- mrsolson.com
... 20. Women with X-linked disorders always pass the genes for the disorder to ______, while men with Xlinked disorders always pass the genes for the disorder to _______. a. only their daughters; only their daughters b. both their daughters and sons; only their sons c. both their daughters and sons; on ...
... 20. Women with X-linked disorders always pass the genes for the disorder to ______, while men with Xlinked disorders always pass the genes for the disorder to _______. a. only their daughters; only their daughters b. both their daughters and sons; only their sons c. both their daughters and sons; on ...
Assessment Schedule – 2007 Biology: Describe the role of DNA in
... base of the codon has been changed from an A to a U BOTH needed. 2(c) Describes the effect on structure and function, eg: • Produces a different mRNA codon, changing the shape of the protein by substituting a different amino acid. This may change the protein’s function by changing how it interacts w ...
... base of the codon has been changed from an A to a U BOTH needed. 2(c) Describes the effect on structure and function, eg: • Produces a different mRNA codon, changing the shape of the protein by substituting a different amino acid. This may change the protein’s function by changing how it interacts w ...
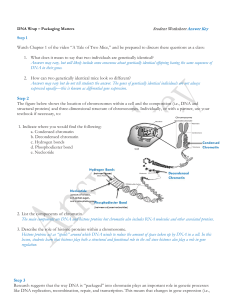
Chromosomes
... • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself and ...
... • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself and ...
document
... Epigenetics is the study of other factors besides the DNA sequence that influence whether or not a gene is transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanent ...
... Epigenetics is the study of other factors besides the DNA sequence that influence whether or not a gene is transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanent ...
Examination 3
... - Codons are read incorrectly - Frame shift – adding or taking away one or two nucleotides causing a shift in the way the message is read - Frameshift can cause immediate nonsense or can cause extensive missense - No frameshift just leaves one amino acid missing o How many insertions/deletions resul ...
... - Codons are read incorrectly - Frame shift – adding or taking away one or two nucleotides causing a shift in the way the message is read - Frameshift can cause immediate nonsense or can cause extensive missense - No frameshift just leaves one amino acid missing o How many insertions/deletions resul ...
Biology 241 Placement Examination General
... What are nucleic acids? What do the initials stand for? Where in the cell are they found? What kinds of bonding are found in nucleotides, nucleoside, and nucleic acids? Make sure you know the differences between RNA and DNA. If I showed you a nucleotide you need to tell me if it is from DNA or RNA. ...
... What are nucleic acids? What do the initials stand for? Where in the cell are they found? What kinds of bonding are found in nucleotides, nucleoside, and nucleic acids? Make sure you know the differences between RNA and DNA. If I showed you a nucleotide you need to tell me if it is from DNA or RNA. ...
Introduction continued
... Locus: location of a gene in a chromosome. Two genes are assorted (or segregated, i.e. are on the same chromosome) if an offspring has about 50% chance of inheriting both characteristics (deduced from the genes) from the same parent. Recombination: due to crossing-over (when cells divide) between ch ...
... Locus: location of a gene in a chromosome. Two genes are assorted (or segregated, i.e. are on the same chromosome) if an offspring has about 50% chance of inheriting both characteristics (deduced from the genes) from the same parent. Recombination: due to crossing-over (when cells divide) between ch ...
to view and/or print October 2016 eDay assignment.
... Read Identical twins: same DNA, different environment and explain how two people with identical DNA can be different: ...
... Read Identical twins: same DNA, different environment and explain how two people with identical DNA can be different: ...
Chapter 25 RNA Metabolism
... The multiple transcripts produced from such a gene may have more than one site for cleavage and polyadenylation (as for immunoglobulin heavy chains), alternative splicing (as for the myosin heavy chains in fruit flies), or both (as for the calcitonin gene in rats). In different cells or at differe ...
... The multiple transcripts produced from such a gene may have more than one site for cleavage and polyadenylation (as for immunoglobulin heavy chains), alternative splicing (as for the myosin heavy chains in fruit flies), or both (as for the calcitonin gene in rats). In different cells or at differe ...
Oct 23, 2006 Handout
... will cause a frameshift: because codons are made of three nucleotides, deleting one base pair disrupts the “reading frame” or division of the sequence into threes. Frameshifts occur if the number of base pairs inserted or deleted is NOT a multiple of three (if three basepairs are inserted or deleted ...
... will cause a frameshift: because codons are made of three nucleotides, deleting one base pair disrupts the “reading frame” or division of the sequence into threes. Frameshifts occur if the number of base pairs inserted or deleted is NOT a multiple of three (if three basepairs are inserted or deleted ...
Sample test in Word
... alga-like protists, but chloroplasts among the groups differ significantly in genetic composition. What do these facts imply about the evolution of the endomembrane organelle system of eukaryotic cells? A. The Golgi apparatus evolved before the endomembrane system. B. Endomembrane systems evolved fr ...
... alga-like protists, but chloroplasts among the groups differ significantly in genetic composition. What do these facts imply about the evolution of the endomembrane organelle system of eukaryotic cells? A. The Golgi apparatus evolved before the endomembrane system. B. Endomembrane systems evolved fr ...
DNA Test Study Guide
... the S phase of the cell cycle. In eukaryotic organisms, it takes place inside the nucleus, in prokaryotes, It takes place in the cytoplasm. The first step is: The DNA double helix unwinds using an enzyme called DNA helicase, the second step is: free floating nucleotides match up with the 2 template ...
... the S phase of the cell cycle. In eukaryotic organisms, it takes place inside the nucleus, in prokaryotes, It takes place in the cytoplasm. The first step is: The DNA double helix unwinds using an enzyme called DNA helicase, the second step is: free floating nucleotides match up with the 2 template ...
teacherstryscience.org
... Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod Experiments with E. Coli showed that it is capable of regulating the expression of its genes An operon consists of the following elements 1. Promoter - where RNA polymerase attaches, signalling the start of the gene 2. Operator - where a repressor binds, stopping th ...
... Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod Experiments with E. Coli showed that it is capable of regulating the expression of its genes An operon consists of the following elements 1. Promoter - where RNA polymerase attaches, signalling the start of the gene 2. Operator - where a repressor binds, stopping th ...
Document
... 1) Describe the basics of prokaryotic gene regulation -operons, negative and positive regulation 2) Illustrate the use of genetics in understanding cellular processes 3) Cover some aspects of DNA-binding proteins ...
... 1) Describe the basics of prokaryotic gene regulation -operons, negative and positive regulation 2) Illustrate the use of genetics in understanding cellular processes 3) Cover some aspects of DNA-binding proteins ...
Bi 430 / 530 Theory of Recombinant DNA Techniques Syllabus
... Questions How are recombinant DNA risks defined and managed? How is useful DNA and RNA isolated? How are DNA, RNA and proteins detected and measured? How can specific DNA, RNA and protein molecules be identified in a complex mixture? How can DNA be modified in the test tube? Why is PCR such a versat ...
... Questions How are recombinant DNA risks defined and managed? How is useful DNA and RNA isolated? How are DNA, RNA and proteins detected and measured? How can specific DNA, RNA and protein molecules be identified in a complex mixture? How can DNA be modified in the test tube? Why is PCR such a versat ...
What are the potential benefits to knowing more - B
... »Fetus and mother share a blood supply »Fetal cells release DNA that enters the maternal ...
... »Fetus and mother share a blood supply »Fetal cells release DNA that enters the maternal ...
Genetics 314 – Spring 2007
... different sequences for initiation and termination of transcription and translation. To make sure you get expression of a gene you need to have the proper promoter, leader and termination sequences to match the organisms enzymes involved in transcription and translation. 6. If a chemical was discove ...
... different sequences for initiation and termination of transcription and translation. To make sure you get expression of a gene you need to have the proper promoter, leader and termination sequences to match the organisms enzymes involved in transcription and translation. 6. If a chemical was discove ...
Loading Complete Instructions: Choose the best answer for each
... A) must have the resource competition from the other wren species. B) eat different foods found in and on the tree. C) have different natural enemies. D) breed at different times. 21) Which of the following statements BEST describes how mutations are related to evolution? A) There is not a strong re ...
... A) must have the resource competition from the other wren species. B) eat different foods found in and on the tree. C) have different natural enemies. D) breed at different times. 21) Which of the following statements BEST describes how mutations are related to evolution? A) There is not a strong re ...
2nd 9 Weeks Study Guide! Aren`t you excited?? Chapter 10
... Learning Target 2: I can indentify and explain Mendal’s law of segregation and law of independent assortment Mendal’s law of segregation states that during meiosis, the factos that control each trait separate, and only ______________________________ from each pair is/are passed to the offspring. The ...
... Learning Target 2: I can indentify and explain Mendal’s law of segregation and law of independent assortment Mendal’s law of segregation states that during meiosis, the factos that control each trait separate, and only ______________________________ from each pair is/are passed to the offspring. The ...
Chapter 9 - HCC Learning Web
... Highly transcribed genes occur in clusters where gene density is high and introns are small. SINEs are more common in these areas (SINEs are short interspersed elements; Alu is an example) Less frequently transcribed genes also cluster, but gene density is lower and introns are larger. LINEs (long i ...
... Highly transcribed genes occur in clusters where gene density is high and introns are small. SINEs are more common in these areas (SINEs are short interspersed elements; Alu is an example) Less frequently transcribed genes also cluster, but gene density is lower and introns are larger. LINEs (long i ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... expression of other cells – how is that possible? B. Signal transduction pathway – a series of molecular events that converts a signal on the target cell’s surface to a specific response within the cell. C. Elements of signal transduction 1. The signaling cell secretes the signal molecule 2. This mo ...
... expression of other cells – how is that possible? B. Signal transduction pathway – a series of molecular events that converts a signal on the target cell’s surface to a specific response within the cell. C. Elements of signal transduction 1. The signaling cell secretes the signal molecule 2. This mo ...
Alveoli - greinerudsd
... mRNA: single stranded linear RNA, carries information from DNA to ribosomes tRNA: short coils of RNA in cytoplasm, matches amino acids to mRNA rRNA: helps form the structure of ribosomes, along with proteins, long coils or RNA Compare and contrast and intron and exon Intron: do not code for proteins ...
... mRNA: single stranded linear RNA, carries information from DNA to ribosomes tRNA: short coils of RNA in cytoplasm, matches amino acids to mRNA rRNA: helps form the structure of ribosomes, along with proteins, long coils or RNA Compare and contrast and intron and exon Intron: do not code for proteins ...
Les 1-DNA Structure-review
... Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
... Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.