RNA AND TYPES
... RIBOSOMAL RNA rRNA, or Ribosomal RNA, contributes significantly to the structure of the ribosomes in a cell. mRNA, and tRNA work together the the ribosomes to synthesize proteins. In eukaryotes, rRNA is transcribed exclusively within the nucleolus while other types of RNA are synthesized through ...
... RIBOSOMAL RNA rRNA, or Ribosomal RNA, contributes significantly to the structure of the ribosomes in a cell. mRNA, and tRNA work together the the ribosomes to synthesize proteins. In eukaryotes, rRNA is transcribed exclusively within the nucleolus while other types of RNA are synthesized through ...
Proteins determine what?
... 25.What are the 4 steps of translation? • 1. mRNA goes to ribosome • 2. tRNA temporarily pair with mRNA • 3. the amino acids at the end of the tRNA bond together and the tRNA leaves • 4. translation stops when STOP codon is ...
... 25.What are the 4 steps of translation? • 1. mRNA goes to ribosome • 2. tRNA temporarily pair with mRNA • 3. the amino acids at the end of the tRNA bond together and the tRNA leaves • 4. translation stops when STOP codon is ...
Chapter 17 Notes
... • Ribosomes facilitate specific coupling of tRNA anticodons with mRNA codons in protein synthesis • The two ribosomal subunits (large and small) are made of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • A ribosome has three binding sites for tRNA – The P site holds the tRNA that carries the growing ...
... • Ribosomes facilitate specific coupling of tRNA anticodons with mRNA codons in protein synthesis • The two ribosomal subunits (large and small) are made of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • A ribosome has three binding sites for tRNA – The P site holds the tRNA that carries the growing ...
protein synthesis
... off, H bonds to break, covalent bonds join nucleotides - end result: polymerized chain of m RNA C. RNA polymerase proofreads newly formed m RNA and then it goes into cytoplasm to the area of ribosomes to make the protein D. DNA becomes double helix again ...
... off, H bonds to break, covalent bonds join nucleotides - end result: polymerized chain of m RNA C. RNA polymerase proofreads newly formed m RNA and then it goes into cytoplasm to the area of ribosomes to make the protein D. DNA becomes double helix again ...
nucleus
... build ribosome subunits from rRNA & proteins exit through nuclear pores to cytoplasm & combine to form functional ribosomes ...
... build ribosome subunits from rRNA & proteins exit through nuclear pores to cytoplasm & combine to form functional ribosomes ...
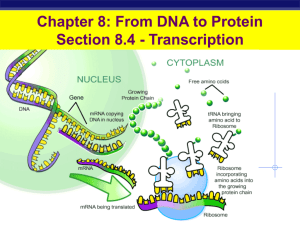
Transcription/translation
... Promoter - area of DNA where RNA polymerase binds. Also area where the “Gene” sequence begins. Operator – area of DNA that turns gene “on” or “off”. It’s the switch ...
... Promoter - area of DNA where RNA polymerase binds. Also area where the “Gene” sequence begins. Operator – area of DNA that turns gene “on” or “off”. It’s the switch ...
Genes
... repressor protein triggering repressor to bind to DNA – blocks (represses) transcription – tend to be anabolic pathways ...
... repressor protein triggering repressor to bind to DNA – blocks (represses) transcription – tend to be anabolic pathways ...
Chapter 16
... two pieces, 2) destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and 3) less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes. 2. Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA molecules, 20-25 ...
... two pieces, 2) destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and 3) less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes. 2. Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA molecules, 20-25 ...
Quiz10ch10.doc
... amino acid 10. DNA a. takes part directly in protein synthesis by leaving the nucleus and being translated on ...
... amino acid 10. DNA a. takes part directly in protein synthesis by leaving the nucleus and being translated on ...
Pre – AP Biology
... bacteria. The bacteria will then be able to Transcribe and Translate off of this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange ...
... bacteria. The bacteria will then be able to Transcribe and Translate off of this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange ...
Protein Synthesis part 2
... addition of the next tRNA molecule. 2. Elongation - This is the actual making of the 1’ sequence of amino acids. a. The ribosome translocates (“walks”) down the mRNA one codon at a time using GTP. b. This adds a single amino acid, using tRNA, to the open A site using GTP each time. c. Another GTP is ...
... addition of the next tRNA molecule. 2. Elongation - This is the actual making of the 1’ sequence of amino acids. a. The ribosome translocates (“walks”) down the mRNA one codon at a time using GTP. b. This adds a single amino acid, using tRNA, to the open A site using GTP each time. c. Another GTP is ...
Gene Expression/Transcription & Translation Practice PowerPoint
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
II. Lecture Section 2 CELL SPECIALIZATION: Regulation of
... 1. Heterochromatin is highly organized and resistant to gene expression 2. Nucleosomes are usually packed together into compact chromatin b. Chromosomal gene arrangements 1. Chromosomes contain long strings of genes 2. Genes can reside on either strand c. Single gene components 1. Coding sequences a ...
... 1. Heterochromatin is highly organized and resistant to gene expression 2. Nucleosomes are usually packed together into compact chromatin b. Chromosomal gene arrangements 1. Chromosomes contain long strings of genes 2. Genes can reside on either strand c. Single gene components 1. Coding sequences a ...
Identification of ORC1/CDC6-interacting factors in
... 7.10. Transcription/splicing: General intro (Genes 10) The basics: Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517-25 RNA decay: Transcriptome-wide analysis of trypanosome mRNA decay reveals com ...
... 7.10. Transcription/splicing: General intro (Genes 10) The basics: Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517-25 RNA decay: Transcriptome-wide analysis of trypanosome mRNA decay reveals com ...
It this a DNA or RNA virus? Is it single
... At the same time, there will be some normal Phe tRNAs, so a mixture of polypeptides will be produced, some with incorrect amino acids and some with the correct amino acids. 9) One phrase is enough for these: a. How do prokaryotic ribosomes recognize the 5’ end of the messenger RNA? Shine delgarno se ...
... At the same time, there will be some normal Phe tRNAs, so a mixture of polypeptides will be produced, some with incorrect amino acids and some with the correct amino acids. 9) One phrase is enough for these: a. How do prokaryotic ribosomes recognize the 5’ end of the messenger RNA? Shine delgarno se ...
Transcription and Translation
... move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
... move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
Bio 121: Chapter 17 Protein Synthesis Assignment Objective
... one activity and complete it in class. Be sure to make a strong effort to clearly explain the concept and to draw connections with the rest of the material in the section. You may work together, but everyone must pass in their own individual, work. Essential Vocabulary There are several important te ...
... one activity and complete it in class. Be sure to make a strong effort to clearly explain the concept and to draw connections with the rest of the material in the section. You may work together, but everyone must pass in their own individual, work. Essential Vocabulary There are several important te ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... General function: promote assembly of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors at the promoter to allow transcription to begin ...
... General function: promote assembly of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors at the promoter to allow transcription to begin ...
560k ppt - UCLA.edu
... •The nuclear cap binding protein. •PABPII bound to the polyA tail. •Proteins retained at spliced exon junctions following RNA splicing that form exon-junction complexes. Thus, mRNP export depends on the additive effects of multiple weak protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions that bind to mRNAs ...
... •The nuclear cap binding protein. •PABPII bound to the polyA tail. •Proteins retained at spliced exon junctions following RNA splicing that form exon-junction complexes. Thus, mRNP export depends on the additive effects of multiple weak protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions that bind to mRNAs ...
Protein Synthesis Study Sheet
... What is the purpose of transcription and where does it take place? What is the purpose of translation and where does it take place? Describe the roles of mRNA and the codon. Draw a model of tRNA and label its parts. Describe the roles of tRNA and the anticodon. Draw and label a ribosome. Distinguish ...
... What is the purpose of transcription and where does it take place? What is the purpose of translation and where does it take place? Describe the roles of mRNA and the codon. Draw a model of tRNA and label its parts. Describe the roles of tRNA and the anticodon. Draw and label a ribosome. Distinguish ...
the code of translation
... 4. A peptide bond forms between the first two amino acids. 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continu ...
... 4. A peptide bond forms between the first two amino acids. 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continu ...
Transcription and Translation - Microbiology and Molecular Genetics
... - Inhibits transcription initiation Actinomycin D - Nonselectively binds to DNA - Inhibits transcription elongation ...
... - Inhibits transcription initiation Actinomycin D - Nonselectively binds to DNA - Inhibits transcription elongation ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.