Document
... 34. The form of ribonucleic acid that carries genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes is ____________________. 35. Cells must regulate gene expression so that genes will be ____________________ only when the proteins are needed. 36. A cluster of genes in a bacterial cell that codes for pro ...
... 34. The form of ribonucleic acid that carries genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes is ____________________. 35. Cells must regulate gene expression so that genes will be ____________________ only when the proteins are needed. 36. A cluster of genes in a bacterial cell that codes for pro ...
Chapter 9 Slide PDF
... (b) The polymerase begins to move along the DNA and unwind it. As it does, it links RNA nucleotides into a strand of RNA in the order specified by the base sequence of the DNA (elongation). The DNA double helix rewinds after the polymerase passes. The structure of the “opened” DNA molecule at the tr ...
... (b) The polymerase begins to move along the DNA and unwind it. As it does, it links RNA nucleotides into a strand of RNA in the order specified by the base sequence of the DNA (elongation). The DNA double helix rewinds after the polymerase passes. The structure of the “opened” DNA molecule at the tr ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
lec07
... 5’ end and a poly A tail at the 3’ end. • UTR is untranslated region even though they are transcribed on the mRNA. ...
... 5’ end and a poly A tail at the 3’ end. • UTR is untranslated region even though they are transcribed on the mRNA. ...
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
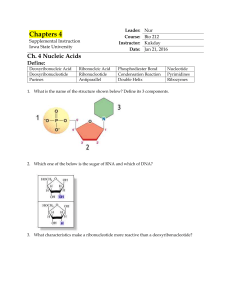
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
university of oslo
... Initially, the ribosome and mRNA are aligned such that the initiator tRNA is positioned in the peptidyl site by codon-anticodon interactions. In the elongation phase of translation tRNAs, charged with amino acids, enter the complex through the A site, mediated by elongation factor 1A (EF-1A). Format ...
... Initially, the ribosome and mRNA are aligned such that the initiator tRNA is positioned in the peptidyl site by codon-anticodon interactions. In the elongation phase of translation tRNAs, charged with amino acids, enter the complex through the A site, mediated by elongation factor 1A (EF-1A). Format ...
Research Questions
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
File
... A.) Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated. B.) Introns are removed during translation C.) In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. ____35.) Which mode of information transfer usually does not occur? A.) DNA to DNA B.) DNA to RNA C.) DNA to protein D.) All ...
... A.) Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated. B.) Introns are removed during translation C.) In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. ____35.) Which mode of information transfer usually does not occur? A.) DNA to DNA B.) DNA to RNA C.) DNA to protein D.) All ...
verbal quiz genetics 2017
... sequence / Mutation 28. What can cause mutations / radiation and chemicals 29. How could a mutation affect protein synthesis / Could change the order of amino acids and cause a different protein to be made 30. The environment can influence the expression of genes an example is / Light and plants, Te ...
... sequence / Mutation 28. What can cause mutations / radiation and chemicals 29. How could a mutation affect protein synthesis / Could change the order of amino acids and cause a different protein to be made 30. The environment can influence the expression of genes an example is / Light and plants, Te ...
2015 Test 3 study guide Bio 105
... • What is a clone? How is it done? Why is it done? • What are stem cells? Chapter 6 • 6.1 DNA intro • Structure of nucleotides • Base pair rules • DNA is double helix and each strand is complementary • DNA strands held together by hydrogen bonds • 6.2 DNA replication • Method of duplication is semi- ...
... • What is a clone? How is it done? Why is it done? • What are stem cells? Chapter 6 • 6.1 DNA intro • Structure of nucleotides • Base pair rules • DNA is double helix and each strand is complementary • DNA strands held together by hydrogen bonds • 6.2 DNA replication • Method of duplication is semi- ...
Resources: http://sciencevideos
... Hemoglobin is a protein composed of two pairs of globin molecules. During the process of development from conception to adulthood, human hemoglobin changes in composition. Adult hemoglobin consists of two alpha- and two beta-globin molecules. Two globin genes occur on chromosome 16: alpha- and zeta- ...
... Hemoglobin is a protein composed of two pairs of globin molecules. During the process of development from conception to adulthood, human hemoglobin changes in composition. Adult hemoglobin consists of two alpha- and two beta-globin molecules. Two globin genes occur on chromosome 16: alpha- and zeta- ...
10 gene expression: transcription
... explanation is that exon 4 in the affected individuals might contain an alternative polyadenylation site. To produce a 3000 nucleotide transcript including exon 2, this site would have to be located 550 nucleotides before the end of exon 4. In this case, the transcript would be 1000 + 500 + 1000 + 8 ...
... explanation is that exon 4 in the affected individuals might contain an alternative polyadenylation site. To produce a 3000 nucleotide transcript including exon 2, this site would have to be located 550 nucleotides before the end of exon 4. In this case, the transcript would be 1000 + 500 + 1000 + 8 ...
Big Picture wkst
... Name: ______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________ ...
... Name: ______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________ ...
NOTE: The provided figures may be useful and beneficial
... 3. Imagine that the non-template sequence in question 3 was transcribed instead of the template sequence. Draw the mRNA sequence and translate it using Figure 17.5. (Be sure to pay attention to the 5’ & 3’ ends.) 4. What enables RNA polymerase to start transcribing a gene at the right place on the D ...
... 3. Imagine that the non-template sequence in question 3 was transcribed instead of the template sequence. Draw the mRNA sequence and translate it using Figure 17.5. (Be sure to pay attention to the 5’ & 3’ ends.) 4. What enables RNA polymerase to start transcribing a gene at the right place on the D ...
DNA paper 1 - DavidHein-CESRC-page
... basic types of RNA which are; mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA is the messenger of genetic information. It carries the information from the DNA is the nucleus to the cytosol. tRNA is transfer RNA. It is about 80 RNA nucleotides. It folds into a hairpin shape and binds to an amino acid to deliver to the ri ...
... basic types of RNA which are; mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA is the messenger of genetic information. It carries the information from the DNA is the nucleus to the cytosol. tRNA is transfer RNA. It is about 80 RNA nucleotides. It folds into a hairpin shape and binds to an amino acid to deliver to the ri ...
First Life Forms Roles of RNA
... First organic compounds Oparin: hypothesized that primitive Earth’s atmosphere was NH3, H2, H2O, and CH4 ...
... First organic compounds Oparin: hypothesized that primitive Earth’s atmosphere was NH3, H2, H2O, and CH4 ...
Gene Regulation - Biomedical Informatics
... 32. What are general transcription factors and their function? 33. What are cis- and trans-acting promoter elements? Examples? 34. What are possible roles of transcription factors (TF)? 35. Describe common bioinformatics methods for finding of TF binding sites. 36. What are enhancers and how they ac ...
... 32. What are general transcription factors and their function? 33. What are cis- and trans-acting promoter elements? Examples? 34. What are possible roles of transcription factors (TF)? 35. Describe common bioinformatics methods for finding of TF binding sites. 36. What are enhancers and how they ac ...
Multiple Choice - saddlespace.org
... a. each with two new strands. b. one with two new strands and the other with two original strands. c. each with one new strand and one original strand. d. each with two original strands. ____ 4. During mitosis, the a. DNA molecules unwind. b. histones and DNA molecules separate. c. DNA molecules bec ...
... a. each with two new strands. b. one with two new strands and the other with two original strands. c. each with one new strand and one original strand. d. each with two original strands. ____ 4. During mitosis, the a. DNA molecules unwind. b. histones and DNA molecules separate. c. DNA molecules bec ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
Genetics 3 - MaxSkyFan
... must be unwound a bit so the two strands can be separated. Then the RNA bases are matched to the DNA strand to complete transcription. Now let’s try translation, where we translate from nucleic acid language to amino acid language. ...
... must be unwound a bit so the two strands can be separated. Then the RNA bases are matched to the DNA strand to complete transcription. Now let’s try translation, where we translate from nucleic acid language to amino acid language. ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.