Slide 1
... The instructions for making a protein are provided by a gene, which is a specific segment of a DNA molecule, and proteins influence our characteristics. For example, most of us have a protein enzyme that can create melanin, the main pigment that gives color to our skin and hair. In contrast, albino ...
... The instructions for making a protein are provided by a gene, which is a specific segment of a DNA molecule, and proteins influence our characteristics. For example, most of us have a protein enzyme that can create melanin, the main pigment that gives color to our skin and hair. In contrast, albino ...
Chapter 18 Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis
... • A regulatory gene that controls transcription; the regulatory gene is not transcribed but has control elements, one of which is the promoter. A promoter is unique to each gene. • There is always a sequence of bases on the DNA strand called an initiation signal. • Promoters also contain consensus s ...
... • A regulatory gene that controls transcription; the regulatory gene is not transcribed but has control elements, one of which is the promoter. A promoter is unique to each gene. • There is always a sequence of bases on the DNA strand called an initiation signal. • Promoters also contain consensus s ...
UCSC Known Genes (by Jim Kent)
... • If edge is supported by at least 2 ESTs. (Single EST likely is same clone as single RNA…) Just use spliced ESTs • Make graph in mouse and map via chains. Reinforce orthologous human edges. • Reinforce exon edges that overlap Exoniphy predictions. • Evidence weight: refSeq 100, each mRNA 2, est pai ...
... • If edge is supported by at least 2 ESTs. (Single EST likely is same clone as single RNA…) Just use spliced ESTs • Make graph in mouse and map via chains. Reinforce orthologous human edges. • Reinforce exon edges that overlap Exoniphy predictions. • Evidence weight: refSeq 100, each mRNA 2, est pai ...
An Aside: X Inactivation in Female Mammals
... histone tails of one nucleosome, the linker DNA, and the nucleosomes on either side. ...
... histone tails of one nucleosome, the linker DNA, and the nucleosomes on either side. ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... 6. What carbohydrate is made from photosynthesis? How can this be used by the plant? 7. Why do plants appear green? 8. What factors will affect the rate of photosynthesis? Cellular Respiration 9. The synthesis of inorganic materials from organic raw materials is called ________________. This occurs ...
... 6. What carbohydrate is made from photosynthesis? How can this be used by the plant? 7. Why do plants appear green? 8. What factors will affect the rate of photosynthesis? Cellular Respiration 9. The synthesis of inorganic materials from organic raw materials is called ________________. This occurs ...
Aim: What is positive feedback of bacterial operons?
... pathways, synthesizing end products. (tryptophan synthesis). Inducible enzymes usually function in catabolic pathways, digesting nutrients to simpler molecules. (lactose metabolism). Both repressible and inducible operons demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negat ...
... pathways, synthesizing end products. (tryptophan synthesis). Inducible enzymes usually function in catabolic pathways, digesting nutrients to simpler molecules. (lactose metabolism). Both repressible and inducible operons demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negat ...
Bio EOC Cram
... 4 Natural Selection Green grasshoppers become more common than yellow grasshoppers in this population over time because: (1) more grasshoppers are born than can survive, (2) individuals vary in color and color is a heritable trait, and (3) green individuals have a higher fitness in their current env ...
... 4 Natural Selection Green grasshoppers become more common than yellow grasshoppers in this population over time because: (1) more grasshoppers are born than can survive, (2) individuals vary in color and color is a heritable trait, and (3) green individuals have a higher fitness in their current env ...
Test 4
... important in the binding of the mRNA to the ribosome. What are these structures, and how are they used in ribosome binding. A diagram like figure 27-27 will help. The two structures I wanted you to remember were the 5' cap and the polyA tail. The 5' cap is bound by the eTF4E to the 40S subunit of th ...
... important in the binding of the mRNA to the ribosome. What are these structures, and how are they used in ribosome binding. A diagram like figure 27-27 will help. The two structures I wanted you to remember were the 5' cap and the polyA tail. The 5' cap is bound by the eTF4E to the 40S subunit of th ...
Exercise 5
... single-copy genomic DNA gives rise to several different maternal transcripts. Furthermore, this maternal RNA also includes many interspersed genomic repeat sequences (sequences of nucleotides which occur many times in the genome) covalently linked to regions of single-copy sequence. The transcribed ...
... single-copy genomic DNA gives rise to several different maternal transcripts. Furthermore, this maternal RNA also includes many interspersed genomic repeat sequences (sequences of nucleotides which occur many times in the genome) covalently linked to regions of single-copy sequence. The transcribed ...
2140401 - Gujarat Technological University
... 5. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry by David L. Nelson and Michael M. Cox, Publisher: W. H. Freeman; 5th edition 6. Biochemistry by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet, Publisher: Wiley; 4th Edition Course Outcomes: After successful completion of the course students should be able to: 1. Develop a fu ...
... 5. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry by David L. Nelson and Michael M. Cox, Publisher: W. H. Freeman; 5th edition 6. Biochemistry by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet, Publisher: Wiley; 4th Edition Course Outcomes: After successful completion of the course students should be able to: 1. Develop a fu ...
Introduction to Bioinformatics
... DNA bps = 3% of total DNA in genome Human have another 2,960,000,000 bps for control information. (e.g. when, where, how long, etc…) ...
... DNA bps = 3% of total DNA in genome Human have another 2,960,000,000 bps for control information. (e.g. when, where, how long, etc…) ...
Protein Synthesis Assign
... c. Look carefully at the important concepts in Chapter 12-3. Most of them are in bold type on the pages of your text. On a large piece of paper create a concept web that clearly shows how the concepts are connected to each other. The design is up to you, but make sure that you clearly show and expla ...
... c. Look carefully at the important concepts in Chapter 12-3. Most of them are in bold type on the pages of your text. On a large piece of paper create a concept web that clearly shows how the concepts are connected to each other. The design is up to you, but make sure that you clearly show and expla ...
Gene Regulation and Mutation Notes and Questions
... • Somatic cell mutations are not passed on to the next generation. Somatic cells are cells in the body that are not sex cells. • Mutations that occur in sex cells are passed on to the organism’s offspring and will be present in every cell of the offspring. The mutations may not change how the cells ...
... • Somatic cell mutations are not passed on to the next generation. Somatic cells are cells in the body that are not sex cells. • Mutations that occur in sex cells are passed on to the organism’s offspring and will be present in every cell of the offspring. The mutations may not change how the cells ...
Chapter Three The Biological Basis of Life
... and associated proteins. During normal cell functions, chromosomes exist as single-stranded structures. During cell division, chromosomes consist of two strands of DNA joined at the centromere. Since the DNA molecules have replicated, one strand of a chromosome is an exact copy of the ...
... and associated proteins. During normal cell functions, chromosomes exist as single-stranded structures. During cell division, chromosomes consist of two strands of DNA joined at the centromere. Since the DNA molecules have replicated, one strand of a chromosome is an exact copy of the ...
Chapter 3,
... Suppose you are a scientist who wants to insert into your dog a gene that encodes a protein that protects dogs from heartworms. A dog’s cells are not competent, so they cannot take up the gene from the environment; but you have a plasmid, a competent bacterium, and a related (though incompetent) F+ ...
... Suppose you are a scientist who wants to insert into your dog a gene that encodes a protein that protects dogs from heartworms. A dog’s cells are not competent, so they cannot take up the gene from the environment; but you have a plasmid, a competent bacterium, and a related (though incompetent) F+ ...
Ch. 10 DNA Review Questions
... 5. Many RNA molecules from eukaryotic genes have sections, called _________ edited out of them before they become functional. The remaining pieces, called _________, are spliced together. 6. True or False: RNA editing occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. ______________ 7. Proteins are made by joinin ...
... 5. Many RNA molecules from eukaryotic genes have sections, called _________ edited out of them before they become functional. The remaining pieces, called _________, are spliced together. 6. True or False: RNA editing occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. ______________ 7. Proteins are made by joinin ...
Structure of the DNA-binding motifs of activators
... implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against any individual in the United States, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age ...
... implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against any individual in the United States, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age ...
Mutations that happen during Transcription and
... • Enzymes proofread the DNA and replace incorrect nucleotides with correct nucleotides. • The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the more likely is the chance that a mistake will not be corrected. ...
... • Enzymes proofread the DNA and replace incorrect nucleotides with correct nucleotides. • The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the more likely is the chance that a mistake will not be corrected. ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... Differs from DNA synthesis in that only one strand of DNA, the template strand, is used to make mRNA Does not need a primer to start Can involve multiple RNA polymerases Divided into 3 stages ...
... Differs from DNA synthesis in that only one strand of DNA, the template strand, is used to make mRNA Does not need a primer to start Can involve multiple RNA polymerases Divided into 3 stages ...
CHEM642-07 Powerpoint
... (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mRNA is ...
... (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mRNA is ...
Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology PPT
... 1. Transcription: Takes place in the nucleus, mRNA reads the DNA strand, then moves to the cytoplasm for translation. 2. Translation: Take place in the cytoplasm, tRNA carries amino acids to the mRNA to the site of a ribosome (rRNA) In RNA ...
... 1. Transcription: Takes place in the nucleus, mRNA reads the DNA strand, then moves to the cytoplasm for translation. 2. Translation: Take place in the cytoplasm, tRNA carries amino acids to the mRNA to the site of a ribosome (rRNA) In RNA ...
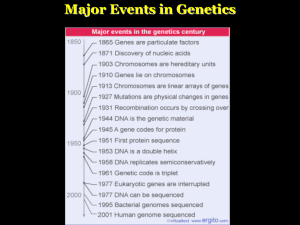
Major Events in Genetics
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
DNA Replication and Protein_Synthesis
... bases on this strand by forming hydrogen bonds RNA polymerase forms sugar-phosphate bonds between nucleotides ...
... bases on this strand by forming hydrogen bonds RNA polymerase forms sugar-phosphate bonds between nucleotides ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.