, so they will be attra ...
... should eb the same (no introns were cut out). However, if the RNA is shorter than the DNA then you could conclude that it went through some post-translational modifications after transcription. 10. a) OUTER b) Most of the amino acids in this section are either polar or charged, so they will be attra ...
REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION
... Inhibiting a gene so that it can’t be transcribed and translated When a cell needs to make a particular protein, the gene is activated and transcription and translation occurs. When a cell no longer needs the protein, the gene is inactivated and transcription and translation can’t occur Some ...
... Inhibiting a gene so that it can’t be transcribed and translated When a cell needs to make a particular protein, the gene is activated and transcription and translation occurs. When a cell no longer needs the protein, the gene is inactivated and transcription and translation can’t occur Some ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
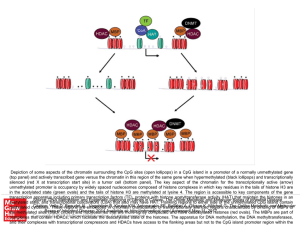
... (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (a ...
... (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (a ...
Chapters 13-20 "Fill in the Blank"
... Now let’s move on to viruses & bacteria. Viruses have 2 general reproductive cycles, the 54._________________ cycle in which virulent viruses immediately kill the host cell, & the 55.________________________ cycle in which temparate virus can “hide” within the host’s genome. Some viruses, like HIV, ...
... Now let’s move on to viruses & bacteria. Viruses have 2 general reproductive cycles, the 54._________________ cycle in which virulent viruses immediately kill the host cell, & the 55.________________________ cycle in which temparate virus can “hide” within the host’s genome. Some viruses, like HIV, ...
DNA to RNA
... information you need—shorter/simpler Think of it like this: DNA = master copy RNA = blueprints…you don’t need the blueprints for the whole house to build the foundation ...
... information you need—shorter/simpler Think of it like this: DNA = master copy RNA = blueprints…you don’t need the blueprints for the whole house to build the foundation ...
Christa Merzdorf, Elena Kalinina-Turner -- Cell
... tube closures. Since mutations in Zic2 or Zic3 genes in mouse and humans are known to cause neural tube defects (Merzdorf, 2007), our hypothesis stated that either Zic2 or Zic3 regulates the aquaporin that aids in closing the neural tube. Morpholino oligonucleotides (MOs) were used to address which ...
... tube closures. Since mutations in Zic2 or Zic3 genes in mouse and humans are known to cause neural tube defects (Merzdorf, 2007), our hypothesis stated that either Zic2 or Zic3 regulates the aquaporin that aids in closing the neural tube. Morpholino oligonucleotides (MOs) were used to address which ...
Document
... gene expression • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining gen ...
... gene expression • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining gen ...
Transcription
... • Chemical signals turn gene for a specific protein on. • Enzymes attach to DNA at the gene’s location and unzip only where that gene is on the DNA. – DNA A T C G ...
... • Chemical signals turn gene for a specific protein on. • Enzymes attach to DNA at the gene’s location and unzip only where that gene is on the DNA. – DNA A T C G ...
Control of Gene Expression
... • Some genes are expressed in all cells all the time. These so-called housekeeping genes are responsible for the routine metabolic functions (e.g. respiration) common to all cells. • Some are expressed as a cell enters a particular pathway of differentiation. • Some are expressed all the time in onl ...
... • Some genes are expressed in all cells all the time. These so-called housekeeping genes are responsible for the routine metabolic functions (e.g. respiration) common to all cells. • Some are expressed as a cell enters a particular pathway of differentiation. • Some are expressed all the time in onl ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.