Naming Conventions The NCBI RefSeq human mRNA
... compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance of matches. BLAST can be used to infer functional and evolutionary relationships between sequences as well as help identify members of gene families. There are five different blast programs, th ...
... compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance of matches. BLAST can be used to infer functional and evolutionary relationships between sequences as well as help identify members of gene families. There are five different blast programs, th ...
INDUCTION OF ß-GALACTOSIDASE IN E.COLI
... One of the best known and most thoroughly studied enzyme induction systems is the lactose operon of E. coli. The structure genes of the lac operon encode the information of three proteins (ß-galactosidase, transacetylase and lactose permease) necessary to be synthesized by the cells utilizing lactos ...
... One of the best known and most thoroughly studied enzyme induction systems is the lactose operon of E. coli. The structure genes of the lac operon encode the information of three proteins (ß-galactosidase, transacetylase and lactose permease) necessary to be synthesized by the cells utilizing lactos ...
lectureMarch7
... the coupling of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and levels during amino acid and nutrient starvation. 1. Ribosome and tRNA synthesis controlled by amino acid levels. 2. rRNA and tRNA levels also controlled by transcription rate which is also constrolled by translation rate-coupled. 3. Ribosome level is also ...
... the coupling of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and levels during amino acid and nutrient starvation. 1. Ribosome and tRNA synthesis controlled by amino acid levels. 2. rRNA and tRNA levels also controlled by transcription rate which is also constrolled by translation rate-coupled. 3. Ribosome level is also ...
Novel Function of the Eukaryotic Polypeptide
... The carboxy-terminal region of GSPT/eRF3 was essentially required for the interaction; GSPT2 deleted with the carboxy-terminal domains 2 and 3 failed to bind eRF1. Moreover, GSPT/eRF3 lacking the unique amino-terminal region could bind to RF1, indicating that the carboxyterminal site of the EF1α-lik ...
... The carboxy-terminal region of GSPT/eRF3 was essentially required for the interaction; GSPT2 deleted with the carboxy-terminal domains 2 and 3 failed to bind eRF1. Moreover, GSPT/eRF3 lacking the unique amino-terminal region could bind to RF1, indicating that the carboxyterminal site of the EF1α-lik ...
Determinants of mRNA localization University
... Therefore, mRNA localization may serve to increase local intracellular concentrations to promote these interactions. Conversely, the effects of non-localized protein synthesis may cause non-productive, promiscuous interactions between polypeptides, or lethal consequences in the case of morphogens. A ...
... Therefore, mRNA localization may serve to increase local intracellular concentrations to promote these interactions. Conversely, the effects of non-localized protein synthesis may cause non-productive, promiscuous interactions between polypeptides, or lethal consequences in the case of morphogens. A ...
From DNA to Protein: Gene Expression
... the β-globin gene with previously isolated βglobin mRNA as the probe. Viewing the hybridized molecules by electron microscopy, they saw that the introns formed loops—stretches of DNA that did not have complementary base sequences on the mature mRNA. If pre-mRNA was used, the result was a linear ...
... the β-globin gene with previously isolated βglobin mRNA as the probe. Viewing the hybridized molecules by electron microscopy, they saw that the introns formed loops—stretches of DNA that did not have complementary base sequences on the mature mRNA. If pre-mRNA was used, the result was a linear ...
File
... "The genetic code is frequently referred to as a blueprint because it contains the instructions a cell requires in order to sustain itself. We now know that there is more to these instructions than simply the sequence of letters in the nucleotide code, however. For example, vast amounts of evidence ...
... "The genetic code is frequently referred to as a blueprint because it contains the instructions a cell requires in order to sustain itself. We now know that there is more to these instructions than simply the sequence of letters in the nucleotide code, however. For example, vast amounts of evidence ...
http://medlib
... whether they take penicillin or not. You can't claim that penicillin causes nausea. But you never would have known this without the proper control. So now, design and describe a control that the Yahoos should do to understand their prolactin data. Remember, your goal is to change one aspect of the ...
... whether they take penicillin or not. You can't claim that penicillin causes nausea. But you never would have known this without the proper control. So now, design and describe a control that the Yahoos should do to understand their prolactin data. Remember, your goal is to change one aspect of the ...
Transcription
... Schematic representation of the major form of E. coli RNA polymerase bound to DNA. By convention, the transcription-initiation site is generally numbered +1. Base pairs extending in the direction of transcription are said to be downstream of the start site; those extending in the opposite directio ...
... Schematic representation of the major form of E. coli RNA polymerase bound to DNA. By convention, the transcription-initiation site is generally numbered +1. Base pairs extending in the direction of transcription are said to be downstream of the start site; those extending in the opposite directio ...
File
... percentage identity to humans which means they are more likely to perform the same function We have decided to investigate CDKL1 as this was the most differentially expressed, persisting for 30 days. CDKL 1(cyclin dependent Kinase 1) has been classed as Cyclin dependent “like” as it contains the con ...
... percentage identity to humans which means they are more likely to perform the same function We have decided to investigate CDKL1 as this was the most differentially expressed, persisting for 30 days. CDKL 1(cyclin dependent Kinase 1) has been classed as Cyclin dependent “like” as it contains the con ...
Chapter 16 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... IV. Sex determination in Drosophila: a comprehensive example of gene regulation A. The X/A ratio regulates expression of the sex lethal (Sxl) gene 1. Numerator subunit homodimers may function as transcription factors that turn on Sxl ...
... IV. Sex determination in Drosophila: a comprehensive example of gene regulation A. The X/A ratio regulates expression of the sex lethal (Sxl) gene 1. Numerator subunit homodimers may function as transcription factors that turn on Sxl ...
handout nucleic acids and DNA replication
... The code for primary structure cannot be carried in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA since this structure is identical in all DNA molecules. The only part of DNA that varies between different molecules is the base sequence. Therefore, the sequence of bases in DNA must determine the sequence of am ...
... The code for primary structure cannot be carried in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA since this structure is identical in all DNA molecules. The only part of DNA that varies between different molecules is the base sequence. Therefore, the sequence of bases in DNA must determine the sequence of am ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. How is a lysogenic viral infection similar to and different from a lytic cycle? A lytic viral infection is similar to a lysogenic viral cycle in that both allow viruses to reproduce. Whereas a lytic infection destroys a cell immediately, a lysogenic virus inserts its DNA into the host chromosome, ...
... 1. How is a lysogenic viral infection similar to and different from a lytic cycle? A lytic viral infection is similar to a lysogenic viral cycle in that both allow viruses to reproduce. Whereas a lytic infection destroys a cell immediately, a lysogenic virus inserts its DNA into the host chromosome, ...
Regulation of Gene Transcription
... enzymes to break down sugars (lactose, glucose, etc.) if all enzymes where transcribed it would be too energetically costly Therefore the must control transcription based on the presence of what sugar is present. They must have the ability to turn on and off specific groups of genes in response to e ...
... enzymes to break down sugars (lactose, glucose, etc.) if all enzymes where transcribed it would be too energetically costly Therefore the must control transcription based on the presence of what sugar is present. They must have the ability to turn on and off specific groups of genes in response to e ...
Microbial Genetics Chromosomes Genes Related to Obesity in the
... • Similar to prokaryotes except – AUG encodes for a different form of methionine – Transcription and translation are not simultaneous in eukaryotes – Eukaryotes must splice out introns to achieve a mature mRNA strand ready to go to the ribosome. ...
... • Similar to prokaryotes except – AUG encodes for a different form of methionine – Transcription and translation are not simultaneous in eukaryotes – Eukaryotes must splice out introns to achieve a mature mRNA strand ready to go to the ribosome. ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS! Read the
... Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS! Read the following to help you complete a successful CHNOPS organism. Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics such as hair color as blood type. Genes consist of DNA molecules that code for the proteins our cells make. The sequen ...
... Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS! Read the following to help you complete a successful CHNOPS organism. Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics such as hair color as blood type. Genes consist of DNA molecules that code for the proteins our cells make. The sequen ...
handout
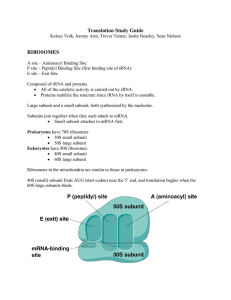
... Proteins stabilize the structure since rRNA by itself is unstable. Large subunit and a small subunit, both synthesized by the nucleolus. Subunits join together when they each attach to mRNA. Small subunit attaches to mRNA first. Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes 30S small subunit 50S large subu ...
... Proteins stabilize the structure since rRNA by itself is unstable. Large subunit and a small subunit, both synthesized by the nucleolus. Subunits join together when they each attach to mRNA. Small subunit attaches to mRNA first. Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes 30S small subunit 50S large subu ...
2013
... Glu-Gly-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser-Lys (c) Suppose the other (complementary) strand is used as a template for transcription. What is the amino acid sequence of the resulting peptide, again starting from the 5' end and using only the first reading frame? The codons translate to Leu-Stop-Stop. No peptide would b ...
... Glu-Gly-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser-Lys (c) Suppose the other (complementary) strand is used as a template for transcription. What is the amino acid sequence of the resulting peptide, again starting from the 5' end and using only the first reading frame? The codons translate to Leu-Stop-Stop. No peptide would b ...
During DNA replication, which of the following segments would be
... Transcription of the DNA sequence below: AAGCTGGGA would most directly result in which of the following? A a sequence of three amino acids, linked by ...
... Transcription of the DNA sequence below: AAGCTGGGA would most directly result in which of the following? A a sequence of three amino acids, linked by ...
Document
... • How can just four nucleotides (A, U, C, and G) be translated into so many different amino acids? • The same way 26 letters of the alphabet can be translated into so many words. – ape – pea The four letters of RNA are put together in different combinations to form many different “words” –A U C G ...
... • How can just four nucleotides (A, U, C, and G) be translated into so many different amino acids? • The same way 26 letters of the alphabet can be translated into so many words. – ape – pea The four letters of RNA are put together in different combinations to form many different “words” –A U C G ...
Honors Biology Module 7 Cellular Reproduction
... When a cell needs to make a protein, its DNA has the plan for making that protein in a long series of threenucleotide base sequences. Messenger RNA reads this sequence and makes a “negative image” of the relevant portion of DNA. It then takes this series of nucleotide base sequences out to the ribo ...
... When a cell needs to make a protein, its DNA has the plan for making that protein in a long series of threenucleotide base sequences. Messenger RNA reads this sequence and makes a “negative image” of the relevant portion of DNA. It then takes this series of nucleotide base sequences out to the ribo ...
doc BIOL 200 Notes up to Midterm
... o As the 5’ end of a nascent RNA chain emerges from RNA polymerase, the 5’ cap structure (7methyl-G) is added to it by several enzymes (5’ to 5’ linkage) o Polyadenylation: addition of 100 to 250 A residues by poly(A) polymerase on 3’ end of mRNA enzymatically o Intron excision, exon ligation (first ...
... o As the 5’ end of a nascent RNA chain emerges from RNA polymerase, the 5’ cap structure (7methyl-G) is added to it by several enzymes (5’ to 5’ linkage) o Polyadenylation: addition of 100 to 250 A residues by poly(A) polymerase on 3’ end of mRNA enzymatically o Intron excision, exon ligation (first ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.