Chapter 3 Wave Properties of Particles Overview
... This section foreshadows chapter 5. Sound waves consist of pressure differences in a medium. Water waves consist of different heights of water. E&M waves consist of measurable oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. What about ...
... This section foreshadows chapter 5. Sound waves consist of pressure differences in a medium. Water waves consist of different heights of water. E&M waves consist of measurable oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. What about ...
Identical particles
... discovered.) There is also a theorem that gives the same result. It is called the spin and statistics theorem. There is no simple proof. It is proven within the structure of relativistic quantum field theory. The essential ingredients seem to be relativity and causality. Perhaps someday there will b ...
... discovered.) There is also a theorem that gives the same result. It is called the spin and statistics theorem. There is no simple proof. It is proven within the structure of relativistic quantum field theory. The essential ingredients seem to be relativity and causality. Perhaps someday there will b ...
Atomic Structure
... Since the atomic mass is the number of protons plus neutrons, two isotopes of an element will have different atomic masses (however the atomic number, Z, will remain the same). ...
... Since the atomic mass is the number of protons plus neutrons, two isotopes of an element will have different atomic masses (however the atomic number, Z, will remain the same). ...
Models of the Atom - Red Hook Central Schools
... Ex 4: A Mercury Atom has an e- excited from the n=a to the n=e energy level. • What is the frequency it will absorb? • To which radiation does the frequency ...
... Ex 4: A Mercury Atom has an e- excited from the n=a to the n=e energy level. • What is the frequency it will absorb? • To which radiation does the frequency ...
Vocabulary:
... Nuclear Atom Model – An atom is mostly empty space with a dense, positively charged nucleus in the center and electrons moving around it. Neils Bohr – ...
... Nuclear Atom Model – An atom is mostly empty space with a dense, positively charged nucleus in the center and electrons moving around it. Neils Bohr – ...
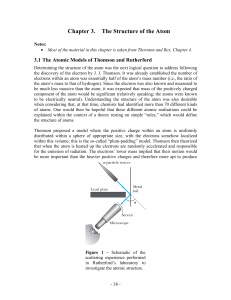
Geiger–Marsden experiment
The Geiger–Marsden experiment(s) (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment) were a landmark series of experiments by which scientists discovered that every atom contains a nucleus where its positive charge and most of its mass are concentrated. They deduced this by measuring how an alpha particle beam is scattered when it strikes a thin metal foil. The experiments were performed between 1908 and 1913 by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the direction of Ernest Rutherford at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester.