DNA - VanityWolveriine
... encoded in the sequence of the bases and is transcribed as the strands unwind and replicate.” ...
... encoded in the sequence of the bases and is transcribed as the strands unwind and replicate.” ...
Name - PSUSDscienceresources
... the tongue. This is because A cells in the tongue do not contain amylase genes. B cells in the tongue do not express the amylase genes. C DNA varies from cell to cell based on the cell's needs. D cells in the tongue send amylase to the salivary gland cells. ...
... the tongue. This is because A cells in the tongue do not contain amylase genes. B cells in the tongue do not express the amylase genes. C DNA varies from cell to cell based on the cell's needs. D cells in the tongue send amylase to the salivary gland cells. ...
General Replication Strategies for RNA Viruses
... When consisdering all of our DNA, including the genes and many other sequences which do not encode proteins, we are talking about our genome. This name also applies to viruses - although a viral genome has much less DNA (or RNA) than a human genome. A cistron is the smallest unit of DNA that can enc ...
... When consisdering all of our DNA, including the genes and many other sequences which do not encode proteins, we are talking about our genome. This name also applies to viruses - although a viral genome has much less DNA (or RNA) than a human genome. A cistron is the smallest unit of DNA that can enc ...
DNA Review Questions
... 41. Together with proteins, rRNA A. provides a site for polypeptide synthesis B. transports amino acids to the ribosome C. travels to the ribosome to direct the assembly of polypeptides D. transcribes DNA E. translates DNA 42. The function of tRNA is to A. provide a place for polypeptide synthesis ...
... 41. Together with proteins, rRNA A. provides a site for polypeptide synthesis B. transports amino acids to the ribosome C. travels to the ribosome to direct the assembly of polypeptides D. transcribes DNA E. translates DNA 42. The function of tRNA is to A. provide a place for polypeptide synthesis ...
Self-Quiz Questions Activity 1: When is a Genome
... Match the correct term with each definition or select the best answer for each question. 1. A series of codons from a single strand of DNA sequence which can be "read" in three different ways, depending on whether one starts at the first nucleotide position, the second or third Reading Frame (RF) Al ...
... Match the correct term with each definition or select the best answer for each question. 1. A series of codons from a single strand of DNA sequence which can be "read" in three different ways, depending on whether one starts at the first nucleotide position, the second or third Reading Frame (RF) Al ...
When Is a Genome Project Finished?
... Match the correct term with each definition or select the best answer for each question. 1. A series of codons from a single strand of DNA sequence which can be "read" in three different ways, depending on whether one starts at the first nucleotide position, the second or third Reading Frame (RF) Al ...
... Match the correct term with each definition or select the best answer for each question. 1. A series of codons from a single strand of DNA sequence which can be "read" in three different ways, depending on whether one starts at the first nucleotide position, the second or third Reading Frame (RF) Al ...
Gene Therapy - MsSunderlandsBiologyClasses
... • Adeno-associated viruses - A class of small, single-stranded DNA viruses that can insert their genetic material at a specific site on chromosome ...
... • Adeno-associated viruses - A class of small, single-stranded DNA viruses that can insert their genetic material at a specific site on chromosome ...
video slide
... their control elements or to components of the transcription machinery or by turning off transcription even in the presence of activators. ...
... their control elements or to components of the transcription machinery or by turning off transcription even in the presence of activators. ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... gene encodes the very first part of the kernel pigment protein. Use the base sequence for mRNA to complete the columns on the following table. Be sure to include the polarity of the DNA and tRNA strands. DNA ...
... gene encodes the very first part of the kernel pigment protein. Use the base sequence for mRNA to complete the columns on the following table. Be sure to include the polarity of the DNA and tRNA strands. DNA ...
Term
... Permanent Loss of (enzyme) function (or activity) This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from p ...
... Permanent Loss of (enzyme) function (or activity) This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from p ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 11. A string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait is a gene. 12. The diagram used to trace a trait through generations of a family is a pedigree. 13. What does each gene have instructions for making? A protein 14. When a plant fertilizes itself, it is called self-pollinating plan ...
... 11. A string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait is a gene. 12. The diagram used to trace a trait through generations of a family is a pedigree. 13. What does each gene have instructions for making? A protein 14. When a plant fertilizes itself, it is called self-pollinating plan ...
Chapter 19.
... control of transcription by regulatory proteins operon system no introns, small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences: promoters, operators ...
... control of transcription by regulatory proteins operon system no introns, small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences: promoters, operators ...
Session 1 Worksheet
... DNA replication occurs, the cell grows by producing proteins and cytoplasmic organelles. ...
... DNA replication occurs, the cell grows by producing proteins and cytoplasmic organelles. ...
Document
... During meiosis, the chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to two different cells. The resulting sex cells have only half as many chromosomes as the other cells in the organism. pg 172-173 the captions to the 7 steps of meiosis EQ 8 What is the relationship between chromosomes and genes? Ch ...
... During meiosis, the chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to two different cells. The resulting sex cells have only half as many chromosomes as the other cells in the organism. pg 172-173 the captions to the 7 steps of meiosis EQ 8 What is the relationship between chromosomes and genes? Ch ...
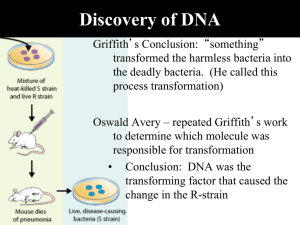
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
Lesson Plan
... 6B(S): SWBAT recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using DNA and RNA models. 6D (S) Recognize that gene expression is a regulated process. 6E (R) Identify and illustrate changes in ...
... 6B(S): SWBAT recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using DNA and RNA models. 6D (S) Recognize that gene expression is a regulated process. 6E (R) Identify and illustrate changes in ...
What is a protein?
... •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a ribosome where it is decoded. Since this is where the DNA language is changed to the protein language, this is called Translation. •The code on the m-RNA is read _______ ba ...
... •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a ribosome where it is decoded. Since this is where the DNA language is changed to the protein language, this is called Translation. •The code on the m-RNA is read _______ ba ...
iclicker - University of Colorado-MCDB
... This paper is about A. RNA can inhibit gene expression B. RNA can destabilize mRNA C. Single stranded RNA can affect gene expression D. Double stranded RNA can affect gene expression E. All of above. ...
... This paper is about A. RNA can inhibit gene expression B. RNA can destabilize mRNA C. Single stranded RNA can affect gene expression D. Double stranded RNA can affect gene expression E. All of above. ...
Organism Genome (kb) Form
... • In eukaryotes, the first level of DNA packing is the chromatin fibre • Chromatin is formed by wrapping the DNA around complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, ta ...
... • In eukaryotes, the first level of DNA packing is the chromatin fibre • Chromatin is formed by wrapping the DNA around complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, ta ...
Chapter 14
... • Mutations occur naturally as accidental changes to DNA or to chromosomes during the cell cycle. • Enzymes repair most DNA that is mismatched during replication, but rarely, some DNA is not repaired. • The rate of mutation can be increased by some environmental factors. Such factors, called mutagen ...
... • Mutations occur naturally as accidental changes to DNA or to chromosomes during the cell cycle. • Enzymes repair most DNA that is mismatched during replication, but rarely, some DNA is not repaired. • The rate of mutation can be increased by some environmental factors. Such factors, called mutagen ...
Name: Biochemistry 465 Hour exam II Spring 2006
... A) fragment of DNA resulting from endonuclease action. B) fragment of RNA that is a subunit of the 30S ribosome. C) piece of DNA that is synthesized in the 3' ® 5' direction. D) segment of DNA that is an intermediate in the synthesis of the lagging strand. E) segment of mRNA synthesized by RNA polym ...
... A) fragment of DNA resulting from endonuclease action. B) fragment of RNA that is a subunit of the 30S ribosome. C) piece of DNA that is synthesized in the 3' ® 5' direction. D) segment of DNA that is an intermediate in the synthesis of the lagging strand. E) segment of mRNA synthesized by RNA polym ...
File
... • Conjugation – the direct transfer of genes between two cells that are temporarily joined • A donor bacterium (F+ or Hfr) produces a tube, or pilus, that connects to the recipient bacterium. ...
... • Conjugation – the direct transfer of genes between two cells that are temporarily joined • A donor bacterium (F+ or Hfr) produces a tube, or pilus, that connects to the recipient bacterium. ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.