Functional genomics analysis of the effects of co- decarboxylase/ornithine decarboxylase
... Plasmodium falciparum, polyamine biosynthesis is regulated by the uniquely bifunctional protein, Sadenosylmethionine decarboxylase/ornithine decarboxylase (PfAdoMetDC/ODC). The unique nature of this protein could provide a selective mechanism for antimalarial treatment. To validate polyamine depleti ...
... Plasmodium falciparum, polyamine biosynthesis is regulated by the uniquely bifunctional protein, Sadenosylmethionine decarboxylase/ornithine decarboxylase (PfAdoMetDC/ODC). The unique nature of this protein could provide a selective mechanism for antimalarial treatment. To validate polyamine depleti ...
6. risk management plan
... Transfer of introduced genes to other organisms ........................................................... 54 Transfer of introduced genes to other plants .................................................................. 54 A: Nature of the gene transfer hazard .................................... ...
... Transfer of introduced genes to other organisms ........................................................... 54 Transfer of introduced genes to other plants .................................................................. 54 A: Nature of the gene transfer hazard .................................... ...
Ret/PTC3 is the most frequent form of gene rearrangement
... papillary thyroid carcinomas only for ret/PTC1 rearrangements and found no rearrangement; Ishizaka et al. (1991) found one ret/PTC1 rearrangement among 11 carcinomas, and Wajjwalku et al. (1992) found only one such alteration among 38 carcinomas. On the basis of those observations, RET gene rearrang ...
... papillary thyroid carcinomas only for ret/PTC1 rearrangements and found no rearrangement; Ishizaka et al. (1991) found one ret/PTC1 rearrangement among 11 carcinomas, and Wajjwalku et al. (1992) found only one such alteration among 38 carcinomas. On the basis of those observations, RET gene rearrang ...
Characterization of the cDNA and Gene Coding for the Biotin
... Recent reports indicate that additional proteins, other than the bioB gene product, may also be required in the catalysis of this reaction (Ifuku et al., 1992; Sanyal et al., 1994; Birch et al., 1995). Furthermore, it is not clear if this reaction occurs via the formation of the intermediate 9-merca ...
... Recent reports indicate that additional proteins, other than the bioB gene product, may also be required in the catalysis of this reaction (Ifuku et al., 1992; Sanyal et al., 1994; Birch et al., 1995). Furthermore, it is not clear if this reaction occurs via the formation of the intermediate 9-merca ...
An AT-hook gene is required for palea formation and floral organ
... other grasses, class A genes in rice remain difficult to determine. Similar to rice, the maize outer whorl organ identity remains elusive that molecular dissection of regulatory pathways has just started (Thompson et al., 2009; Whipple et al., 2010). In order to understand the molecular regulation of ...
... other grasses, class A genes in rice remain difficult to determine. Similar to rice, the maize outer whorl organ identity remains elusive that molecular dissection of regulatory pathways has just started (Thompson et al., 2009; Whipple et al., 2010). In order to understand the molecular regulation of ...
The C-terminal domain of the Rhizobium leguminosarum
... in the presence of hesperetin. Derivatives of pIJ1089 and pIJ1887 containing TnphoA were transferred to R. leguminosarum strain 8401 by conjugation. NodC–PhoA fusions expressing high levels of alkaline phosphatase could be identified in R. leguminosarum on plates containing hesperetin to induce nod ...
... in the presence of hesperetin. Derivatives of pIJ1089 and pIJ1887 containing TnphoA were transferred to R. leguminosarum strain 8401 by conjugation. NodC–PhoA fusions expressing high levels of alkaline phosphatase could be identified in R. leguminosarum on plates containing hesperetin to induce nod ...
The Genes of Watermelon
... crop in the world, accounting for 6.8% of the world area devoted to vegetable crops. Watermelon is a useful vegetable crop for genetic research because of its small genome size, and the many available gene mutants. The watermelon genes were originally organized and summarized in 1944, and have been ...
... crop in the world, accounting for 6.8% of the world area devoted to vegetable crops. Watermelon is a useful vegetable crop for genetic research because of its small genome size, and the many available gene mutants. The watermelon genes were originally organized and summarized in 1944, and have been ...
Mar22_24
... Note that in each of the cases (in fact, all cases except p0 = 0 or 1) The dominant allele will eventually make up 80% of the gene pool and the recessive will make up 20%. This result is called a stable equilibrium. Can we determine what this equilibrium will be? ...
... Note that in each of the cases (in fact, all cases except p0 = 0 or 1) The dominant allele will eventually make up 80% of the gene pool and the recessive will make up 20%. This result is called a stable equilibrium. Can we determine what this equilibrium will be? ...
PDF
... In insects, the precise timing of molting and metamorphosis is strictly guided by a principal steroid hormone, ecdysone. Among the multiple conversion steps for synthesizing ecdysone from dietary cholesterol, the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to 5ketodiol, the so-called ‘Black Box’, is thought ...
... In insects, the precise timing of molting and metamorphosis is strictly guided by a principal steroid hormone, ecdysone. Among the multiple conversion steps for synthesizing ecdysone from dietary cholesterol, the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to 5ketodiol, the so-called ‘Black Box’, is thought ...
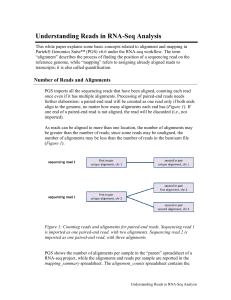
Understanding Reads in RNA-Seq Analysis
... read is a read that fits the transcript model from the chosen annotation database. Compatible reads must be an exonic read (fully mapped to exon); however not all the exonic reads are compatible with a transcript, e.g., in paired end reads, both end reads have to be exonic as well as they both have ...
... read is a read that fits the transcript model from the chosen annotation database. Compatible reads must be an exonic read (fully mapped to exon); however not all the exonic reads are compatible with a transcript, e.g., in paired end reads, both end reads have to be exonic as well as they both have ...
34386 - PubAg
... address the question of whether the intimate structural similarity of IGL and BX1 reflects the same enzymatic mechanism, i.e., the conversion of IGP to indole, Igl was expressed in E. coli, purified, and used for the determination of the steady-state kinetic constants as described for BX1 (10). The ...
... address the question of whether the intimate structural similarity of IGL and BX1 reflects the same enzymatic mechanism, i.e., the conversion of IGP to indole, Igl was expressed in E. coli, purified, and used for the determination of the steady-state kinetic constants as described for BX1 (10). The ...
Scriver Charles R. Garrod`s Croonian Lectures (1908)
... link between Mendel_s factors (genes), and enzymes, when the latter became a major field of inquiry in biochemistry. Meanwhile, in medicine, the apparent rarity of the inborn errors of metabolism made them irrelevant to the medical profession and efforts to show their inheritance and congenital natu ...
... link between Mendel_s factors (genes), and enzymes, when the latter became a major field of inquiry in biochemistry. Meanwhile, in medicine, the apparent rarity of the inborn errors of metabolism made them irrelevant to the medical profession and efforts to show their inheritance and congenital natu ...
Gene Section MLL (myeloid/lymphoid or mixed lineage leukemia) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... • t(11;11)(q23;q24)/ANLL → MLL - TIRAP • t(11;12)(q23;q13)/ANLL → MLL - CIP29 • t(11;14)(q23;q24)/ANLL, AUL → MLL - GPHN • t(11;15)(q23;q14)/ANLL, ALL → MLL - CASC5 (AF15q14) • t(11;15)(q23;q14) → MLL - MPFYVE • t(11;15)(q23;q15) → MLL - AF15 • t(11;16)(q23;p13)/MDS, ANLL, t-ANLL, ALL → MLL - CREBBP ...
... • t(11;11)(q23;q24)/ANLL → MLL - TIRAP • t(11;12)(q23;q13)/ANLL → MLL - CIP29 • t(11;14)(q23;q24)/ANLL, AUL → MLL - GPHN • t(11;15)(q23;q14)/ANLL, ALL → MLL - CASC5 (AF15q14) • t(11;15)(q23;q14) → MLL - MPFYVE • t(11;15)(q23;q15) → MLL - AF15 • t(11;16)(q23;p13)/MDS, ANLL, t-ANLL, ALL → MLL - CREBBP ...
Pyruvate : NADP+ Oxidoreductase from the Mitochondrion of
... their anaerobic energy metabolism (Müller 1993, 1998; Fenchel and Finlay 1995; Biagini, Finlay, and Lloyd 1997), the evolutionary origin of this enzyme bears heavily on views concerning the metabolic lifestyle of the earliest eukaryotic cells (Martin and Müller 1998). In principle, three alternati ...
... their anaerobic energy metabolism (Müller 1993, 1998; Fenchel and Finlay 1995; Biagini, Finlay, and Lloyd 1997), the evolutionary origin of this enzyme bears heavily on views concerning the metabolic lifestyle of the earliest eukaryotic cells (Martin and Müller 1998). In principle, three alternati ...
Richard Goldschmidt: hopeful monsters and other `heresies`
... frequently appeared as mosaics of different sexual characteristics, some male, some female, some intermediate. The absence of sex-specific traits that were uniformly expressed was a significant problem for a general genetic theory of sex determination. His solution was formulated in the ‘time law of ...
... frequently appeared as mosaics of different sexual characteristics, some male, some female, some intermediate. The absence of sex-specific traits that were uniformly expressed was a significant problem for a general genetic theory of sex determination. His solution was formulated in the ‘time law of ...
Pyruvate : NADP+ Oxidoreductase from the Mitochondrion of
... their anaerobic energy metabolism (Müller 1993, 1998; Fenchel and Finlay 1995; Biagini, Finlay, and Lloyd 1997), the evolutionary origin of this enzyme bears heavily on views concerning the metabolic lifestyle of the earliest eukaryotic cells (Martin and Müller 1998). In principle, three alternati ...
... their anaerobic energy metabolism (Müller 1993, 1998; Fenchel and Finlay 1995; Biagini, Finlay, and Lloyd 1997), the evolutionary origin of this enzyme bears heavily on views concerning the metabolic lifestyle of the earliest eukaryotic cells (Martin and Müller 1998). In principle, three alternati ...
Gene Section ATF4 (activating transcription factor 4 (tax responsive enhancer element B67)) -
... amino acids. Therefore, lack of ATF4 results in reduced concentration of amino acids, attributed to reduced TOR input. Thus, there is a close relationship between ATF4 function, the TOR pathway, and metabolism. This function of ATF4 also explains why type I collagen synthesis is specifically reduced ...
... amino acids. Therefore, lack of ATF4 results in reduced concentration of amino acids, attributed to reduced TOR input. Thus, there is a close relationship between ATF4 function, the TOR pathway, and metabolism. This function of ATF4 also explains why type I collagen synthesis is specifically reduced ...
Whole-Cell Bacterial Biosensors and the Detection of - CLU-IN
... However, toxicity, solubility, and mobility can all vary depending upon which species of arsenic is present, thus affecting the bioavailability of the arsenic contamination. The bioavailable fraction is the portion of arsenic that is available for biological uptake. Risk assessments could be over or ...
... However, toxicity, solubility, and mobility can all vary depending upon which species of arsenic is present, thus affecting the bioavailability of the arsenic contamination. The bioavailable fraction is the portion of arsenic that is available for biological uptake. Risk assessments could be over or ...
Molecular cloning of a laccase isozyme gene from
... the absorbance spectrum of native laccase. All these copper ions appear to be involved in the catalytic mechanism. Amino acid sequence analysis of different laccases indicates that the copper-binding sites, involving ten-histidine residues, are very highly conserved. Various fungi, several insects ( ...
... the absorbance spectrum of native laccase. All these copper ions appear to be involved in the catalytic mechanism. Amino acid sequence analysis of different laccases indicates that the copper-binding sites, involving ten-histidine residues, are very highly conserved. Various fungi, several insects ( ...
Inference of natural selection on quantitative traits
... In this thesis, I combine aspects of both fields to study the evolutionary history of quantitative traits. Based on established results from population genetics theory I construct a model for the evolution of quantitative traits. This model quantifies the strength of evidence for selection acting on ...
... In this thesis, I combine aspects of both fields to study the evolutionary history of quantitative traits. Based on established results from population genetics theory I construct a model for the evolution of quantitative traits. This model quantifies the strength of evidence for selection acting on ...
C 2: A A -
... but also imipenem to a minor extent. This enzyme was identified in P. aeruginosa from a university hospital in Pretoria, South Africa, and was associated with an outbreak occurring in the same hospital from March to July 2000 (51). Seventy-two ceftazidimeresistant isolates were isolated from nine pa ...
... but also imipenem to a minor extent. This enzyme was identified in P. aeruginosa from a university hospital in Pretoria, South Africa, and was associated with an outbreak occurring in the same hospital from March to July 2000 (51). Seventy-two ceftazidimeresistant isolates were isolated from nine pa ...
Gene expression analysis
... Why find genes that behave differently in two classes (e.g. normal and tumor)? Better understanding of the genetic circumstances that cause the difference (disease) hopefully leads to better therapy. Detection of marker-genes enables the early recognition of diseases as well as the recognition of su ...
... Why find genes that behave differently in two classes (e.g. normal and tumor)? Better understanding of the genetic circumstances that cause the difference (disease) hopefully leads to better therapy. Detection of marker-genes enables the early recognition of diseases as well as the recognition of su ...
Characterization of the Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase Gene
... © 2001 Horizon Scientific Press ...
... © 2001 Horizon Scientific Press ...
Section 1 The application - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... must follow when considering an application for a licence to intentionally release a genetically modified organism (GMO) into the environment. For a licence to be issued, the Regulator must be satisfied that the release will not pose any risks to human health and safety and the environment that can ...
... must follow when considering an application for a licence to intentionally release a genetically modified organism (GMO) into the environment. For a licence to be issued, the Regulator must be satisfied that the release will not pose any risks to human health and safety and the environment that can ...
Product description P048-C1-0315 LMNA-MYOT - MRC
... 35-50% reduced relative peak height of the amplification product of that probe. Note that a mutation or polymorphism in the sequence detected by a probe can also cause a reduction in relative peak height, even when not located exactly on the ligation site! In addition, some probe signals are more se ...
... 35-50% reduced relative peak height of the amplification product of that probe. Note that a mutation or polymorphism in the sequence detected by a probe can also cause a reduction in relative peak height, even when not located exactly on the ligation site! In addition, some probe signals are more se ...