Genetically Modified Organisms and Food All modern agricultural
... modification, and introduction of DNA into a target organism; when the target organism is a crop plant or domesticated animal used for food, the purpose is usually to impart to the target organism a desired trait that is unknown or very difficult to obtain by traditional methods (those in use befo ...
... modification, and introduction of DNA into a target organism; when the target organism is a crop plant or domesticated animal used for food, the purpose is usually to impart to the target organism a desired trait that is unknown or very difficult to obtain by traditional methods (those in use befo ...
AP Bio Review - Genetics Jeopardy
... DNA is more heat-sensitive and therefore varies more 1,400,P ...
... DNA is more heat-sensitive and therefore varies more 1,400,P ...
Case 18: Student Organizer-‐ Elaborate Case 18: Which gene is
... 2. Based on the description, select the gene you think could be related to bog breath. 3. Click “Sequence it” to send a blood sample from BOG BREATH DRAKES to the lab for DNA sequencing. 4. When ...
... 2. Based on the description, select the gene you think could be related to bog breath. 3. Click “Sequence it” to send a blood sample from BOG BREATH DRAKES to the lab for DNA sequencing. 4. When ...
Slide 1
... Basic studies to reveal conditions and mechanisms involved in induction of akinetes formation, dormancy and desiccation: Nutrient Depletion (P), Light, Temp, O2 (hypoxia) Specialized envelopes Storage of metabolites [carbohydrates, cyanophycin (N)] – enzymes involved, e.g cyanophycine synthase Toler ...
... Basic studies to reveal conditions and mechanisms involved in induction of akinetes formation, dormancy and desiccation: Nutrient Depletion (P), Light, Temp, O2 (hypoxia) Specialized envelopes Storage of metabolites [carbohydrates, cyanophycin (N)] – enzymes involved, e.g cyanophycine synthase Toler ...
Genetic Technology 13.1 and 13.2 notes
... • Transgenic = “across” “race”. A transgenic organism contains genes from another species. ...
... • Transgenic = “across” “race”. A transgenic organism contains genes from another species. ...
Document
... • Cells identify and respond to their position in developmental fields. • Daughter cells may differ with respect to regulatory instructions and developmental fate. ...
... • Cells identify and respond to their position in developmental fields. • Daughter cells may differ with respect to regulatory instructions and developmental fate. ...
DNA: Structure and Function
... Watson & Crick Model • DNA is composed of 2 chains of nucleotides that form a double helix shape • The two strands are antiparallel. • The backbone of the DNA molecule is composed of alternating phosphate groups and sugars • The complimentary bases form hydrogen bonds between the strands • A is c ...
... Watson & Crick Model • DNA is composed of 2 chains of nucleotides that form a double helix shape • The two strands are antiparallel. • The backbone of the DNA molecule is composed of alternating phosphate groups and sugars • The complimentary bases form hydrogen bonds between the strands • A is c ...
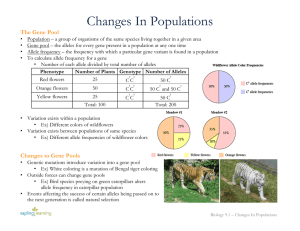
Changes In Populations
... Population – a group of organisms of the same species living together in a given area Gene pool – the alleles for every gene present in a population at any one time Allele frequency – the frequency with which a particular gene variant is found in a population To calculate allele frequency for a gene ...
... Population – a group of organisms of the same species living together in a given area Gene pool – the alleles for every gene present in a population at any one time Allele frequency – the frequency with which a particular gene variant is found in a population To calculate allele frequency for a gene ...
AP Biology (An Introduction)
... Such as pBLU or pGLO pBLU = Blue coloration pGLO = fluorescent green under UV light In Lab 6, we will insert the ...
... Such as pBLU or pGLO pBLU = Blue coloration pGLO = fluorescent green under UV light In Lab 6, we will insert the ...
genexpres
... Cascades of gene expression and cell-to-cell signaling direct development of an animal •An example of these cascades can be seen in the determination of which end of a fruit fly egg cell will become the head and which end will become the tail. These events occur within the ovaries of the mother fly ...
... Cascades of gene expression and cell-to-cell signaling direct development of an animal •An example of these cascades can be seen in the determination of which end of a fruit fly egg cell will become the head and which end will become the tail. These events occur within the ovaries of the mother fly ...
Ghost in Your Genes Response
... 3. A tag or mark is a methyl molecule that either affixes to DNA and shuts it down OR what? ...
... 3. A tag or mark is a methyl molecule that either affixes to DNA and shuts it down OR what? ...
IV. DNA connection A. genetic code 1. genes function to control
... the specified amino acid. The amino acids are attached in a correct sequence to form a protein molecule. b) What is mRNA? Describe how it performs its functions. It is RNA that copies the coded message from the DNA in the nucleus and carries the message to the ribosome in the cytoplasm. c) Does tRNA ...
... the specified amino acid. The amino acids are attached in a correct sequence to form a protein molecule. b) What is mRNA? Describe how it performs its functions. It is RNA that copies the coded message from the DNA in the nucleus and carries the message to the ribosome in the cytoplasm. c) Does tRNA ...
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations
... 4E) Explain 3 effects mutations can have on genes. If these mutagens interact with DNA, they can produce mutations at high rates: Some compounds interfere with base-pairing, increasing the error rate of DNA replication. • Others weaken the DNA strand, causing breaks and inversions that produce chro ...
... 4E) Explain 3 effects mutations can have on genes. If these mutagens interact with DNA, they can produce mutations at high rates: Some compounds interfere with base-pairing, increasing the error rate of DNA replication. • Others weaken the DNA strand, causing breaks and inversions that produce chro ...
Complex Patterns of Inheritance
... • Caused by mutation in gene for creating the enzyme that breaks down the amino acid phenylalanine • This mutation makes the person unable to break down phenylalanine, leading to toxic levels that can damage the body in many ways. • PKU is manageable with medications and by following a diet free of ...
... • Caused by mutation in gene for creating the enzyme that breaks down the amino acid phenylalanine • This mutation makes the person unable to break down phenylalanine, leading to toxic levels that can damage the body in many ways. • PKU is manageable with medications and by following a diet free of ...
Lecture 6
... markers for individuality. The number of tandem repeats of STR are unique to an individual. • STRs are amplified from unique sequence outside the tandem repeats. • RNA can be amplified by PCR; first reverse transcribing it to DNA (cDNA) through reverse transcriptase. ...
... markers for individuality. The number of tandem repeats of STR are unique to an individual. • STRs are amplified from unique sequence outside the tandem repeats. • RNA can be amplified by PCR; first reverse transcribing it to DNA (cDNA) through reverse transcriptase. ...
DNA Technology
... stem cells (bone marrow), but they can only develop into certain types of tissue • Embryonic stem cells have the potential to help people with disabling diseases that affect tissues ...
... stem cells (bone marrow), but they can only develop into certain types of tissue • Embryonic stem cells have the potential to help people with disabling diseases that affect tissues ...
chapter 19 the organization and control of eukaryotic genomes
... Eukaryotic repressors can cause inhibition of gene expression by blocking the binding of activators to their control elements or to components of the transcription machinery or by turning off transcription even in the presence of activators. ...
... Eukaryotic repressors can cause inhibition of gene expression by blocking the binding of activators to their control elements or to components of the transcription machinery or by turning off transcription even in the presence of activators. ...
Genetic information determines structure
... What is the difference between the 3’ and 5’ ends and how is this used in the genetic code? Explain what is meant by the phrase “the genetic code is redundant but never ambiguous”. What is meant by the phrase “the genetic code is universal”. Why is this important to biologist? Describe the process o ...
... What is the difference between the 3’ and 5’ ends and how is this used in the genetic code? Explain what is meant by the phrase “the genetic code is redundant but never ambiguous”. What is meant by the phrase “the genetic code is universal”. Why is this important to biologist? Describe the process o ...
C10 Lesson 3
... 1. _______________ In the process of cloning, breeders cross two genetically different individuals. 2. _______________ Crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics is called genetic engineering. 3. _______________ In selective breeding, organisms with desired traits are chose ...
... 1. _______________ In the process of cloning, breeders cross two genetically different individuals. 2. _______________ Crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics is called genetic engineering. 3. _______________ In selective breeding, organisms with desired traits are chose ...
1-1 - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... Another nucleic acid intermediary would have to be produced first. According to base-pairing rules, a single-stranded RNA molecule could not directly replicate itself. However, if either a complementary DNA or RNA molecule were produced as an intermediary, that intermediary could produce more of the ...
... Another nucleic acid intermediary would have to be produced first. According to base-pairing rules, a single-stranded RNA molecule could not directly replicate itself. However, if either a complementary DNA or RNA molecule were produced as an intermediary, that intermediary could produce more of the ...