12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
History of Genetics
... with minor nucleotide changes that yield slightly different proteins. • For a given gene, many different alleles can exist in a population (members of the same species), but an individual diploid organism can have 2 alleles at most: one from each parent. Diploid = having 2 copies of each gene and ea ...
... with minor nucleotide changes that yield slightly different proteins. • For a given gene, many different alleles can exist in a population (members of the same species), but an individual diploid organism can have 2 alleles at most: one from each parent. Diploid = having 2 copies of each gene and ea ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (4-2) Discuss problems and limitations of the “One gene – one enzyme hypothesis” and how it can be better formulated. (4-3) Explain one example of how mutations in either the α- or β-hemoglobins can produce an altered phenotype that may be adaptive to a particular geographic region. (5-1) Distingui ...
... (4-2) Discuss problems and limitations of the “One gene – one enzyme hypothesis” and how it can be better formulated. (4-3) Explain one example of how mutations in either the α- or β-hemoglobins can produce an altered phenotype that may be adaptive to a particular geographic region. (5-1) Distingui ...
Biology EOC Words for Pages 64-80, Teacher Key Codominance
... Insertion Mutation- a sizeable length of DNA is inserted into a gene. An insertion changes the number of DNA bases in a gene by adding a piece of DNA. As a result, the protein made by the gene may not function properly. Duplication Mutation- A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormall ...
... Insertion Mutation- a sizeable length of DNA is inserted into a gene. An insertion changes the number of DNA bases in a gene by adding a piece of DNA. As a result, the protein made by the gene may not function properly. Duplication Mutation- A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormall ...
1) Genetics Vocabulary
... DNA – a chemical inside cells that contains hereditary information and controls how an organism will look and function. Fertilization – process in which sperm and egg join, resulting in a new organism. Gene – small section of DNA on a chromosome that carries information about a trait. Genetics – the ...
... DNA – a chemical inside cells that contains hereditary information and controls how an organism will look and function. Fertilization – process in which sperm and egg join, resulting in a new organism. Gene – small section of DNA on a chromosome that carries information about a trait. Genetics – the ...
DNA Day research - DNA model construction
... ~leading strand elongates as DNA unwinds, lagging strand elongates away from replication * JOINING ~DNA polymerase replaces RNA primer with nucleotides. ~DNA ligase links 2 sections ...
... ~leading strand elongates as DNA unwinds, lagging strand elongates away from replication * JOINING ~DNA polymerase replaces RNA primer with nucleotides. ~DNA ligase links 2 sections ...
Document
... • some RNA’s are active and can function in the cell on their own • some RNA’s are incorporated into protein complexes to function * The main functions of non-coding RNA’s are in protein production and regulation of gene expression ...
... • some RNA’s are active and can function in the cell on their own • some RNA’s are incorporated into protein complexes to function * The main functions of non-coding RNA’s are in protein production and regulation of gene expression ...
Standard Genetic Code
... instructions are used by translating the code into protein. The code of DNA/RNA nucleotides come in sets of three bases called a codon. Most of these codons are translated to an amino acid, but a few of the codons signal for the ribosome to let go of the growing protein, thus stopping translation. A ...
... instructions are used by translating the code into protein. The code of DNA/RNA nucleotides come in sets of three bases called a codon. Most of these codons are translated to an amino acid, but a few of the codons signal for the ribosome to let go of the growing protein, thus stopping translation. A ...
scientists and philosophers find that gene has a multitude of meanings
... I owe an apology to my genes. For years I offhandedly blamed them for certain personal defects conventionally associated with one’s hereditary starter pack — my Graves’ autoimmune disease, for example, or my hair, which looks like the fibers left behind on the rim of an aspirin bottle after the cott ...
... I owe an apology to my genes. For years I offhandedly blamed them for certain personal defects conventionally associated with one’s hereditary starter pack — my Graves’ autoimmune disease, for example, or my hair, which looks like the fibers left behind on the rim of an aspirin bottle after the cott ...
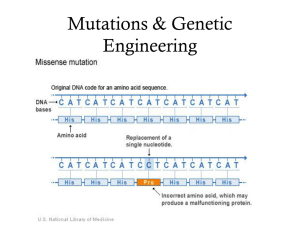
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense ...
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense ...
«題目»
... The molecular basis of epigenetics involves modifications to DNA and histone proteins that associate with the regulation of gene expression but that do not result from mutation or changes to the DNA sequence. The four core histone proteins are subject to post-translational modifications, such as ace ...
... The molecular basis of epigenetics involves modifications to DNA and histone proteins that associate with the regulation of gene expression but that do not result from mutation or changes to the DNA sequence. The four core histone proteins are subject to post-translational modifications, such as ace ...
Genetics 1. What do the letters DNA stand for? 2. Two scientists are
... Genetics 7. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimides. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. ...
... Genetics 7. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimides. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. ...
2.2 Sequencing learning grid File
... What does thermophilic mean? What four things are required in the reaction mixture at the beginning of automated sequencing? What is special about some of the free nucleotides in automated sequencing? What is significant about these ...
... What does thermophilic mean? What four things are required in the reaction mixture at the beginning of automated sequencing? What is special about some of the free nucleotides in automated sequencing? What is significant about these ...
No Slide Title
... The DNA sequence of the entire haploid set of chromosomes constitutes the genome of an organism (and, more broadly, species). The sequence of many genomes has been (many bacteria, yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, human) or is being (mouse, maize) determined. WHY do we want to determine ge ...
... The DNA sequence of the entire haploid set of chromosomes constitutes the genome of an organism (and, more broadly, species). The sequence of many genomes has been (many bacteria, yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, human) or is being (mouse, maize) determined. WHY do we want to determine ge ...
Q on Genetic Control of Protein Structure and function – Chapter 5
... The mRNA leaves the nucleus via a nuclear pore. The ribosome moves to the next mRNA codon. A second tRNA molecule binds to the next codon. The amino acids attached to the tRNA molecules join together with a peptide bond. An anticodon on a tRNA molecule attaches to the first mRNA codon. The first tRN ...
... The mRNA leaves the nucleus via a nuclear pore. The ribosome moves to the next mRNA codon. A second tRNA molecule binds to the next codon. The amino acids attached to the tRNA molecules join together with a peptide bond. An anticodon on a tRNA molecule attaches to the first mRNA codon. The first tRN ...
Slide 1 - tacademy.ca
... Chromosome – a thread-like structure made mostly of DNA, found in the nucleus of a cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – material found in the cell nucleus that contains genetic information Gene – a segment of DNA that controls protein production ...
... Chromosome – a thread-like structure made mostly of DNA, found in the nucleus of a cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – material found in the cell nucleus that contains genetic information Gene – a segment of DNA that controls protein production ...
Lecture 2 PSY391S John Yeomans
... • Can separate and then self-replicate. • Hold all genetic information in higher animals. • Human genome 3.1 billion bases (2000). ...
... • Can separate and then self-replicate. • Hold all genetic information in higher animals. • Human genome 3.1 billion bases (2000). ...
protein synthesis (simplified)
... If the protein is the wrong shape it will not work properly (it may work differently) So if the sequence in the DNA is wrong it may result in a genetic disease ...
... If the protein is the wrong shape it will not work properly (it may work differently) So if the sequence in the DNA is wrong it may result in a genetic disease ...
File
... • A donor bacterium (F+ or Hfr) produces a tube, or pilus, that connects to the recipient bacterium. ...
... • A donor bacterium (F+ or Hfr) produces a tube, or pilus, that connects to the recipient bacterium. ...
Antibody Diversity 02/16/06
... Problem…the immune system makes over one billion different antibody proteins • In 1950’s: central dogma stated DNA—to RNA—to protein • One gene for each protein • Required millions of genes just for the immune system • Does not seem possible, but most scientists thought it might be • Today we know ...
... Problem…the immune system makes over one billion different antibody proteins • In 1950’s: central dogma stated DNA—to RNA—to protein • One gene for each protein • Required millions of genes just for the immune system • Does not seem possible, but most scientists thought it might be • Today we know ...