Mouse Genetics (One Trait)
... 3. Observe: Drag two offspring into the Holding Cages. These mice are called hybrids because their parents had different traits. Click Clear, and then breed the two hybrids. What do you see now? ______________________________________________________ 4. Experiment: Turn on Show statistics. Click Bree ...
... 3. Observe: Drag two offspring into the Holding Cages. These mice are called hybrids because their parents had different traits. Click Clear, and then breed the two hybrids. What do you see now? ______________________________________________________ 4. Experiment: Turn on Show statistics. Click Bree ...
What is an Evolutionary Algorithm?
... integer representations Selection mechanism sensitive for converging populations with close fitness values Generational population model (step 5 in SGA repr. cycle) can be improved with explicit survivor selection ...
... integer representations Selection mechanism sensitive for converging populations with close fitness values Generational population model (step 5 in SGA repr. cycle) can be improved with explicit survivor selection ...
2. In guinea pigs, rough coat (R) is dominant over smooth coat (r
... 1. Color blindness is a recessive, sex-linked trait. A man with normal color vision marries a woman with normal color vision whose father is color blind. If they have a son, what is the chance that he will be color blind? 2. What percentage of the male offspring produced by a father with normal visi ...
... 1. Color blindness is a recessive, sex-linked trait. A man with normal color vision marries a woman with normal color vision whose father is color blind. If they have a son, what is the chance that he will be color blind? 2. What percentage of the male offspring produced by a father with normal visi ...
Concepts of Biology
... combination of unit factors was equally likely. The results of Mendel’s research can be explained in terms of probabilities, which are mathematical measures of likelihood. The probability of an event is calculated by the number of times the event occurs divided by the total number of opportunities f ...
... combination of unit factors was equally likely. The results of Mendel’s research can be explained in terms of probabilities, which are mathematical measures of likelihood. The probability of an event is calculated by the number of times the event occurs divided by the total number of opportunities f ...
KEY TERMS FOR Characteristics of Life
... Mendel’s Plant Breeding Experiments In the 1800’s, a scientist named Gregor Mendel applied an experimental approach to study inheritance His work eventually gave rise to genetics: the study of heredity. For seven years, Mendel bred pea plants and recorded inheritance patterns in the offspring. ...
... Mendel’s Plant Breeding Experiments In the 1800’s, a scientist named Gregor Mendel applied an experimental approach to study inheritance His work eventually gave rise to genetics: the study of heredity. For seven years, Mendel bred pea plants and recorded inheritance patterns in the offspring. ...
Chapter 2: Mendelian Inheritance
... 1. Mendel conducted crosses using two-factors to see if additional information regarding patterns of inheritance could be determined. These are now known as dihybrid crosses. 2. In a two-factor cross there are two possibilities of how the traits can be inherited (Figure 2.7) a. They may be linked to ...
... 1. Mendel conducted crosses using two-factors to see if additional information regarding patterns of inheritance could be determined. These are now known as dihybrid crosses. 2. In a two-factor cross there are two possibilities of how the traits can be inherited (Figure 2.7) a. They may be linked to ...
Chap 2 - Genetics
... sex steroids like testosterone have some effect on body size, especially during maturation phases of growth. Undoubtedly, many other genes that influence metabolism have small, but measurable effects on size. Additive effects within and between loci. The simplest additive genetic relationship occurs ...
... sex steroids like testosterone have some effect on body size, especially during maturation phases of growth. Undoubtedly, many other genes that influence metabolism have small, but measurable effects on size. Additive effects within and between loci. The simplest additive genetic relationship occurs ...
Genetics lectures 1
... When heterozygotes mate their offspring will have different phenotypes: If A is domia or the phenotype of nant to a, the two possible phenotypes will be the phenotype of a/a A/A A and A/a a. When we do breeding experiments it is important to know the genotypes of the parents. But as you can see from ...
... When heterozygotes mate their offspring will have different phenotypes: If A is domia or the phenotype of nant to a, the two possible phenotypes will be the phenotype of a/a A/A A and A/a a. When we do breeding experiments it is important to know the genotypes of the parents. But as you can see from ...
2014 Genetics Review
... _______________________ the branch of biology that studies how characteristics are transmitted from parent to offspring _______________________ the passing of characteristics from parent to offspring _______________________ The alternative choices for a gene (such as brown, green, or blue eyes) ____ ...
... _______________________ the branch of biology that studies how characteristics are transmitted from parent to offspring _______________________ the passing of characteristics from parent to offspring _______________________ The alternative choices for a gene (such as brown, green, or blue eyes) ____ ...
The Genetic Theory of Natural Selection
... frequencies (which we would expect for a novel mutation) change is very slow at the beginning, but speeds up as the number of heterozygotes increases. Once a high frequency of A is reached in the population per generation change slows down significantly, as only few mice with aa genotypes are ‘seen’ ...
... frequencies (which we would expect for a novel mutation) change is very slow at the beginning, but speeds up as the number of heterozygotes increases. Once a high frequency of A is reached in the population per generation change slows down significantly, as only few mice with aa genotypes are ‘seen’ ...
Supplementary Material for Autozygome Sequencing Expands the
... script in preparation for loading into our database. Essentially we extracted a slightly summarized view of the dataset removing non-autosomal alleles and redundant reports (by grouping on allele position and mutation type). We also anchored the variant calls to the reference genome allele and calcu ...
... script in preparation for loading into our database. Essentially we extracted a slightly summarized view of the dataset removing non-autosomal alleles and redundant reports (by grouping on allele position and mutation type). We also anchored the variant calls to the reference genome allele and calcu ...
Bio 6 – Principles of Genetic Inheritance Lab Overview
... (imagine if you could simply have children identical to yourself, no partner necessary), it has one extremely significant shortcoming: NO genetic diversity. For some species asexual reproduction works quite well, however for most plants and animals (including humans) this just won’t cut it, genetic ...
... (imagine if you could simply have children identical to yourself, no partner necessary), it has one extremely significant shortcoming: NO genetic diversity. For some species asexual reproduction works quite well, however for most plants and animals (including humans) this just won’t cut it, genetic ...
Practice with Punnett Squares
... 5. In mice the ability to run normally is a dominant trait. The recessive trait causes mice to run in circles (geneticists call these ‘waltzing’ mice). Determine the probability of each genotype and each phenotype of the potential offspring when a male heterozygous normal mouse mates with a female h ...
... 5. In mice the ability to run normally is a dominant trait. The recessive trait causes mice to run in circles (geneticists call these ‘waltzing’ mice). Determine the probability of each genotype and each phenotype of the potential offspring when a male heterozygous normal mouse mates with a female h ...
Test Information Sheet
... 5-34 repeats, premutation (mutable normal) alleles have 35-49 repeats, and disease alleles have greater than 50 repeats (Martorell et al., 2001). The clinical subtypes associated with disease alleles fall within a spectrum that is loosely based on CTG repeat number, where the mildest, latest onset f ...
... 5-34 repeats, premutation (mutable normal) alleles have 35-49 repeats, and disease alleles have greater than 50 repeats (Martorell et al., 2001). The clinical subtypes associated with disease alleles fall within a spectrum that is loosely based on CTG repeat number, where the mildest, latest onset f ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... A common misconception is that individuals evolve. While individuals may have favorable and heritable traits that are advantageous for survival and reproduction, the impact of selection is only apparent in the changes in phenotypes and genotypes observed in the population over time. The study of pop ...
... A common misconception is that individuals evolve. While individuals may have favorable and heritable traits that are advantageous for survival and reproduction, the impact of selection is only apparent in the changes in phenotypes and genotypes observed in the population over time. The study of pop ...
Mendelian Genetics
... Code the alleles and identify which is dominant/recessive Determine parental (or given) genotypes Determine parental (or given) gametes Draw Punnett square Re-read problem to be sure you are answering the ...
... Code the alleles and identify which is dominant/recessive Determine parental (or given) genotypes Determine parental (or given) gametes Draw Punnett square Re-read problem to be sure you are answering the ...
introduction to genetics
... Meiosis Chromosomes Forming gametes haploid and diploid cells Haploid having one copy of each chromosome Diploid having two copies of each chromosome ...
... Meiosis Chromosomes Forming gametes haploid and diploid cells Haploid having one copy of each chromosome Diploid having two copies of each chromosome ...
Bloodline- A Human Genetics Case
... Lisa Keller both look into their family backgrounds. • Factor V Leiden can exhibit incomplete dominance. It is possible that either parent could carry the dominant allele and have not exhibited symptoms, so they may wish to be tested. They wish to look at their family pedigrees to narrow down who is ...
... Lisa Keller both look into their family backgrounds. • Factor V Leiden can exhibit incomplete dominance. It is possible that either parent could carry the dominant allele and have not exhibited symptoms, so they may wish to be tested. They wish to look at their family pedigrees to narrow down who is ...
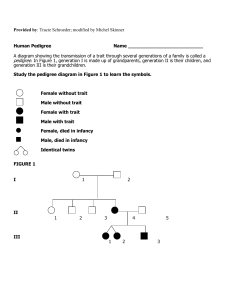
Pedigrees - sciencewithskinner
... 2. Are individuals 1 and 2 in generation I homozygous or heterozygous? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. What gender is individual 3 of generation II? ____________________ 4. What relationship do individuals 6 & 7 of generation II share? _____ ...
... 2. Are individuals 1 and 2 in generation I homozygous or heterozygous? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. What gender is individual 3 of generation II? ____________________ 4. What relationship do individuals 6 & 7 of generation II share? _____ ...
Chapter 23 Population Genetics
... After the MN blood groups have been determined for a sample, allele frequencies can be calculated. © John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Allele : It is the alternative form of a gene for a character producing different effects. ...
... After the MN blood groups have been determined for a sample, allele frequencies can be calculated. © John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Allele : It is the alternative form of a gene for a character producing different effects. ...
Learn How to Solve Punnet Squares
... Sometimes this already done in the question for you. If the question says "Cross two organisms with the following genotype: Tt & tt", it's all right there in the question already. More likely is a question like this: "Cross a short pea plant with one that is heterozygous for tallness". Here, you hav ...
... Sometimes this already done in the question for you. If the question says "Cross two organisms with the following genotype: Tt & tt", it's all right there in the question already. More likely is a question like this: "Cross a short pea plant with one that is heterozygous for tallness". Here, you hav ...
Composite Beef Breeds - FSA3057 - University of Arkansas Division
... individual is not exactly intermediate between the two homozygotes. Epistasis is the interaction between different loci. When composite breeds are formed, some loss of heterosis occurs as the crossbred parents are pro duced and mated. Once the composite is completely established and random (closed ...
... individual is not exactly intermediate between the two homozygotes. Epistasis is the interaction between different loci. When composite breeds are formed, some loss of heterosis occurs as the crossbred parents are pro duced and mated. Once the composite is completely established and random (closed ...
Mouse Genetics (1 Trait)
... *****Switch roles with your partner. The recorder now works the simulation and the person who was on the computer now records. 11. Breed a black parent mouse with one of your offspring from the black parent-white parent cross (these mice should be in the bottom right cages). What are the genotypes o ...
... *****Switch roles with your partner. The recorder now works the simulation and the person who was on the computer now records. 11. Breed a black parent mouse with one of your offspring from the black parent-white parent cross (these mice should be in the bottom right cages). What are the genotypes o ...