Translation Worksheet
... 2. The main goal of translation is to turn ____________ into ___________. ...
... 2. The main goal of translation is to turn ____________ into ___________. ...
How Genes and Genomes Evolve
... functional RNAs – Processing requires variety of small RNAs (90 – 300 nucleotides long) & their associated proteins ...
... functional RNAs – Processing requires variety of small RNAs (90 – 300 nucleotides long) & their associated proteins ...
5 - Parkway C-2
... • These modifications share several functions: – They seem to facilitate the export of mRNA – They protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes – They help ribosomes attach to the 5’ end ...
... • These modifications share several functions: – They seem to facilitate the export of mRNA – They protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes – They help ribosomes attach to the 5’ end ...
PPT
... Strand which is complementary to the template strand Strand of which the sequence is the same as that of the RNA transcript ...
... Strand which is complementary to the template strand Strand of which the sequence is the same as that of the RNA transcript ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... Cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs) are synthesized from intra- and intergenic regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and are rapidly degraded by RNA surveillance pathways, but their function(s) remain(s) elusive. Here, we show that an antisense TY1 CUT, starting within the Ty1 retrotransposon and enco ...
... Cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs) are synthesized from intra- and intergenic regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and are rapidly degraded by RNA surveillance pathways, but their function(s) remain(s) elusive. Here, we show that an antisense TY1 CUT, starting within the Ty1 retrotransposon and enco ...
Chapter-Translation (Prokaryotes)
... fact ribosomes form the backbone for many molecules during the process of protein synthesis. The ribosomes on assembly can have many small grooves or tunnels. These are the active sites dedicated to specific tasks during protein synthesis. During the process of translation of mRNA, a number of ribos ...
... fact ribosomes form the backbone for many molecules during the process of protein synthesis. The ribosomes on assembly can have many small grooves or tunnels. These are the active sites dedicated to specific tasks during protein synthesis. During the process of translation of mRNA, a number of ribos ...
Lecture genes to proteins translation - IIT
... Figure 17.14a Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Figure 17.14a Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
DNA Review (study guide)
... 3. Base pairing rule states that the DNA of any species contains equal amounts of __________________ & ____________ and also equal amounts of __________________ & ____________________ 4. Wilkins and Franklin studied the structure of DNA using _________________________. 5. In DNA, thymine is compleme ...
... 3. Base pairing rule states that the DNA of any species contains equal amounts of __________________ & ____________ and also equal amounts of __________________ & ____________________ 4. Wilkins and Franklin studied the structure of DNA using _________________________. 5. In DNA, thymine is compleme ...
Foundations of Biology
... In addition to promoters, enhancers also influence the expression of genes Control of gene expression in eukaryotes involves many more factors than control in prokaryotes This allows much finer control of gene expression ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
... In addition to promoters, enhancers also influence the expression of genes Control of gene expression in eukaryotes involves many more factors than control in prokaryotes This allows much finer control of gene expression ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
outline of translation
... The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a site on the DNA at the start of a gene (The sequence of DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene). RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and synthesises a complementary RNA copy from the antisense DNA strand Once the RNA sequence has been synthesised: ...
... The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a site on the DNA at the start of a gene (The sequence of DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene). RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and synthesises a complementary RNA copy from the antisense DNA strand Once the RNA sequence has been synthesised: ...
Translation
... A) UUU and UUC both code for Phe; UUU codes only for Phe. B) UUU codes only for Phe; UUU and UUC both code for Phe. C) UUU codes for both Phe and Ser; UUU and UUC both code for Phe and Ser. D) UUU and UUC both code for Phe and Ser; UUU codes for both Phe and Ser. ...
... A) UUU and UUC both code for Phe; UUU codes only for Phe. B) UUU codes only for Phe; UUU and UUC both code for Phe. C) UUU codes for both Phe and Ser; UUU and UUC both code for Phe and Ser. D) UUU and UUC both code for Phe and Ser; UUU codes for both Phe and Ser. ...
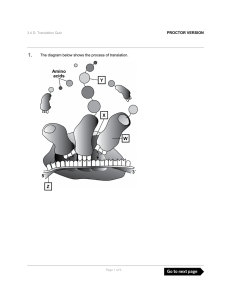
The diagram below shows the process of translation. PROCTOR
... (D) Structure Z is a growing polypeptide chain that is being synthesized by tRNA and rRNA, and that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction o ...
... (D) Structure Z is a growing polypeptide chain that is being synthesized by tRNA and rRNA, and that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction o ...
problem set
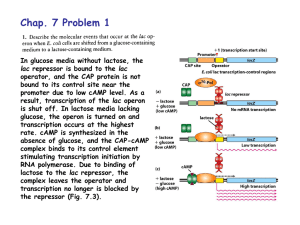
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard - Broken Arrow Public Schools
... • DNA, the genetic material of organisms, is composed of four kinds of nucleotides. A DNA molecule consists of two strands of nucleotides with sugars and phosphates on the outside and bases paired by hydrogen bonding on the inside. The paired strands form a twisted-zipper shape called a double ...
... • DNA, the genetic material of organisms, is composed of four kinds of nucleotides. A DNA molecule consists of two strands of nucleotides with sugars and phosphates on the outside and bases paired by hydrogen bonding on the inside. The paired strands form a twisted-zipper shape called a double ...
Genetic Code, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... It is believed that snRNAs in the snRNPS serve as the catalysts for the intron excision and splicing of the exons, as well as in the formation of spliceosomes and the exon splice sites. This is unusual, since our familiar catalysts in living organisms are all enzymes. It is not unheard of, however. ...
... It is believed that snRNAs in the snRNPS serve as the catalysts for the intron excision and splicing of the exons, as well as in the formation of spliceosomes and the exon splice sites. This is unusual, since our familiar catalysts in living organisms are all enzymes. It is not unheard of, however. ...
Ch. 10, DNA and Proteins
... The amount and kind of proteins produced in a cell determine its structure & function ...
... The amount and kind of proteins produced in a cell determine its structure & function ...
1. Ribonucleic acid is not normally associated with the (1) cytoplasm
... 9. In a cell, the transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA occurs in the (1) cell membrane (3) nucleus (2) endoplasmic reticulum (4) nucleolus 10. Which nucleic acid carries instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? (3) Transfer RNA, only (1) DNA, only (4) DNA, messenger RNA, and transf ...
... 9. In a cell, the transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA occurs in the (1) cell membrane (3) nucleus (2) endoplasmic reticulum (4) nucleolus 10. Which nucleic acid carries instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? (3) Transfer RNA, only (1) DNA, only (4) DNA, messenger RNA, and transf ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... At the end of this unit, I will: Know how to transcribe DNA to RNA and translate RNA to protein. Be able to find the amino acids represented on a codon table. Appreciate the fact that there can be some mutations in DNA that won’t show up in protein, but some mutations will. Know where in the ...
... At the end of this unit, I will: Know how to transcribe DNA to RNA and translate RNA to protein. Be able to find the amino acids represented on a codon table. Appreciate the fact that there can be some mutations in DNA that won’t show up in protein, but some mutations will. Know where in the ...
Gene Expression
... To react quickly to the environment, a cell must be able to remove outdated signals quickly. Many proteins, especially regulatory signaling proteins, are degraded by ubiquitinmediated proteolysis. Ubiquitin is a small protein that is highly conserved in evolution. In this system, multiple copies of ...
... To react quickly to the environment, a cell must be able to remove outdated signals quickly. Many proteins, especially regulatory signaling proteins, are degraded by ubiquitinmediated proteolysis. Ubiquitin is a small protein that is highly conserved in evolution. In this system, multiple copies of ...
genetic code and tra..
... The figure shows the repetitive cycle of elongation of chain. Each cycle is consisting of: 1) codon recognition and the entrance of the new aminoacyl tRNA acid (amino acid carried on tRNA) into A site, 2) The growing chain in P site will moved to A site with peptide bond formation with the new amino ...
... The figure shows the repetitive cycle of elongation of chain. Each cycle is consisting of: 1) codon recognition and the entrance of the new aminoacyl tRNA acid (amino acid carried on tRNA) into A site, 2) The growing chain in P site will moved to A site with peptide bond formation with the new amino ...
Molecular biology Tools
... Technique based on antigen-antibody reaction Examples: HIV tests &PGE2 ...
... Technique based on antigen-antibody reaction Examples: HIV tests &PGE2 ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition TRANSCRIPTION
... acids to ribosome for protein synthesis. RNAi (interference) a class of small non coding RNAs that function in post transcription regulation as a silencing mechanism Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) extensively transcribed RNAs that do NOT code for proteins that form extensive networks of ribonucleoprote ...
... acids to ribosome for protein synthesis. RNAi (interference) a class of small non coding RNAs that function in post transcription regulation as a silencing mechanism Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) extensively transcribed RNAs that do NOT code for proteins that form extensive networks of ribonucleoprote ...
Control of human β-globin mRNA stability and its impact on beta
... Citation: Peixeiro I, Silva AL and Romão L. Control of human beta-globin mRNA stability and its impact on beta-thalassemia phenotype. Haematologica 2011;96(6):905-913. doi:10.3324/haematol.2010.039206 ...
... Citation: Peixeiro I, Silva AL and Romão L. Control of human beta-globin mRNA stability and its impact on beta-thalassemia phenotype. Haematologica 2011;96(6):905-913. doi:10.3324/haematol.2010.039206 ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.