The Crusades - Ms. Hairyes
... The Church also had its eye on the rich empire of the Byzantines. Although Pope Urban II had agreed to help the Byzantine emperor, the two were rivals. The pope hoped to weaken the Byzantine Empire and control its wealthy trade routes. This possibly encouraged European merchants to join the Crusades ...
... The Church also had its eye on the rich empire of the Byzantines. Although Pope Urban II had agreed to help the Byzantine emperor, the two were rivals. The pope hoped to weaken the Byzantine Empire and control its wealthy trade routes. This possibly encouraged European merchants to join the Crusades ...
Crusades notes
... o Nobles die, kings often get land o Currency allows for paid armies = kings don’t need nobles Broadened worldview through exposure to Byzantine and Arab world ...
... o Nobles die, kings often get land o Currency allows for paid armies = kings don’t need nobles Broadened worldview through exposure to Byzantine and Arab world ...
The Crusades
... Holy Land- Region that was sacred to Muslims, Jews and Christians (Jerusalem/Palestine) Pope Urban II- Pope of the Roman Catholic Church who ordered the Crusades to take place Byzantine Empire- The eastern half of the Roman Empire that lasted until 1450 C.E. (capital at Constantinople) ...
... Holy Land- Region that was sacred to Muslims, Jews and Christians (Jerusalem/Palestine) Pope Urban II- Pope of the Roman Catholic Church who ordered the Crusades to take place Byzantine Empire- The eastern half of the Roman Empire that lasted until 1450 C.E. (capital at Constantinople) ...
The Crusades
... Start of First Crusade 1096: 5,000 Crusaders left Europe for the Holy Land Why go on a Crusade? Hoped to save their soul Doing what God wanted God look favorably on them for fighting Wanted land and treasure Looking for adventure ...
... Start of First Crusade 1096: 5,000 Crusaders left Europe for the Holy Land Why go on a Crusade? Hoped to save their soul Doing what God wanted God look favorably on them for fighting Wanted land and treasure Looking for adventure ...
Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide 1. What was one effect of the Seljuk
... Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide 1. What was one effect of the Seljuk Turks invasion of Palestine? 2. Who had control over Jerusalem after each of the first 3 Crusades? First Crusade: Second Crusade: Third Crusade: 3. How did the Crusades affect Europe? 4. What is one loss Muslims suffered as a result o ...
... Name: Chapter 11 Study Guide 1. What was one effect of the Seljuk Turks invasion of Palestine? 2. Who had control over Jerusalem after each of the first 3 Crusades? First Crusade: Second Crusade: Third Crusade: 3. How did the Crusades affect Europe? 4. What is one loss Muslims suffered as a result o ...
THE CRUSADES 1095 AD Seljuk Turks invade
... • The Fourth Crusade, 1202-1204, saw the capture of Constantinople, which at the time was occupied by Greek-speaking Eastern Orthodox Christians, who did not recognize the authority of the Roman Pope. • The Children's Crusade, 1212, sent thousands of children for the Holy Land, where they were captu ...
... • The Fourth Crusade, 1202-1204, saw the capture of Constantinople, which at the time was occupied by Greek-speaking Eastern Orthodox Christians, who did not recognize the authority of the Roman Pope. • The Children's Crusade, 1212, sent thousands of children for the Holy Land, where they were captu ...
Middle Ages 2 Study Guide
... 12. ________________wanted people to study natural law to learn how they could live the way God wanted. 13. The church established some of the earliest ...
... 12. ________________wanted people to study natural law to learn how they could live the way God wanted. 13. The church established some of the earliest ...
CH 10-3 Lesson 2
... Byzantines asked Pope Urban II for help defeating the Muslim forces. 1095 the Pope asks the Nobles to begin a Crusade to free the Holy Land. ...
... Byzantines asked Pope Urban II for help defeating the Muslim forces. 1095 the Pope asks the Nobles to begin a Crusade to free the Holy Land. ...
The Crusades: not a walk in the park
... Goals: Get that Holy Land! • Religious Goal: Holy Land = Palestine, the land land where Jesus lived, preached, and died. ...
... Goals: Get that Holy Land! • Religious Goal: Holy Land = Palestine, the land land where Jesus lived, preached, and died. ...
The Crusades & Church Reform
... Conquered Palestine & attacked Asia Minor (Byz) Threatened Constantinople Appealed to Pope ...
... Conquered Palestine & attacked Asia Minor (Byz) Threatened Constantinople Appealed to Pope ...
chapter 11 religion
... THEY ACT IN DIRESPECTFUL WAYS TO PEOPLE OF OTHER RELIGIONS. THE GOSPEL OF JESUS CHRIST NEVER CALLS UPON US TO DISRESPECT ANYONE FOR ANY REASON! ...
... THEY ACT IN DIRESPECTFUL WAYS TO PEOPLE OF OTHER RELIGIONS. THE GOSPEL OF JESUS CHRIST NEVER CALLS UPON US TO DISRESPECT ANYONE FOR ANY REASON! ...
Crusade
... Goals of the Crusades • Economic, social, political, and religious goals – Stop Muslim attacks on Constantinople – Reclaim the Holy Land and reunite Eastern and Western Christendom – Get rid of knights who were constantly fighting each other, which threatened peace in the kingdoms – Younger sons, w ...
... Goals of the Crusades • Economic, social, political, and religious goals – Stop Muslim attacks on Constantinople – Reclaim the Holy Land and reunite Eastern and Western Christendom – Get rid of knights who were constantly fighting each other, which threatened peace in the kingdoms – Younger sons, w ...
Jerusalem
... • After Pope Urban's speech a visiting monk reported that the crowd shouted out "God wills it! God wills it!" They began preparing for war, Holy war. ...
... • After Pope Urban's speech a visiting monk reported that the crowd shouted out "God wills it! God wills it!" They began preparing for war, Holy war. ...
The Crusades
... Causes of the Crusades 1. Muslim invasions of and attacks on Christian lands, especially Jerusalem 2. Desire to spread and unite Christianity 3. Desire to open up trade routes to the East 4. Individuals hoped to gain land and riches 5. Protection of Christian pilgrims headed to Jerusalem ...
... Causes of the Crusades 1. Muslim invasions of and attacks on Christian lands, especially Jerusalem 2. Desire to spread and unite Christianity 3. Desire to open up trade routes to the East 4. Individuals hoped to gain land and riches 5. Protection of Christian pilgrims headed to Jerusalem ...
Nations and Crusade
... Papal Support: Leo IX and Nicholas II Gregory VII (1073-1085), Henry IV (10561106) and the Investiture Struggle ...
... Papal Support: Leo IX and Nicholas II Gregory VII (1073-1085), Henry IV (10561106) and the Investiture Struggle ...
Good or Bad? Sources - WordPress @ Clark U
... animals, he was relatively tolerant of the Christians who lived among the Muslims in his home country of Syria. Usamah did not fear death during battle because he felt deeply that he was fighting for a just cause—to save and protect the Holy Land (Jerusalem) from the Crusaders. ...
... animals, he was relatively tolerant of the Christians who lived among the Muslims in his home country of Syria. Usamah did not fear death during battle because he felt deeply that he was fighting for a just cause—to save and protect the Holy Land (Jerusalem) from the Crusaders. ...
Name
... The Children's Crusade in 1212 was a terrible tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected ...
... The Children's Crusade in 1212 was a terrible tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected ...
The Crusades
... Jerusalem and the city of Constantinople comes a grievous report … An accursed race … has violently invaded the lands of those Christians.” The Pope called for a Crusade to free the Holy Land from the invading Muslims. He said people who joined the Crusades would have all their sins forgiven. By 109 ...
... Jerusalem and the city of Constantinople comes a grievous report … An accursed race … has violently invaded the lands of those Christians.” The Pope called for a Crusade to free the Holy Land from the invading Muslims. He said people who joined the Crusades would have all their sins forgiven. By 109 ...
ED–The_Middle_Ages - Reeths
... • Fighting continued in the Holy Land between crusaders and Muslims, who were fighting in the name of Allah. • Led by Saladin, sultan of Egypt, the Muslims conquered Jerusalem and most of the Holy Land in 1187. ...
... • Fighting continued in the Holy Land between crusaders and Muslims, who were fighting in the name of Allah. • Led by Saladin, sultan of Egypt, the Muslims conquered Jerusalem and most of the Holy Land in 1187. ...
The Crusades
... volunteered for the crusade would be called crusaders, meaning that they took the cross of Jesus upon them. These crusaders were promised that they would receive eternal life if they died while fighting non-Christians. As a result of the rhetoric these Christians killed thousands of nonChristians, i ...
... volunteered for the crusade would be called crusaders, meaning that they took the cross of Jesus upon them. These crusaders were promised that they would receive eternal life if they died while fighting non-Christians. As a result of the rhetoric these Christians killed thousands of nonChristians, i ...
The Crusades - St John Brebeuf
... did not perceive this until they saw the Saracens jumping from the top of the wall. Seeing this, they joyfully ran to the city as quickly as they could, and helped the others pursue and kill the wicked enemy. Then some, both Arabs and Ethiopians, fled into the Tower of David; others shut themselves ...
... did not perceive this until they saw the Saracens jumping from the top of the wall. Seeing this, they joyfully ran to the city as quickly as they could, and helped the others pursue and kill the wicked enemy. Then some, both Arabs and Ethiopians, fled into the Tower of David; others shut themselves ...
NAME - Union Academy
... Section 3: Art and Culture of the Middle Ages Many writings of the Middle Ages dealt with religion. People wrote things such as the way people should live their lives to their own interpretation of the Holy Bible. Epics and romances were other popular writing choices of the day. These poems were pe ...
... Section 3: Art and Culture of the Middle Ages Many writings of the Middle Ages dealt with religion. People wrote things such as the way people should live their lives to their own interpretation of the Holy Bible. Epics and romances were other popular writing choices of the day. These poems were pe ...
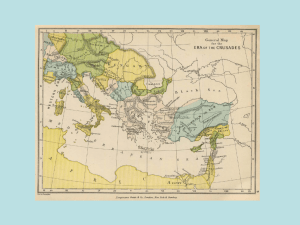
First Crusade

The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a number of crusades that attempted to capture the Holy Lands, called by Pope Urban II in 1095. It started as a widespread pilgrimage in western christendom and ended as a military expedition by Roman Catholic Europe to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquests of the Levant (632–661), ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem in 1099. It was launched on 27 November 1095 by Pope Urban II with the primary goal of responding to an appeal from Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos, who requested that western volunteers come to his aid and help to repel the invading Seljuq Turks from Anatolia. An additional goal soon became the principal objective—the Christian reconquest of the sacred city of Jerusalem and the Holy Land and the freeing of the Eastern Christians from Muslim rule.During the crusade, knights, peasants and serfs from many nations of Western Europe travelled over land and by sea, first to Constantinople and then on towards Jerusalem. The Crusaders arrived at Jerusalem, launched an assault on the city, and captured it in July 1099, massacring many of the city's Muslim, Christian, and Jewish inhabitants. They also established the crusader states of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, and the County of Edessa.The First Crusade was followed by the Second to the Ninth Crusades. It was also the first major step towards reopening international trade in the West since the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Because the First Crusade was largely concerned with Jerusalem, a city which had not been under Christian dominion for 461 years, and the crusader army had refused to return the land to the control of the Byzantine Empire, the status of the First Crusade as defensive or as aggressive in nature remains controversial.