Document
... 1. Damage the DNA of the affected cancer cells. 2. Inhibit the synthesis of new DNA strands to stop the cell from replicating, because the replication of the cell is what allows the tumor to grow. 3. Stop mitosis or the actual splitting of the original cell into two new cells. Stopping mitosis stops ...
... 1. Damage the DNA of the affected cancer cells. 2. Inhibit the synthesis of new DNA strands to stop the cell from replicating, because the replication of the cell is what allows the tumor to grow. 3. Stop mitosis or the actual splitting of the original cell into two new cells. Stopping mitosis stops ...
Genetic Disorders
... to treat diseases by altering our very genes‚ giving us new ones if ours are nonfunctional, changing bad genes for good ones. For the first time in our existence, we are closer to understanding just what we are. We now have the tools to make the whole world better through science ‚ the science of th ...
... to treat diseases by altering our very genes‚ giving us new ones if ours are nonfunctional, changing bad genes for good ones. For the first time in our existence, we are closer to understanding just what we are. We now have the tools to make the whole world better through science ‚ the science of th ...
PCR and diagnostics II
... • If incorrect size know there was a mutation • Screening of the protein product allows screening of a very large pieceof DNA when you don’t know specifically what you are looking for ...
... • If incorrect size know there was a mutation • Screening of the protein product allows screening of a very large pieceof DNA when you don’t know specifically what you are looking for ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis
... Post Lab Questions: List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
... Post Lab Questions: List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
For SNP microarray analysis processed before Oct. 15, 2012
... approximately 1,140,419 probes including both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and non-SNP alleles. The test is used to identify chromosomal imbalances throughout the human genome. These imbalances include deletions, duplications and aneuploidy. Microarray testing is not designed to detect bala ...
... approximately 1,140,419 probes including both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and non-SNP alleles. The test is used to identify chromosomal imbalances throughout the human genome. These imbalances include deletions, duplications and aneuploidy. Microarray testing is not designed to detect bala ...
Document
... specific function (i.e. tubulin microtubules, catalase in cells, helicase to unwind DNA, etc.). There are only 20 amino acids; we are able to make 12 in our bodies (termed nonessential) and we must intake the other 8 in the food we eat (essential - isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalan ...
... specific function (i.e. tubulin microtubules, catalase in cells, helicase to unwind DNA, etc.). There are only 20 amino acids; we are able to make 12 in our bodies (termed nonessential) and we must intake the other 8 in the food we eat (essential - isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalan ...
Human Alu Insertion Polymorphism Experiment
... •Primers are single stranded synthetic sequences of DNA normally 20-30 bp. •One primer is complementary to the beginning of the target gene on one strand while the other primer is complementary to end of the target gene on the complementary strand. ...
... •Primers are single stranded synthetic sequences of DNA normally 20-30 bp. •One primer is complementary to the beginning of the target gene on one strand while the other primer is complementary to end of the target gene on the complementary strand. ...
DNA Review Questions (answers) no applications
... tRNA that are the complement to the codons. This ensures that the proper amino acid is brought in during translation. 11. How does translation begin and end? Begins with a start codon (AUG) and ends with a stop codon (UAG, UGA, UAA). 12. How is tRNA used in protein synthesis? tRNA has the complement ...
... tRNA that are the complement to the codons. This ensures that the proper amino acid is brought in during translation. 11. How does translation begin and end? Begins with a start codon (AUG) and ends with a stop codon (UAG, UGA, UAA). 12. How is tRNA used in protein synthesis? tRNA has the complement ...
Genes
... Lac repressor (R) bound to the operator unless it forms a complex with allolactose (A) in a glucose-poor and lactose-rich environment Blocks transcription Lac Z: contains 3075 bases and encodes β-galactosidase, which splits the disaccharide lactose into monosaccharides glucose and galactose RNAp b ...
... Lac repressor (R) bound to the operator unless it forms a complex with allolactose (A) in a glucose-poor and lactose-rich environment Blocks transcription Lac Z: contains 3075 bases and encodes β-galactosidase, which splits the disaccharide lactose into monosaccharides glucose and galactose RNAp b ...
AS 90729 version 2 Describe genetic processes Level 3 Credits 4
... produced. Polypeptide chains are made by using the DNA code (gene) to create the RNA code, then the polypeptide chain / protein. The first step is to transcribe the gene into the mRNA inside the nucleus. The mRNA is made by complementary base pairing with the DNA. In the mRNA, there is no T instead ...
... produced. Polypeptide chains are made by using the DNA code (gene) to create the RNA code, then the polypeptide chain / protein. The first step is to transcribe the gene into the mRNA inside the nucleus. The mRNA is made by complementary base pairing with the DNA. In the mRNA, there is no T instead ...
Chp 11.2: Nucleic Acid structure and sequence
... 1. Adenine (A) 2. Thymine (T) 3. Cytosine (C) 4. Guanine (G) ...
... 1. Adenine (A) 2. Thymine (T) 3. Cytosine (C) 4. Guanine (G) ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
Answer all the questions Time allowed : 49 minutes 1. State two
... random assortment and crossing over at meiosis. Thus in a deep sea environment fish may have good vision, degenerated vision but with alternative forms of sense. More offspring are produced than the environment can support, which lead to struggle for existence among different varieties. The environm ...
... random assortment and crossing over at meiosis. Thus in a deep sea environment fish may have good vision, degenerated vision but with alternative forms of sense. More offspring are produced than the environment can support, which lead to struggle for existence among different varieties. The environm ...
Biologists have learned to manipulate DNA
... a. When the repressor changes shape it no longer binds to the operator b. The operator is open and RNA polymerase binds to the promoter c. The lactose processing genes are turned on d. When lactose is no longer present – the repressor can rebind to the operator D. Prokaryotes waste little energy on ...
... a. When the repressor changes shape it no longer binds to the operator b. The operator is open and RNA polymerase binds to the promoter c. The lactose processing genes are turned on d. When lactose is no longer present – the repressor can rebind to the operator D. Prokaryotes waste little energy on ...
DNA Replication
... The entire genome is on one circular chromosome = DNA molecule. The chromosome replicates once to produce two chromosomes that are identical (except for rare mutations). The two identical daughter chromosomes move toward opposite end of the cell. When the cell divides the daughter chromosomes are pa ...
... The entire genome is on one circular chromosome = DNA molecule. The chromosome replicates once to produce two chromosomes that are identical (except for rare mutations). The two identical daughter chromosomes move toward opposite end of the cell. When the cell divides the daughter chromosomes are pa ...
Cell Cycle Quiz key
... D. The nucleus translates the ribosomal RNA for the enzymes to be synthesized in mitochondria. 15. _____During a stage of protein synthesis, codons in mRNA molecules are used to specify the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains. What is this process called? A. transcription B. gene expressio ...
... D. The nucleus translates the ribosomal RNA for the enzymes to be synthesized in mitochondria. 15. _____During a stage of protein synthesis, codons in mRNA molecules are used to specify the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains. What is this process called? A. transcription B. gene expressio ...
BioSc 231 Exam 5 2003
... _____ Which of the following is NOT necessary in order for a population to maintain Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A. random mating B. high rate of migration C. large population size D. allele frequencies are the same in males and females _____ In a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium the frequenc ...
... _____ Which of the following is NOT necessary in order for a population to maintain Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A. random mating B. high rate of migration C. large population size D. allele frequencies are the same in males and females _____ In a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium the frequenc ...
CH 3 RG 2014 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... 9. Do you remember we said, “To change the structure will change the function”? Explain how this principle applies to sickle–cell disease. Why is the structure changed? ...
... 9. Do you remember we said, “To change the structure will change the function”? Explain how this principle applies to sickle–cell disease. Why is the structure changed? ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
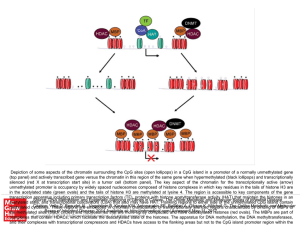
... (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (a ...
... (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (a ...
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the
... 1) Nucleic acids are organic molecules (biomolecules) that allow organisms to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next. 2) There are two types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid, known as DNA and ribonucleic acid, known as RNA. ...
... 1) Nucleic acids are organic molecules (biomolecules) that allow organisms to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next. 2) There are two types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid, known as DNA and ribonucleic acid, known as RNA. ...