4.1 Le Noyau
... • Genes can be composed of hundreds or thousands nitrogen bases. • Produces a particular trait. • Each chromosome is made up of thousands of genes. • Therefore, can produce thousands of ...
... • Genes can be composed of hundreds or thousands nitrogen bases. • Produces a particular trait. • Each chromosome is made up of thousands of genes. • Therefore, can produce thousands of ...
Document
... Yeast, unicellular eukaryote 13 Mbp Worm (Caenorhabditis elegans) 100 Mbp Fly, invertebrate (Drosophila melanogaster) 170 Mbp ...
... Yeast, unicellular eukaryote 13 Mbp Worm (Caenorhabditis elegans) 100 Mbp Fly, invertebrate (Drosophila melanogaster) 170 Mbp ...
Grade 9 Science Ch 4 - Answers to Comprehensive Questions
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
Special Topics gene expression
... A. Where does this occur? IV. Translation –RNA to protein A. Where does this occur? VI. Why do we care about gene expression as allied health students? VII. Terminology to be aware of throughout the semester ...
... A. Where does this occur? IV. Translation –RNA to protein A. Where does this occur? VI. Why do we care about gene expression as allied health students? VII. Terminology to be aware of throughout the semester ...
Genetics 101 - People @ EECS at UC Berkeley
... • Low error rate (10^-9) due to error correcting processes • Dissociation during conformation -- for new nucleotide to be covalently bound to growing polymer, DNA polymerase must undergo conformational change -- incorrect nucleotide more likely to dissociate • Exonucleolytic proofreading -- a mismat ...
... • Low error rate (10^-9) due to error correcting processes • Dissociation during conformation -- for new nucleotide to be covalently bound to growing polymer, DNA polymerase must undergo conformational change -- incorrect nucleotide more likely to dissociate • Exonucleolytic proofreading -- a mismat ...
History of Genetics
... • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. ...
... • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. ...
Human Molecular Genetics
... in the DNA code of a living organism. DNA Extraction: cells are opened and the DNA is separated from the other cell parts Cutting DNA: biologists cut them into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes Separating DNA: Gel Electrophoresis separates DNA fragments according to their size. ...
... in the DNA code of a living organism. DNA Extraction: cells are opened and the DNA is separated from the other cell parts Cutting DNA: biologists cut them into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes Separating DNA: Gel Electrophoresis separates DNA fragments according to their size. ...
DNA Discovery - Biology Junction
... Frederick Griffith – bacterial transformation Oswald Avery – DNA = key to transformation Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase – Bacteriophage transformation experiment Erwin Chargaff – base-pairing rules ...
... Frederick Griffith – bacterial transformation Oswald Avery – DNA = key to transformation Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase – Bacteriophage transformation experiment Erwin Chargaff – base-pairing rules ...
DNA - Lemon Bay High School
... stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the next. ...
... stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the next. ...
DNA
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
Gen660_Week4a_HGT_2014
... • Phage can package random or adjacent donor DNA • DNA size limited by capsid packaging (but still can be 100 kb) • Recipient must be able to take up phage (through specific receptors, etc) ...
... • Phage can package random or adjacent donor DNA • DNA size limited by capsid packaging (but still can be 100 kb) • Recipient must be able to take up phage (through specific receptors, etc) ...
Slide () - Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research
... (blue) attaches to a cell (see Subpanel B). Once attached, the DNA of the virus (see black vertical line) will be inserted into the cytoplasm of the host cell (see Subpanels 1C and 1D), where the viral DNA will incorporate into the DNA of the host cell (red; see Subpanel 1E). Viral DNA consists of s ...
... (blue) attaches to a cell (see Subpanel B). Once attached, the DNA of the virus (see black vertical line) will be inserted into the cytoplasm of the host cell (see Subpanels 1C and 1D), where the viral DNA will incorporate into the DNA of the host cell (red; see Subpanel 1E). Viral DNA consists of s ...
How Do You Like Your Genes?
... “The prices have come down to the point where it is less expensive for many researchers to have a gene synthesized than to make the equivalent molecule themselves,” said John Mulligan, chairman and chief scientist at Blue Heron Biotechnology, a gene-synthesis company in Bothell, Wash. Genetic engine ...
... “The prices have come down to the point where it is less expensive for many researchers to have a gene synthesized than to make the equivalent molecule themselves,” said John Mulligan, chairman and chief scientist at Blue Heron Biotechnology, a gene-synthesis company in Bothell, Wash. Genetic engine ...
DNA!
... DNA SCREENING • The process of testing individuals to determine whether they have the gene(s) associated with certain disorders. ...
... DNA SCREENING • The process of testing individuals to determine whether they have the gene(s) associated with certain disorders. ...
DNA
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... How did Griffith arrive at the conclusion that a gene from one kind of bacteria transformed another kind of bacteria? Avery, Macleod and McCarty – What did Avery conclude caused transformation? Hershey and Chase – ...
... How did Griffith arrive at the conclusion that a gene from one kind of bacteria transformed another kind of bacteria? Avery, Macleod and McCarty – What did Avery conclude caused transformation? Hershey and Chase – ...
GENETICS 310-PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY
... EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answers can be accessed via the internet at: Genetics 310 TAMU . GRADES: Your grade will be determined by your performance on 3 in-class exams, a comprehensive final, and an outside paper on a re ...
... EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answers can be accessed via the internet at: Genetics 310 TAMU . GRADES: Your grade will be determined by your performance on 3 in-class exams, a comprehensive final, and an outside paper on a re ...
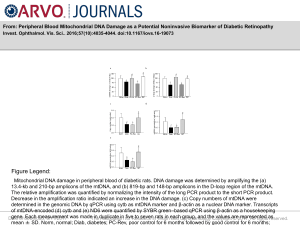
Slide
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
Cloze passage 3
... p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a family tree u) A colourblind male need onl ...
... p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a family tree u) A colourblind male need onl ...
Microbial Genetics
... mRNA is copy of DNA gene Created by transcription Protein made during translation ...
... mRNA is copy of DNA gene Created by transcription Protein made during translation ...
Gen677_Week5a_HGT_2012
... • Phage can package random or adjacent donor DNA • DNA size limited by capsid packaging (but still can be 100 kb) • Recipient must be able to take up phage (through specific receptors, etc) ...
... • Phage can package random or adjacent donor DNA • DNA size limited by capsid packaging (but still can be 100 kb) • Recipient must be able to take up phage (through specific receptors, etc) ...
Practicing Protein Synthesis
... both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest sugars the same way others can, and they have a disease called diabetes. Using the DNA sequence, make a co ...
... both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest sugars the same way others can, and they have a disease called diabetes. Using the DNA sequence, make a co ...
Project proposal MSc in Computational Genetics and Bioinformatics
... The problem of identifying genes in genomic DNA sequences by computational methods has attracted considerable research attention in recent years. The problem is closely related to the fundamental biochemical issues of specifying the precise sequence determinants of transcription, translation and spl ...
... The problem of identifying genes in genomic DNA sequences by computational methods has attracted considerable research attention in recent years. The problem is closely related to the fundamental biochemical issues of specifying the precise sequence determinants of transcription, translation and spl ...