Glencoe Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom for the Wiki
... • Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. • In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, sepa ...
... • Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. • In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, sepa ...
history of the atom ppt student copy
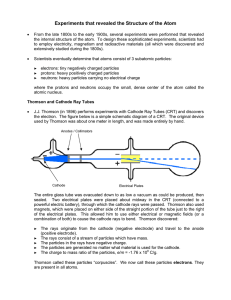
... 1897 - JJ Thomson º used CRT to discover the electron. -modified CRT with poles (magnetic field) to attract cathode rays. - passed electricity through a gas at first; then used several samples of other elements. -behavior was same for all elements - rays were attracted to the anode (+). (___________ ...
... 1897 - JJ Thomson º used CRT to discover the electron. -modified CRT with poles (magnetic field) to attract cathode rays. - passed electricity through a gas at first; then used several samples of other elements. -behavior was same for all elements - rays were attracted to the anode (+). (___________ ...
Rutherford gold foil abstract
... by encounters with the atoms of matter. On account of its smaller momentum and energy, the scattering of the particles is in general far more pronounced than for the particles. There seems to be no doubt that these swiftly moving particles actually pass through the atomic system, and a close stu ...
... by encounters with the atoms of matter. On account of its smaller momentum and energy, the scattering of the particles is in general far more pronounced than for the particles. There seems to be no doubt that these swiftly moving particles actually pass through the atomic system, and a close stu ...
The Quantum Atom (section 18)
... Section 18: The Quantum Atom JJ Thomson 1899 – discovered electron using cathode ray tube (diagrams p210 Adams& Allday, p784 Muncaster). Particles given off from cathode always have the same charge to mass ratio, no matter what element the cathode is made of. Conclusion – they are subatomic particle ...
... Section 18: The Quantum Atom JJ Thomson 1899 – discovered electron using cathode ray tube (diagrams p210 Adams& Allday, p784 Muncaster). Particles given off from cathode always have the same charge to mass ratio, no matter what element the cathode is made of. Conclusion – they are subatomic particle ...
Early models of the atom
... The finding of Geiger and Marsden was that, while most of the alpha particles emerged with little deflection in passing through the foil, a few particles where scattered through very large angles. Some particles were actually reflected back along their path. To Rutherford this was absolutely unbelie ...
... The finding of Geiger and Marsden was that, while most of the alpha particles emerged with little deflection in passing through the foil, a few particles where scattered through very large angles. Some particles were actually reflected back along their path. To Rutherford this was absolutely unbelie ...
File
... b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflected right back b. some alpha parti ...
... b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflected right back b. some alpha parti ...
Geiger–Marsden experiment
The Geiger–Marsden experiment(s) (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment) were a landmark series of experiments by which scientists discovered that every atom contains a nucleus where its positive charge and most of its mass are concentrated. They deduced this by measuring how an alpha particle beam is scattered when it strikes a thin metal foil. The experiments were performed between 1908 and 1913 by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the direction of Ernest Rutherford at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester.