Keystone Review: Quiz 4
... 1.) A scientist observes that a certain trait is determined by a single allele. An organism inherited one version of the trait from one parent and another version from the other parent. Both versions of the trait are expressed in the phenotype of the offspring. Which pattern of inheritance best clas ...
... 1.) A scientist observes that a certain trait is determined by a single allele. An organism inherited one version of the trait from one parent and another version from the other parent. Both versions of the trait are expressed in the phenotype of the offspring. Which pattern of inheritance best clas ...
DNA Notes
... • Was able to tell that DNA had an “X” like structure where the strands are twisted around each other • All of these discoveries led to the following…. ...
... • Was able to tell that DNA had an “X” like structure where the strands are twisted around each other • All of these discoveries led to the following…. ...
Genomes & their evolution
... # genes in given length of DNA eukaryotes generally have larger genomes but fewer genes in given # of bps humans have 100’s – 1000’s times more bps but only 5 – 15 times as many genes Sooooo: gene density lower in humans than in bacteria ...
... # genes in given length of DNA eukaryotes generally have larger genomes but fewer genes in given # of bps humans have 100’s – 1000’s times more bps but only 5 – 15 times as many genes Sooooo: gene density lower in humans than in bacteria ...
Document
... 1) Werner Arber: enzymes which cut DNA at specific sites called "restriction enzymes” because restrict host range for certain bacteriophage ...
... 1) Werner Arber: enzymes which cut DNA at specific sites called "restriction enzymes” because restrict host range for certain bacteriophage ...
Mutations - Hicksville Public Schools
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
Genomics
... • Knockout studies are one experimental method for understanding the function of DNA sequences and the proteins they encode. Researchers inactivate genes in living organisms and monitor any changes that could reveal the function of specific genes. • Comparative genomics—analyzing DNA sequence patter ...
... • Knockout studies are one experimental method for understanding the function of DNA sequences and the proteins they encode. Researchers inactivate genes in living organisms and monitor any changes that could reveal the function of specific genes. • Comparative genomics—analyzing DNA sequence patter ...
II. Principles of Cell
... • DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond in a DNA strand by connecting a 5’ phosphate of a nucleotide and the 3’ -OH group of a neighboring nucleotide. This is the cloning enzyme that links a DNA fragment (gene) into a cloning vector creating a recombinant vector. • Plasmid ve ...
... • DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond in a DNA strand by connecting a 5’ phosphate of a nucleotide and the 3’ -OH group of a neighboring nucleotide. This is the cloning enzyme that links a DNA fragment (gene) into a cloning vector creating a recombinant vector. • Plasmid ve ...
DNA vaccination
... the antigen expression unit composed of promoter sequences AND antigenencoding and polyadenylation sequences (termination signal) ...
... the antigen expression unit composed of promoter sequences AND antigenencoding and polyadenylation sequences (termination signal) ...
Freshwater ecosystem assessment - Centre for Marine Biodiversity
... Ecoinformatics bottlenecks: Taxonomy Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species ...
... Ecoinformatics bottlenecks: Taxonomy Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 5. If a protein has 150 amino acids, how many DNA nucleotides would make up the coding region of the gene? ...
... 5. If a protein has 150 amino acids, how many DNA nucleotides would make up the coding region of the gene? ...
Ch 12.DNA and RNA.Biology.Landis
... 33. Where does translation occur? 34. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation can occur, messenger RNA must be transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid i ...
... 33. Where does translation occur? 34. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation can occur, messenger RNA must be transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid i ...
Document
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
S1.A hypothetical sequence at the beginning of an mRNA molecule
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
Audesirk, Audesirk, Byers BIOLOGY: Life on Earth Eighth Edition
... nucleotides different from their normal meaning. ...
... nucleotides different from their normal meaning. ...
unit 4 study guide
... Know the differences between DNA and RNA Know the structure of DNA and RNA Know Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription 2. M-RNA Processing 3. Translation Know DNA Replication Know all about DNA, mRNA, and tRNA; Know diagrams of such molecules and be able to match parts to them. Know the monomers (buildi ...
... Know the differences between DNA and RNA Know the structure of DNA and RNA Know Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription 2. M-RNA Processing 3. Translation Know DNA Replication Know all about DNA, mRNA, and tRNA; Know diagrams of such molecules and be able to match parts to them. Know the monomers (buildi ...
Name
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The process of making proteins is called protein ...
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The process of making proteins is called protein ...
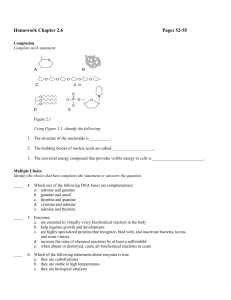
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... b. help regulate growth and development c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
... b. help regulate growth and development c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
Name - WordPress.com
... In class we’ve been talking about how offspring inherit traits from their parents. We know that they inherit alleles, which are copies of genes, by receiving DNA from their parents. We also know that the DNA is located within a chromosome inside the nucleus of a gamete, or sex cell. We can actually ...
... In class we’ve been talking about how offspring inherit traits from their parents. We know that they inherit alleles, which are copies of genes, by receiving DNA from their parents. We also know that the DNA is located within a chromosome inside the nucleus of a gamete, or sex cell. We can actually ...
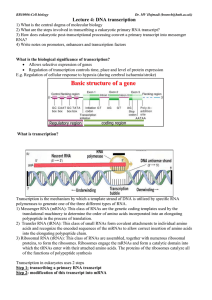
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
Transcription and Translation
... DNA sequence has coding regions (exons) and noncoding regions (introns) Introns must be removed before primary transcript is mRNA and can leave nucleus ...
... DNA sequence has coding regions (exons) and noncoding regions (introns) Introns must be removed before primary transcript is mRNA and can leave nucleus ...
Genomics
... • Knockout studies are one experimental method for understanding the function of DNA sequences and the proteins they encode. Researchers inactivate genes in living organisms and monitor any changes that could reveal the function of specific genes. • Comparative genomics—analyzing DNA sequence patter ...
... • Knockout studies are one experimental method for understanding the function of DNA sequences and the proteins they encode. Researchers inactivate genes in living organisms and monitor any changes that could reveal the function of specific genes. • Comparative genomics—analyzing DNA sequence patter ...
repair - Molecular and Cell Biology
... (2) …often progeny from mutated sperm are genetically mosaic for new mutations only one of the two complementary bases in sperm are modified: GC -> G *C -> G*T & GC in sperm ...
... (2) …often progeny from mutated sperm are genetically mosaic for new mutations only one of the two complementary bases in sperm are modified: GC -> G *C -> G*T & GC in sperm ...