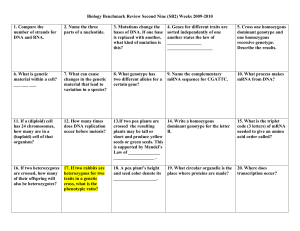
Learning Targets
... 9. Hereditary code consists of 64 different base sequences and is “read” in groups of three (codons). What is a codon, and what does it code for? 10. Using a model (create one), explain the steps of DNA replication in cells and hereditary coding. 11. What are the roles of the DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, ...
... 9. Hereditary code consists of 64 different base sequences and is “read” in groups of three (codons). What is a codon, and what does it code for? 10. Using a model (create one), explain the steps of DNA replication in cells and hereditary coding. 11. What are the roles of the DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, ...
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 4. Genes for different traits are sorted independently of one another states the law of ...
... 4. Genes for different traits are sorted independently of one another states the law of ...
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... ribose that lacks one oxygen atom); and RNA has the base uracil rather than thymine that is present in DNA. RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA ...
... ribose that lacks one oxygen atom); and RNA has the base uracil rather than thymine that is present in DNA. RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA ...
Protein Synthesis
... ________________. There are only 3 of the codons: _______; ________ and _______. We are always going to assume that the coding side of DNA will be the __________ side. Opposite the coding side is called the __________ side. Two enzymes play a role in transcription: ____________ unzips the DNA molecu ...
... ________________. There are only 3 of the codons: _______; ________ and _______. We are always going to assume that the coding side of DNA will be the __________ side. Opposite the coding side is called the __________ side. Two enzymes play a role in transcription: ____________ unzips the DNA molecu ...
Is DNA the Genetic Material?
... Hypothetically, which of the following molecules could work as a replacement for tRNA? 1) A protein that can bind to the major groove of DNA and a specific amino acid. 2) A carbohydrate that can recognize a short RNA sequence and bind to a particular amino acid. 3) A lipid that can basepair with ...
... Hypothetically, which of the following molecules could work as a replacement for tRNA? 1) A protein that can bind to the major groove of DNA and a specific amino acid. 2) A carbohydrate that can recognize a short RNA sequence and bind to a particular amino acid. 3) A lipid that can basepair with ...
Gene Expression
... Remember that the codon chart gives codons, and that you are matching based on anticodons! 4. Align the small ribosomal subunit with the start codon. Match the appropriate charged tRNA with the anticodon that complements the start codon. Attach the large ribosomal subunit such that the charged tRNA ...
... Remember that the codon chart gives codons, and that you are matching based on anticodons! 4. Align the small ribosomal subunit with the start codon. Match the appropriate charged tRNA with the anticodon that complements the start codon. Attach the large ribosomal subunit such that the charged tRNA ...
Alien Protein Synthesis
... amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes the message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a p ...
... amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes the message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a p ...
No Slide Title
... DNA/RNA hybrid and releases RNA transcript • In some cases, termination depends on the rho () termination factor ...
... DNA/RNA hybrid and releases RNA transcript • In some cases, termination depends on the rho () termination factor ...
chapter review answers
... 4. The main enzyme involved in linking DNA nucleotides together is called… a. tRNA b. RNA polymerase c. anticodons d. DNA polymerase 5. The process by which DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA is called… a. translation b.TRANSCRIPTION c. DNA Replication d. transformation 6. In messenger RNA, each co ...
... 4. The main enzyme involved in linking DNA nucleotides together is called… a. tRNA b. RNA polymerase c. anticodons d. DNA polymerase 5. The process by which DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA is called… a. translation b.TRANSCRIPTION c. DNA Replication d. transformation 6. In messenger RNA, each co ...
Chapter 17
... 10. A biologist inserts a gene from a human liver cell into the chromosome of a bacterium. The bacterium then transcribes this gene into mRNA and translates the mRNA into protein. The protein produced is useless. The biologist extracts the protein and mature mRNA that codes for it. When analyzed yo ...
... 10. A biologist inserts a gene from a human liver cell into the chromosome of a bacterium. The bacterium then transcribes this gene into mRNA and translates the mRNA into protein. The protein produced is useless. The biologist extracts the protein and mature mRNA that codes for it. When analyzed yo ...
problem set
... The sequences in a pre-mRNA that dictate where splicing occurs are located at the exon/intron boundaries of the message (Fig. 8.7 below). These sequences are bound by the snRNA components of the snRNPs that make up spliceosomes (Fig. 8.9). Thus, the intron sequences ultimately tell the splicing mach ...
... The sequences in a pre-mRNA that dictate where splicing occurs are located at the exon/intron boundaries of the message (Fig. 8.7 below). These sequences are bound by the snRNA components of the snRNPs that make up spliceosomes (Fig. 8.9). Thus, the intron sequences ultimately tell the splicing mach ...
Sex linked inheritance, sex linkage in Drosophila and man, XO, XY
... •A complementary tRNA molecule attached on the ribosome in the first position P. •Another tRNA base pairs with the other three mRNA bases in the ribosome at position A. •The enzyme peptidyl transferase forms a peptide bond between the two amino acids. •The first tRNA (without its amino acid) leaves ...
... •A complementary tRNA molecule attached on the ribosome in the first position P. •Another tRNA base pairs with the other three mRNA bases in the ribosome at position A. •The enzyme peptidyl transferase forms a peptide bond between the two amino acids. •The first tRNA (without its amino acid) leaves ...
Teaching the Concept of Protein Synthesis Rebecca
... Protein Synthesis Role Play Continued DNA students and mRNA students remain in nucleus during transcription. After transcription, mRNA students move into cytoplasm, where tRNA students are waiting for translation. DNA students begin by writing down the complimentary RNA sequence to their DNA seq ...
... Protein Synthesis Role Play Continued DNA students and mRNA students remain in nucleus during transcription. After transcription, mRNA students move into cytoplasm, where tRNA students are waiting for translation. DNA students begin by writing down the complimentary RNA sequence to their DNA seq ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein.
... RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. An RNA molecule almost always consists of a single strand. ...
... RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. An RNA molecule almost always consists of a single strand. ...
SECTION D What Does DNA Do?
... IT IS WIDELY BELIEVED that the breaking of the Enigma Code (the secret code used by the German armed forces) was the single most important event leading to the eventual victory of the Allied Forces in World War II. Whether or not that is true, the breaking of the genetic code in the 1960s surely rat ...
... IT IS WIDELY BELIEVED that the breaking of the Enigma Code (the secret code used by the German armed forces) was the single most important event leading to the eventual victory of the Allied Forces in World War II. Whether or not that is true, the breaking of the genetic code in the 1960s surely rat ...
Exam 3
... advantageous to have multiple rrn operons close to the oriC (hint: think fast growth). What is involved in the initiation of transcription (promoter regions, sigma factors, RNA polymerase). The operator is involved in controlling gene transcription. The control region and structural gene regions tog ...
... advantageous to have multiple rrn operons close to the oriC (hint: think fast growth). What is involved in the initiation of transcription (promoter regions, sigma factors, RNA polymerase). The operator is involved in controlling gene transcription. The control region and structural gene regions tog ...
Inheritance and the Structure of DNA
... • Each sequence of 3 bases on mRNA encodes for either an amino acid or stop/start signal • Some amino acids will have 1,2,or 3 different codons – No codon codes for more than one amino acid – 64 mRNA codons • There are special codons that act as start and stop to the sequence • For example, AUG acts ...
... • Each sequence of 3 bases on mRNA encodes for either an amino acid or stop/start signal • Some amino acids will have 1,2,or 3 different codons – No codon codes for more than one amino acid – 64 mRNA codons • There are special codons that act as start and stop to the sequence • For example, AUG acts ...
Lecture 15 Biol302 Spring 2011
... How often is this site found in the genome? 1/45 Once every 1000 nucleotides 109 nucleotides or 106 times ...
... How often is this site found in the genome? 1/45 Once every 1000 nucleotides 109 nucleotides or 106 times ...
Transcription & Translation - mvhs
... Nucleic Acid Structure • DNA is double stranded • Hydrogen bonds between bases – A pairs with T – C pairs with G ...
... Nucleic Acid Structure • DNA is double stranded • Hydrogen bonds between bases – A pairs with T – C pairs with G ...
emboj7601881-sup
... system, we can detect virus genome replication independent of viral transcription since ...
... system, we can detect virus genome replication independent of viral transcription since ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... • Explain why gene expression control is necessary in a eukaryotic cell? • Describe how expression is regulated in before & during transcription? • Tell me what differentiation is? Euchromatin? A silencer sequence? • Explain how gene expression regulation is different in eukaryotes/prokaryotes? ...
... • Explain why gene expression control is necessary in a eukaryotic cell? • Describe how expression is regulated in before & during transcription? • Tell me what differentiation is? Euchromatin? A silencer sequence? • Explain how gene expression regulation is different in eukaryotes/prokaryotes? ...
DNA Replication
... • Within the operon, there are three genes that code for proteins (structural protein) and an upstream control region including promoter and a regulatory site called the operator • Laying outside the operon is the repressor gene, which codes for a protein (lac repressor) that binds to the operator s ...
... • Within the operon, there are three genes that code for proteins (structural protein) and an upstream control region including promoter and a regulatory site called the operator • Laying outside the operon is the repressor gene, which codes for a protein (lac repressor) that binds to the operator s ...
RNA interference was popularized by work in C
... endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which generates pre-mRNAs that then process to form mature mRNAs. These mRNAs are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where they are translated. RNAi can r ...
... endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which generates pre-mRNAs that then process to form mature mRNAs. These mRNAs are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where they are translated. RNAi can r ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.