The Crusades - Muslim Population
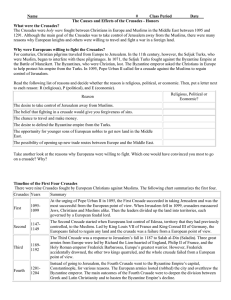
... In 1144 CE, the Muslims recaptured Edessa. This city was vital for the safety of the Frankish holdings as it guarded their back door. News of the fall of Edessa spread throughout Europe and a second crusade was called by Pope Eugenius III. The Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad III and the French king, Loui ...
... In 1144 CE, the Muslims recaptured Edessa. This city was vital for the safety of the Frankish holdings as it guarded their back door. News of the fall of Edessa spread throughout Europe and a second crusade was called by Pope Eugenius III. The Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad III and the French king, Loui ...
Chapter 1
... The leadership of Saladin Reaction to the fall of Jerusalem Led by Frederick I Barbarossa of Germany, Richard the Lionhearted of England, and Philip Augustus of France ...
... The leadership of Saladin Reaction to the fall of Jerusalem Led by Frederick I Barbarossa of Germany, Richard the Lionhearted of England, and Philip Augustus of France ...
The Crusades - GlobalHistory9H
... • Emperor Alexuis I asks Pope Urban III for help • Started when Muslim Turks attack the Holy Land • Many ordinary people were motivated by riches. ...
... • Emperor Alexuis I asks Pope Urban III for help • Started when Muslim Turks attack the Holy Land • Many ordinary people were motivated by riches. ...
Pope Urban persuaded the knights of Europe to join the Crusades
... He wanted to make safe travel routes to and from the Holy Land, as many pilgrims were traveling to the area and being killed on route. This would support the later formation, in 1118, of the Knights Templar. Put an end to the fighting among landowners and feudal societies in Europe. By redirecting h ...
... He wanted to make safe travel routes to and from the Holy Land, as many pilgrims were traveling to the area and being killed on route. This would support the later formation, in 1118, of the Knights Templar. Put an end to the fighting among landowners and feudal societies in Europe. By redirecting h ...
The Crusades Reading Guide
... Economic, Social, and Political Goals of the Crusades Economic Goals: ...
... Economic, Social, and Political Goals of the Crusades Economic Goals: ...
High Middle Ages
... and attacked Jews and other Christians as well as infidels. They were killed by the Turks when they reached the Holy Land 5000 priests, workers, knights, prostitutes and lords dressed as Crusaders and seized the cities of Antioch and Jerusalem, setting up three kingdoms: the Principality of Antioch, ...
... and attacked Jews and other Christians as well as infidels. They were killed by the Turks when they reached the Holy Land 5000 priests, workers, knights, prostitutes and lords dressed as Crusaders and seized the cities of Antioch and Jerusalem, setting up three kingdoms: the Principality of Antioch, ...
File
... The Second Crusade started when Europeans lost control of Edessa, territory that they had previously controlled, to the Muslims. Led by King Louis VII of France and King Conrad III of Germany, the Europeans failed to regain any land and the crusade was a failure from a European point of view. ...
... The Second Crusade started when Europeans lost control of Edessa, territory that they had previously controlled, to the Muslims. Led by King Louis VII of France and King Conrad III of Germany, the Europeans failed to regain any land and the crusade was a failure from a European point of view. ...
Crusades - Mr. L. Goldsack
... • The Holy Grail (cup that held some of Christ’s blood from cross) • Spear of Destiny (spear which Roman Soldier poked Christ on cross) • Ark of the Covenant (held the 10 Commandments) • Christ Burial Shroud (cloth that covered Christ in tomb) • Cross (Christ’s) Pieces scattered all throughout the w ...
... • The Holy Grail (cup that held some of Christ’s blood from cross) • Spear of Destiny (spear which Roman Soldier poked Christ on cross) • Ark of the Covenant (held the 10 Commandments) • Christ Burial Shroud (cloth that covered Christ in tomb) • Cross (Christ’s) Pieces scattered all throughout the w ...
The Crusades
... Events Leading Up to the Crusades-- Why did the European Christians begin going on crusades at the end of the 11th century? To answer this question, we need to look at what was happening in Muslim lands at this time. During the 11th century, the Seljuk Turks established a new Muslim dynasty. The Tur ...
... Events Leading Up to the Crusades-- Why did the European Christians begin going on crusades at the end of the 11th century? To answer this question, we need to look at what was happening in Muslim lands at this time. During the 11th century, the Seljuk Turks established a new Muslim dynasty. The Tur ...
The Middle Ages
... A. The Byzantine Empire sent Pope Urban II a message that the Seljuk Turks had captured Jerusalem 1. The message claimed that the churches had been turned into mosques 2. The message also said that Christians were being sold as slaves and in order to have enough power to recapture Jerusalem, the pop ...
... A. The Byzantine Empire sent Pope Urban II a message that the Seljuk Turks had captured Jerusalem 1. The message claimed that the churches had been turned into mosques 2. The message also said that Christians were being sold as slaves and in order to have enough power to recapture Jerusalem, the pop ...
Aim: What role did the Byzantine Empire play in world history
... A. The Byzantine Empire sent Pope Urban II a message that the Seljuk Turks had captured Jerusalem 1. The message claimed that the churches had been turned into mosques 2. The message also said that Christians were being sold as slaves and in order to have enough power to recapture Jerusalem, the pop ...
... A. The Byzantine Empire sent Pope Urban II a message that the Seljuk Turks had captured Jerusalem 1. The message claimed that the churches had been turned into mosques 2. The message also said that Christians were being sold as slaves and in order to have enough power to recapture Jerusalem, the pop ...
Ch. 14.1 / 14.2 WS
... A. Perceiving Cause and Effect As you read about reforms in the Catholic Church and the Crusades, note one or more reasons for each of the following developments. 1. The Benedictine monastery was founded at Cluny. ...
... A. Perceiving Cause and Effect As you read about reforms in the Catholic Church and the Crusades, note one or more reasons for each of the following developments. 1. The Benedictine monastery was founded at Cluny. ...
Crusades Activity
... Christians were still allowed to visit the city. By the 11th century, however, the situation had changed. Just as the number and frequency of pilgrimages to Jerusalem was at new peaks, the Seljuk Turks took over control of Jerusalem and prevented pilgrimages. For thousands of years, Jews, Christians ...
... Christians were still allowed to visit the city. By the 11th century, however, the situation had changed. Just as the number and frequency of pilgrimages to Jerusalem was at new peaks, the Seljuk Turks took over control of Jerusalem and prevented pilgrimages. For thousands of years, Jews, Christians ...
Crusades: The Other Side
... • Many people in the west believe that all Muslims were the same • The Islamic World was split into many factions based on politics, geography, and religious interpretation ...
... • Many people in the west believe that all Muslims were the same • The Islamic World was split into many factions based on politics, geography, and religious interpretation ...
The Knight`s Templar
... “I think it only right that at so solemn a moment, when my life has so little time to run, I should reveal the deception which has been practiced, and speak up for the truth. Before heaven and earth, and with all of you here as my witnesses, I admit that I am guilty of the grossest iniquity. But t ...
... “I think it only right that at so solemn a moment, when my life has so little time to run, I should reveal the deception which has been practiced, and speak up for the truth. Before heaven and earth, and with all of you here as my witnesses, I admit that I am guilty of the grossest iniquity. But t ...
File
... How did he spread the crusading message across Europe? Why did King Richard I still go on the Third Crusade even after he was crowned? In total, King Richard spent around ___________________ pounds in preparation for the Crusade, which accounted for ½ of the Crown’s annual revenue. King Richard’s f ...
... How did he spread the crusading message across Europe? Why did King Richard I still go on the Third Crusade even after he was crowned? In total, King Richard spent around ___________________ pounds in preparation for the Crusade, which accounted for ½ of the Crown’s annual revenue. King Richard’s f ...
Crusades Packet - Ms. Gleason`s Classroom
... Crusade comes from the Latin word crux, meaning a ‘cross’. It referred to the cross on which Jesus Christ was crucified and to go on a crusade meant going to fight for Christ. In 1100, it meant going to fight the Muslims in the Holy Land, around Jerusalem, where Christ had lived. Muhammad and Muslim ...
... Crusade comes from the Latin word crux, meaning a ‘cross’. It referred to the cross on which Jesus Christ was crucified and to go on a crusade meant going to fight for Christ. In 1100, it meant going to fight the Muslims in the Holy Land, around Jerusalem, where Christ had lived. Muhammad and Muslim ...
Formation of Western Europe
... • 1st Crusade was the only successful one for the Christians • Were able to recapture Jerusalem and establish the Crusader States ...
... • 1st Crusade was the only successful one for the Christians • Were able to recapture Jerusalem and establish the Crusader States ...
The Crusades of the Holy Roman Empire
... Holy Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire respectively, believed in their own eyes that they were Christian Empires. The Crusades. The Crusades were military expeditions, organized mainly to recapture Palestine during the Middle Ages. Palestine, also called the Holy Land, was important to Christians be ...
... Holy Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire respectively, believed in their own eyes that they were Christian Empires. The Crusades. The Crusades were military expeditions, organized mainly to recapture Palestine during the Middle Ages. Palestine, also called the Holy Land, was important to Christians be ...
Missionary Mercenaries - Tallwood
... From the Frankish point of view, an oath made to a non-Christian was no oath at all. ...
... From the Frankish point of view, an oath made to a non-Christian was no oath at all. ...
FIFTH CRUSADE
... movements until July, when the Crusaders moved into position around Mansourah (Mayer, 1988, p. 225-26). They failed to notice the rising Nile, and their camp was soon flooded (Armstrong, 1988, p. 408). Added to this problem were the reinforcements sent by Al-Ashraf which cut them off from Damietta ...
... movements until July, when the Crusaders moved into position around Mansourah (Mayer, 1988, p. 225-26). They failed to notice the rising Nile, and their camp was soon flooded (Armstrong, 1988, p. 408). Added to this problem were the reinforcements sent by Al-Ashraf which cut them off from Damietta ...
File
... Jerusalem was stormed (soldiers try to take over the city) successfully in 1099 and a Christian kingdom set up. The Second Crusade ran from 1147 to 1149 and was led by Louis VII of France and the Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad III. The two quarrelled (fought) and the barons (rulers) of the Kingdom of Je ...
... Jerusalem was stormed (soldiers try to take over the city) successfully in 1099 and a Christian kingdom set up. The Second Crusade ran from 1147 to 1149 and was led by Louis VII of France and the Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad III. The two quarrelled (fought) and the barons (rulers) of the Kingdom of Je ...
Fourth Crusade

The Fourth Crusade (1202–04) was a Western European armed expedition originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. However, in January 1203, en route to Jerusalem, the majority of the crusader leadership entered into an agreement with the Byzantine prince Alexios Angelos to divert to Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire and restore his deposed father as emperor. The intention of the crusaders was to then continue to the Holy Land with promised Byzantine financial and military assistance. On 23 June 1203 the main crusader fleet reached Constantinople. Smaller contingents continued to Acre.In August 1203, following clashes outside Constantinople, Alexios Angelos was crowned as co-Emperor (Alexios IV Angelos) with crusader support. However, in January 1204, he was deposed by a popular uprising in Constantinople. The Western crusaders were no longer able to receive their promised payments, and when Alexios IV was murdered on 8 February 1204, the crusaders and Venetians decided on the outright conquest of Constantinople. In April 1204, they captured and brutally sacked the city, and set up a new Latin Empire as well as partitioning other Byzantine territories between themselves.Byzantine resistance based on unconquered sections of the empire such as Nicaea, Trebizond, and Epirus ultimately recovered Constantinople.The Fourth Crusade is considered to be one of the final acts in the Great Schism between the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church, and a key turning point in the decline of the Byzantine Empire.