The KetelD Dominant-Negative Mutations Identify
... intriguing biological phenomena and raises questions about the origin and function of factors required for the initiation of a new life. What are those factors? Where and how are they made? What are their functions? It has long been known that most of the factors that are required during early embry ...
... intriguing biological phenomena and raises questions about the origin and function of factors required for the initiation of a new life. What are those factors? Where and how are they made? What are their functions? It has long been known that most of the factors that are required during early embry ...
ontology design patterns for the formalisation of biological ontologies
... 25 years. As a consequence of that revolution, large amounts of complex information are being created and stored. This information is very heterogeneous, including data that range from plain DNA sequences to complex protein 3D structures. All those data are annotated, including information about ori ...
... 25 years. As a consequence of that revolution, large amounts of complex information are being created and stored. This information is very heterogeneous, including data that range from plain DNA sequences to complex protein 3D structures. All those data are annotated, including information about ori ...
Endonucleolytic processing of CCAless tRNA precursors by RNase
... Condon and Putzer, 2002), with Aquifex aeolicus being the only documented species in any of the three kingdoms not possessing RNase P activity (Willkomm et al., 2002). In bacteria, RNase P is a two-component enzyme consisting of a protein and an RNA subunit, with the RNA subunit providing the cataly ...
... Condon and Putzer, 2002), with Aquifex aeolicus being the only documented species in any of the three kingdoms not possessing RNase P activity (Willkomm et al., 2002). In bacteria, RNase P is a two-component enzyme consisting of a protein and an RNA subunit, with the RNA subunit providing the cataly ...
Practice Genetic Problems PMB 220 1. In working with a haploid
... 2. Wild-type strains of the haploid fungus Neurospora crassa can make their own tryptophan. An abnormal allele td renders the fungus incapable of making its own tryptophan, and thus it is a tryptophan auxotroph (tryptophan must be added to the media to allow the mutant to grow). A mutation at a seco ...
... 2. Wild-type strains of the haploid fungus Neurospora crassa can make their own tryptophan. An abnormal allele td renders the fungus incapable of making its own tryptophan, and thus it is a tryptophan auxotroph (tryptophan must be added to the media to allow the mutant to grow). A mutation at a seco ...
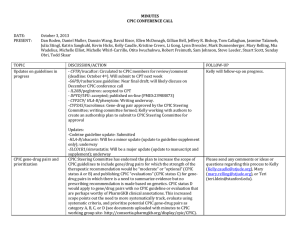
minutes cpic October 2013
... Details on how to group CPIC evaluations and mechanisms for publishing are not yet decided. Members provided feedback and there was support for the need for these evaluations, particularly for drugs whose genes are already the subject of other CPIC guidelines or genes that are commonly included in c ...
... Details on how to group CPIC evaluations and mechanisms for publishing are not yet decided. Members provided feedback and there was support for the need for these evaluations, particularly for drugs whose genes are already the subject of other CPIC guidelines or genes that are commonly included in c ...
About Neurofibromatosis 1 - Children`s Tumor Foundation
... providers with the hope that readers will seek additional information about the disorder according to their own individual needs. Physicians knowledgeable about NF, local genetics clinics, specialized NF clinics throughout the country, and the Children’s Tumor Foundation all serve as helpful sourc ...
... providers with the hope that readers will seek additional information about the disorder according to their own individual needs. Physicians knowledgeable about NF, local genetics clinics, specialized NF clinics throughout the country, and the Children’s Tumor Foundation all serve as helpful sourc ...
NO sensing by FNR: regulation of the Escherichia coli NO
... the ¯avohaemoglobin-encoding gene of E.coli, hmp, is upregulated by NO and RNS; this appears not to involve SoxRS (Poole et al., 1996). We have reported (MembrilloHernaÂndez et al., 1998) a mechanism of hmp gene regulation that involves interaction between S-nitrosothiols and Hcy. Intracellular Hcy ...
... the ¯avohaemoglobin-encoding gene of E.coli, hmp, is upregulated by NO and RNS; this appears not to involve SoxRS (Poole et al., 1996). We have reported (MembrilloHernaÂndez et al., 1998) a mechanism of hmp gene regulation that involves interaction between S-nitrosothiols and Hcy. Intracellular Hcy ...
DEPARTAMENT DE GENÈTICA GENOME EVOLUTION AND SYSTEMS BIOLOGY IN
... sequencing projects, from the sequencing of representative isolates culturable bacteria, mainly important human pathogens, to metagenomic studies in which the objective is the sequencing of entire microbial communities of a given environment providing a way to study the structure of microbial commun ...
... sequencing projects, from the sequencing of representative isolates culturable bacteria, mainly important human pathogens, to metagenomic studies in which the objective is the sequencing of entire microbial communities of a given environment providing a way to study the structure of microbial commun ...
Engineering the pentose phosphate pathway of
... The baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a long tradition in alcohol production from D-glucose of e.g. starch. However, without genetic modifications it is unable to utilise the 5-carbon sugars D-xylose and L-arabinose present in plant biomass. In this study, one key metabolic step of the cata ...
... The baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a long tradition in alcohol production from D-glucose of e.g. starch. However, without genetic modifications it is unable to utilise the 5-carbon sugars D-xylose and L-arabinose present in plant biomass. In this study, one key metabolic step of the cata ...
Analysis of the genetic potential of the spongederived fungus
... lab and for introducing me into the puzzling world of polyketides. I am grateful for all suggestions that I got from him during the practical work in the lab, as well as for the writing of my thesis. Moreover, I want to thank him for his trust and unique experience in building up a laboratory togeth ...
... lab and for introducing me into the puzzling world of polyketides. I am grateful for all suggestions that I got from him during the practical work in the lab, as well as for the writing of my thesis. Moreover, I want to thank him for his trust and unique experience in building up a laboratory togeth ...
Databases - HSLS - University of Pittsburgh
... http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/molbio/videos/play?v=19 http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/guides/genetics ...
... http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/molbio/videos/play?v=19 http://www.hsls.pitt.edu/guides/genetics ...
gemini Documentation
... Note: we now recommend splitting variants with multiple alternates and left-aligning, and trimming all variants before loading into gemini. See Step 1. split, left-align, and trim variants for a detailed explanation. Before we can use GEMINI to explore genetic variation, we must first load our VCF f ...
... Note: we now recommend splitting variants with multiple alternates and left-aligning, and trimming all variants before loading into gemini. See Step 1. split, left-align, and trim variants for a detailed explanation. Before we can use GEMINI to explore genetic variation, we must first load our VCF f ...
The Genera Staphylococcus and Macrococcus
... (Roseville, Australia), is distributed by International Bioproducts, Inc. (Redmond, WA, USA), and an RPLA is available from Oxoid (Columbia, MD, USA). Molecular methods are being investigated for their usefulness in detecting staphylococcal enterotoxin. For example, Western immunoblotting has been u ...
... (Roseville, Australia), is distributed by International Bioproducts, Inc. (Redmond, WA, USA), and an RPLA is available from Oxoid (Columbia, MD, USA). Molecular methods are being investigated for their usefulness in detecting staphylococcal enterotoxin. For example, Western immunoblotting has been u ...
Attachment 2.2 Sequencing results
... On the other hand, AHR deficient mice have a reduced body weight, display reduced fecundity and are defective in development of both liver and immune system. In these mice fetal vascular structures are found in the eyes, kidneys and liver. [1] Objective: to study the conservation of the AHR gene and ...
... On the other hand, AHR deficient mice have a reduced body weight, display reduced fecundity and are defective in development of both liver and immune system. In these mice fetal vascular structures are found in the eyes, kidneys and liver. [1] Objective: to study the conservation of the AHR gene and ...
Functional characterization of the Mycobacterium
... regulator. The histidine kinase undergoes autophosphorylation in response to an environmental signal, and subsequently phosphorylates an aspartate residue in the response regulator, which binds to specific DNA sequences (Inouye & Nariya, 2008). This two-component system is ubiquitous in prokaryotes ...
... regulator. The histidine kinase undergoes autophosphorylation in response to an environmental signal, and subsequently phosphorylates an aspartate residue in the response regulator, which binds to specific DNA sequences (Inouye & Nariya, 2008). This two-component system is ubiquitous in prokaryotes ...
Novel pathogen-specific primers for the detection of Agrobacterium
... limits the efficiency of PCR. For example, the virC-specific primers amplify the corresponding sequences from A. tumefaciens (SAWADA et al. 1995), but not from A. vitis (SZEGEDI and BOTTKA, 2002). Although an improved virCspecific primer pair detected some A. vitis strains (KAWAGUCHI et al. 2005), comp ...
... limits the efficiency of PCR. For example, the virC-specific primers amplify the corresponding sequences from A. tumefaciens (SAWADA et al. 1995), but not from A. vitis (SZEGEDI and BOTTKA, 2002). Although an improved virCspecific primer pair detected some A. vitis strains (KAWAGUCHI et al. 2005), comp ...
GENETIC AND MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF THE garnet EYE
... be responsible for the parental imprinting of the mini-chromosome The results suggest that heterochromatin formation is responsible for the somatic expression of the genomic imprint, but a different system may operate to establish the imprint. ...
... be responsible for the parental imprinting of the mini-chromosome The results suggest that heterochromatin formation is responsible for the somatic expression of the genomic imprint, but a different system may operate to establish the imprint. ...
2.1.databases_intro - T
... •Write down the PubMed Identifier (the number in the PMID field) of that interesting paper you just find. It could be very useful in your subsequent search for related items such as associated gene and protein sequences ...
... •Write down the PubMed Identifier (the number in the PMID field) of that interesting paper you just find. It could be very useful in your subsequent search for related items such as associated gene and protein sequences ...
and Rhizobiales-Like PPP-Family Protein Phosphatases from
... elucidate the evolutionary, biochemical, cellular and biological characteristics of two recently identified PPP-family protein phosphatase subclasses from the model photosynthetic Eukaryote Arabidopsis thaliana. These two subclasses included the Shewanella-like (SLP1 and 2) and Rhizobiales-like (RLP ...
... elucidate the evolutionary, biochemical, cellular and biological characteristics of two recently identified PPP-family protein phosphatase subclasses from the model photosynthetic Eukaryote Arabidopsis thaliana. These two subclasses included the Shewanella-like (SLP1 and 2) and Rhizobiales-like (RLP ...
Environmental factors influence virulence of Pseudomonas
... Moreover, P. aeruginosa causes infections in a wide range of eukaryotic organisms including plants, invertebrates and vertebrates rendering it an important opportunistic pathogen (Vasil, 1986; Rahme et al., 1995; Walker et al., 2004). While it rarely infects healthy individuals, it is the most commo ...
... Moreover, P. aeruginosa causes infections in a wide range of eukaryotic organisms including plants, invertebrates and vertebrates rendering it an important opportunistic pathogen (Vasil, 1986; Rahme et al., 1995; Walker et al., 2004). While it rarely infects healthy individuals, it is the most commo ...
ADRC2010_GetTheMostOutofFlyBase
... particular subject/class, organized into a hierarchical tree • Tree structure indicates how each specific CV term relates to others within that particular vocabulary • aka ‘ontologies’ ...
... particular subject/class, organized into a hierarchical tree • Tree structure indicates how each specific CV term relates to others within that particular vocabulary • aka ‘ontologies’ ...
"RNA Interference in Caenorhabditis elegans".
... et al., 2000). In the microinjection and soaking protocols, in vitro preparations of dsRNA are delivered mechanically using a needle to inject dsRNA directly into the body or passively by soaking worms in dsRNA solution. In the feeding protocols, dsRNA is transcribed in E. coli and ingested by anima ...
... et al., 2000). In the microinjection and soaking protocols, in vitro preparations of dsRNA are delivered mechanically using a needle to inject dsRNA directly into the body or passively by soaking worms in dsRNA solution. In the feeding protocols, dsRNA is transcribed in E. coli and ingested by anima ...
Genetic Determinants Differences between Vibrio cholerae Biotypes
... Classical and El Tor are differentiated primarily based on a number of phenotypic properties such as susceptibility to polymyxin B, chicken cell (erythrocytes) agglutination (CCA), haemolysis of sheep erythrocytes, Voges-Proskauer (VP) test and phage susceptibilities (2, 9). The V. cholerae biotypes ...
... Classical and El Tor are differentiated primarily based on a number of phenotypic properties such as susceptibility to polymyxin B, chicken cell (erythrocytes) agglutination (CCA), haemolysis of sheep erythrocytes, Voges-Proskauer (VP) test and phage susceptibilities (2, 9). The V. cholerae biotypes ...
Chromosome location and characterization of genes for grain
... The three lines LDN(521-3A) (207.4 g m-1), LDN(742-2B) (212.2 g m-1), and LDN(742-7B) (233.7 g m-1) had the lowest yields among the LDN-DIC lines.. The three lines all had unique characteristics contributing to their low grain yield. LDN(521-3A) produced weak plants and were the shortest in plant he ...
... The three lines LDN(521-3A) (207.4 g m-1), LDN(742-2B) (212.2 g m-1), and LDN(742-7B) (233.7 g m-1) had the lowest yields among the LDN-DIC lines.. The three lines all had unique characteristics contributing to their low grain yield. LDN(521-3A) produced weak plants and were the shortest in plant he ...
Virulence factors of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis
... Serovar Enteritidis and serovar Typhimurium can colonize both humans and chicken. In humans, the infection can manifest as a non-bloody diarrhea with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and fever. The disease (non-typhoidal fever) is usually self-limiting and recovery follows within a few days to a wee ...
... Serovar Enteritidis and serovar Typhimurium can colonize both humans and chicken. In humans, the infection can manifest as a non-bloody diarrhea with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and fever. The disease (non-typhoidal fever) is usually self-limiting and recovery follows within a few days to a wee ...