When is the gene not DNA? - Physicians and Scientists for Global
... is not literally accurate because more than just an existing molecule of DNA and a pile of unused components is needed to synthesise another molecule of DNA. What some realised at the time, but a few generations since seem to have forgotten, is that the existence of one way to replicate and pass on ...
... is not literally accurate because more than just an existing molecule of DNA and a pile of unused components is needed to synthesise another molecule of DNA. What some realised at the time, but a few generations since seem to have forgotten, is that the existence of one way to replicate and pass on ...
Diapositiva 1
... and the other light (the L strand). Both strands encode genes, although more are on the H strand. A short region (1121 bp), the D loop (D = “displacement”), is a DNA triple helix: there are 2 overlapping copies of the H strand there. The D loop is also the site where most of replication and transcri ...
... and the other light (the L strand). Both strands encode genes, although more are on the H strand. A short region (1121 bp), the D loop (D = “displacement”), is a DNA triple helix: there are 2 overlapping copies of the H strand there. The D loop is also the site where most of replication and transcri ...
DNA Detectives What is Your DNA Alias? The central dogma of
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
Document
... PTGS -Post-transcriptional gene silencing Dicer is an RNaseIII-like enzyme. siRNAs guide an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to mRNA degradation. ...
... PTGS -Post-transcriptional gene silencing Dicer is an RNaseIII-like enzyme. siRNAs guide an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to mRNA degradation. ...
Document
... 2. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) --> expression of 4 genes are sufficient to transform differentiated cells to “stem” cells ...
... 2. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) --> expression of 4 genes are sufficient to transform differentiated cells to “stem” cells ...
Gene Regulation Notes
... • Differences between cell types result from differential gene expression, the expression of different genes by cells with the same genome ...
... • Differences between cell types result from differential gene expression, the expression of different genes by cells with the same genome ...
ZNF232: structure and expression analysis of a novel human C2H2
... green £uorescent protein (GFP) open reading frame combined with the ZNF232 coding region. This was prepared by co-ligation of the linearized pEGFP-C1 vector (Clontech) with a PCR product (primers : 5P-AGGATGGCTGTATCACTAAC-3P and 5P-GATCCAGTCCTAAAGTAGATTAGAC-3P, nt positions 123^142 and 1418^1444, re ...
... green £uorescent protein (GFP) open reading frame combined with the ZNF232 coding region. This was prepared by co-ligation of the linearized pEGFP-C1 vector (Clontech) with a PCR product (primers : 5P-AGGATGGCTGTATCACTAAC-3P and 5P-GATCCAGTCCTAAAGTAGATTAGAC-3P, nt positions 123^142 and 1418^1444, re ...
Ancient Ciphers: Minireview Translation in
... repeats surrounding both the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. In bacteria, these repeats form helical structures within the primary transcript that are recognized and cleaved by the duplex-specific endonuclease, RNaseIII. Although RNaseIII is not an essential activity in E. coli, the alternate routes for pre ...
... repeats surrounding both the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. In bacteria, these repeats form helical structures within the primary transcript that are recognized and cleaved by the duplex-specific endonuclease, RNaseIII. Although RNaseIII is not an essential activity in E. coli, the alternate routes for pre ...
-1- Biophysics 204 Graphics problem set - nucleic acid
... Graphics problem set - nucleic acid-protein interactions DNA-binding proteins often recognize specific binding sites by making sets of hydrogen bonds and van der Waals contacts to functional groups in the DNA major groove. Zinc finger proteins are especially useful for examining sequence-specific in ...
... Graphics problem set - nucleic acid-protein interactions DNA-binding proteins often recognize specific binding sites by making sets of hydrogen bonds and van der Waals contacts to functional groups in the DNA major groove. Zinc finger proteins are especially useful for examining sequence-specific in ...
Ribosome stalls at trp codons, allowing 2+3 pairing Transcription
... cAMP is produced when glucose levels are low. cAMP activates CAP. Active CAP binds to the promoter to increase RNA polymerase binding. RNA polymerase ...
... cAMP is produced when glucose levels are low. cAMP activates CAP. Active CAP binds to the promoter to increase RNA polymerase binding. RNA polymerase ...
Title goes here
... • We have very vague ideas about the steps/parameters for the majority of genes/phenotypes • If we design a relational database for gene/phenotype ...
... • We have very vague ideas about the steps/parameters for the majority of genes/phenotypes • If we design a relational database for gene/phenotype ...
The Microarray Platform of IVM/IZKF
... availability of robust hardware- and software platforms to produce and evaluate microarrays have enabled genome-wide gene expression analyses, i.e. to quantify all mRNAs (> 30 000) of a total RNA extract relative to another RNA extract, within 48 hours. The platform used by the IVM (Affymetrix) is e ...
... availability of robust hardware- and software platforms to produce and evaluate microarrays have enabled genome-wide gene expression analyses, i.e. to quantify all mRNAs (> 30 000) of a total RNA extract relative to another RNA extract, within 48 hours. The platform used by the IVM (Affymetrix) is e ...
Microarray Technology
... • Microarray experiments – After hybridization, the slides are scanned using a laser device to determine the amount of fluorescent label that is attached to each cDNA on the slide. – The amount of fluorescence is displayed as a spot on a matrix corresponding to the original slide. – The intensity ...
... • Microarray experiments – After hybridization, the slides are scanned using a laser device to determine the amount of fluorescent label that is attached to each cDNA on the slide. – The amount of fluorescence is displayed as a spot on a matrix corresponding to the original slide. – The intensity ...
Quantification and identification of allele specific proteins
... The phenotype is controlled by different protein isoform(s) / transcript(s) / gene copy(s). This integrative workflow allows to unravel genetic diversity in polyploid (non-) model crops at the gene variant level. We identified 2754 proteins 260 identified SAAP 130 with differential peptide abundance ...
... The phenotype is controlled by different protein isoform(s) / transcript(s) / gene copy(s). This integrative workflow allows to unravel genetic diversity in polyploid (non-) model crops at the gene variant level. We identified 2754 proteins 260 identified SAAP 130 with differential peptide abundance ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... • Gene regulation in eukaryotes is more complex and variable than gene regulation in prokaryotes. • Gene expression in eukaryotes involves more steps and interactions than gene expression in prokaryotes. • Regulation can occur before transcription, after transcription, or after translation. ...
... • Gene regulation in eukaryotes is more complex and variable than gene regulation in prokaryotes. • Gene expression in eukaryotes involves more steps and interactions than gene expression in prokaryotes. • Regulation can occur before transcription, after transcription, or after translation. ...
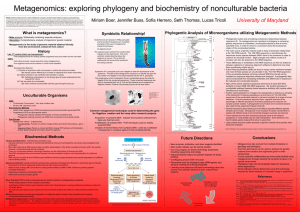
Metagenomics - University of Maryland, College Park
... Nucleic Acid Extraction: Cell Extraction and Direct Lysis • Cell lysis (chemical, enzymatic or mechanical) followed by removal of cell fragments and nucleic acid precipitation and purification. • More often used due to DNA recovery that is a better representation of the entire microbial community wi ...
... Nucleic Acid Extraction: Cell Extraction and Direct Lysis • Cell lysis (chemical, enzymatic or mechanical) followed by removal of cell fragments and nucleic acid precipitation and purification. • More often used due to DNA recovery that is a better representation of the entire microbial community wi ...
Cat Coat Color Genetics Part 1
... The red coloration, sometimes called orange is due to the Orange gene, which still remains to be found (hence no DNA test yet). The orange gene is found on the X-chromosome, and as such the color is called a sex-linked trait. This is be ...
... The red coloration, sometimes called orange is due to the Orange gene, which still remains to be found (hence no DNA test yet). The orange gene is found on the X-chromosome, and as such the color is called a sex-linked trait. This is be ...
An intron nucleotide sequence variant in a
... globin gene (36). It is not obvious how this sequence variant could produce a |?tthalassaemic phenotype. The gene codes for a normal ^-globin mRNA. Therefore defective mRNA translation can be excluded as the cause of this thalassaemia. Similarly, the 5'- and 3'-flanking sequences, extending for 114 ...
... globin gene (36). It is not obvious how this sequence variant could produce a |?tthalassaemic phenotype. The gene codes for a normal ^-globin mRNA. Therefore defective mRNA translation can be excluded as the cause of this thalassaemia. Similarly, the 5'- and 3'-flanking sequences, extending for 114 ...
Review Sheet Scientific Method and Characteristics of Life
... a. Give an example of a phenotype for hairline. __________________ What is its genotype? ________________ b. What is the dominant trait for freckles? ____________________ recessive? ________________________ c. What is the genotype for a carrier of sickle cell blood? _________________________________ ...
... a. Give an example of a phenotype for hairline. __________________ What is its genotype? ________________ b. What is the dominant trait for freckles? ____________________ recessive? ________________________ c. What is the genotype for a carrier of sickle cell blood? _________________________________ ...
Chapter Eleven: Chromosome Structure and Transposable Elements
... Euchromatin is less condensed and capable of being transcribed, whereas heterochromatin is highly condensed and rarely transcribed. Since chromosomal puffs are sites of active transcription, they should occur primarily in euchromatin. (b) Would you expect to observe more puffs in unique-sequence DNA ...
... Euchromatin is less condensed and capable of being transcribed, whereas heterochromatin is highly condensed and rarely transcribed. Since chromosomal puffs are sites of active transcription, they should occur primarily in euchromatin. (b) Would you expect to observe more puffs in unique-sequence DNA ...
Immunoglobulin Genes: Organization and Expression
... Class Switching With Activated B Cell Differentiation And Division • After activation, B cells switch from membrane-bound IgM and IgD to secreted IgM by differential splicing. • As the activated B cells continue to differentiate and divide, they class switch to production of IgG by DNA rearrangemen ...
... Class Switching With Activated B Cell Differentiation And Division • After activation, B cells switch from membrane-bound IgM and IgD to secreted IgM by differential splicing. • As the activated B cells continue to differentiate and divide, they class switch to production of IgG by DNA rearrangemen ...
Lecture 10 Types of mutations Substitutions that occur in protein
... • pigmented lesions on areas of the skin exposed to the sun and • an elevated incidence of skin cancer. It turns out that XP can be caused by mutations in any one of several genes - all of which have roles to play in NER. James Cleaver went around and collected cells from hundreds of these patients. ...
... • pigmented lesions on areas of the skin exposed to the sun and • an elevated incidence of skin cancer. It turns out that XP can be caused by mutations in any one of several genes - all of which have roles to play in NER. James Cleaver went around and collected cells from hundreds of these patients. ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.