Mechanisms of Evolution
... Recently, bears have been found in the Arctic Circle that are hybrids between grizzly bears and polar bears. Which type of isolating mechanism usually keeps these species from producing ...
... Recently, bears have been found in the Arctic Circle that are hybrids between grizzly bears and polar bears. Which type of isolating mechanism usually keeps these species from producing ...
Lecture #10 Date
... • 4- Nonrandom mating: inbreeding and assortive mating (both shift frequencies of different genotypes) ...
... • 4- Nonrandom mating: inbreeding and assortive mating (both shift frequencies of different genotypes) ...
Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change – “Microevolutionary Processes”
... Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change – “Microevolutionary Processes” (1) Mutation: Ultimate natural resource of evolution, occurs at the molecular level in DNA. (2) Natural Selection: A difference, on average, between the survival or fecundity of individuals with certain arrays of phenotypes as compare ...
... Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change – “Microevolutionary Processes” (1) Mutation: Ultimate natural resource of evolution, occurs at the molecular level in DNA. (2) Natural Selection: A difference, on average, between the survival or fecundity of individuals with certain arrays of phenotypes as compare ...
Chapter 17
... 1. Nonrandom mating (sexual selection = individuals select mates based on traits) *Video 2. Small population (genetic drift will occur easily) 3. Immigration or Emigration (if individuals leave, frequencies change!) 4. Mutations (can introduce new alleles) 5. Natural Selection (different fitness lev ...
... 1. Nonrandom mating (sexual selection = individuals select mates based on traits) *Video 2. Small population (genetic drift will occur easily) 3. Immigration or Emigration (if individuals leave, frequencies change!) 4. Mutations (can introduce new alleles) 5. Natural Selection (different fitness lev ...
Enriched Biology Dremann Metzendorf Bag 3
... 13. The separation of populations by barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies of water is called… 14. To be useful as an index fossil, a species must have existed for a… 16. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells arose from… 17. The first organisms on Earth were most like … 18. ...
... 13. The separation of populations by barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies of water is called… 14. To be useful as an index fossil, a species must have existed for a… 16. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells arose from… 17. The first organisms on Earth were most like … 18. ...
Date of quizzz: ______ My goal is to earn _____
... Questions to be able to answer in your own words using scientific vocabulary: 1. Define biological evolution and give a specific example to support your definition. 2. Explain the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific fact. 3. Explain how the process of natural selection can cause ...
... Questions to be able to answer in your own words using scientific vocabulary: 1. Define biological evolution and give a specific example to support your definition. 2. Explain the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific fact. 3. Explain how the process of natural selection can cause ...
MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION
... – In the absence of other factors the segregation and recombination of alleles during meiosis and fertilization will not alter the overall genetic makeup of a population. (i.e. A population will stay the ...
... – In the absence of other factors the segregation and recombination of alleles during meiosis and fertilization will not alter the overall genetic makeup of a population. (i.e. A population will stay the ...
Evolution
... populations are capable of interbreeding but have different mating rituals or routines. i.e. eastern & western meadowlarks ...
... populations are capable of interbreeding but have different mating rituals or routines. i.e. eastern & western meadowlarks ...
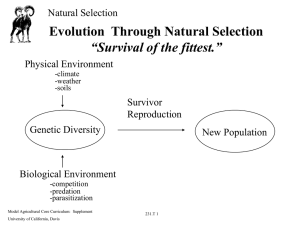
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
15.2 - sciencewithskinner
... In your textbook, read about population genetics and evolution. Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. ...
... In your textbook, read about population genetics and evolution. Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. ...
What do I need to know for the test?
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? Be able to identify examples of each of ...
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? Be able to identify examples of each of ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... Sexual recombination is the source of most genetic differences between individuals in a population. Diploidy often hides genetic variation from selection in the form of recessive alleles. Dominant alleles “hide” recessive alleles in heterozygotes Neutral variation: genetic variation that res ...
... Sexual recombination is the source of most genetic differences between individuals in a population. Diploidy often hides genetic variation from selection in the form of recessive alleles. Dominant alleles “hide” recessive alleles in heterozygotes Neutral variation: genetic variation that res ...
Evolution of Populations
... maladaptive to be good looking and have a reasonable number of spines. Low spine-number plants are not picked because they don't "look right", and high spine-number varieties are left alone because they are too hard to pick. Gradually, the gene pool changes in favor of the two extreme spine number t ...
... maladaptive to be good looking and have a reasonable number of spines. Low spine-number plants are not picked because they don't "look right", and high spine-number varieties are left alone because they are too hard to pick. Gradually, the gene pool changes in favor of the two extreme spine number t ...
statgen3
... alone may eliminate certain members out of proportion to their numbers in the population. In such cases, the frequency of an allele may begin to drift toward higher or lower values. Ultimately, the allele may represent 100% of the gene pool or, just as likely, disappear from it. Drift produces evol ...
... alone may eliminate certain members out of proportion to their numbers in the population. In such cases, the frequency of an allele may begin to drift toward higher or lower values. Ultimately, the allele may represent 100% of the gene pool or, just as likely, disappear from it. Drift produces evol ...
Neo Darwinian Evolution - Fall River Public Schools
... Introduction • There are many different models of evolution, but for this class we are going to learn about Neo-Darwinian evolution • Darwin believed that natural selection was the primary way certain individuals were able to survive and pass on their traits, but there are other things working. ...
... Introduction • There are many different models of evolution, but for this class we are going to learn about Neo-Darwinian evolution • Darwin believed that natural selection was the primary way certain individuals were able to survive and pass on their traits, but there are other things working. ...
Intro to Evolution ppt
... Organisms better suited to the environment are more likely to survive & reproduce than organisms less suited to the environment. ...
... Organisms better suited to the environment are more likely to survive & reproduce than organisms less suited to the environment. ...
Evolution of Populations
... • The two main sources of genetic variation are mutations and gene shuffling • A mutation is any change in a sequence of DNA • Gene shuffling occurs during gamete formation (crossingover) ...
... • The two main sources of genetic variation are mutations and gene shuffling • A mutation is any change in a sequence of DNA • Gene shuffling occurs during gamete formation (crossingover) ...
ppt - Courses
... • Will not change the overall allele frequencies; will change _______________ frequencies ...
... • Will not change the overall allele frequencies; will change _______________ frequencies ...
Shaping Evolutionary Theory - Biology-RHS
... of the population Darwin wondered why some qualities of sexual attractiveness appeared to be the opposite of qualities that might enhance ...
... of the population Darwin wondered why some qualities of sexual attractiveness appeared to be the opposite of qualities that might enhance ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.