Honors Biology II Chapter 14 Genetics Guided Notes
... features, or characters (such as flower color); character variants (such as purple or white flowers) are called traits – Mating can be controlled – Each flower has sperm-producing organs (stamens) and an egg-producing organ (carpel) – Cross-pollination (fertilization between different plants) involv ...
... features, or characters (such as flower color); character variants (such as purple or white flowers) are called traits – Mating can be controlled – Each flower has sperm-producing organs (stamens) and an egg-producing organ (carpel) – Cross-pollination (fertilization between different plants) involv ...
For those mutants where the enhancement bred true, if
... +/ +; Df(3R)p13, e, */ TM6B were selected by the presence of the ebony marker, and the absence of the p[w+] marker, and used to create independent stocks. Those mutants which segregated with the X chromosome were discarded. ...
... +/ +; Df(3R)p13, e, */ TM6B were selected by the presence of the ebony marker, and the absence of the p[w+] marker, and used to create independent stocks. Those mutants which segregated with the X chromosome were discarded. ...
Genetics packet_simple
... 21. In shorthorn cattle, when a red bull (CRCR) is crossed with a white cow (CWCW), the offspring are roan (intermingled red and white hairs). How could a rancher establish a herd of roan cattle? 22. In cows, black is incompletely dominant to white, producing dark gray offspring when crossed. Cross ...
... 21. In shorthorn cattle, when a red bull (CRCR) is crossed with a white cow (CWCW), the offspring are roan (intermingled red and white hairs). How could a rancher establish a herd of roan cattle? 22. In cows, black is incompletely dominant to white, producing dark gray offspring when crossed. Cross ...
Crosses - Intermediate School Biology
... 11. Hair length in rabbits is a genetically inherited characteristic; the possible alleles are short-haired or long-haired. When a pure-breeding long haired rabbit was crossed with a pure breeding short haired rabbit, all the offspring were short-haired. (i) Show, by means of a cross, how these offs ...
... 11. Hair length in rabbits is a genetically inherited characteristic; the possible alleles are short-haired or long-haired. When a pure-breeding long haired rabbit was crossed with a pure breeding short haired rabbit, all the offspring were short-haired. (i) Show, by means of a cross, how these offs ...
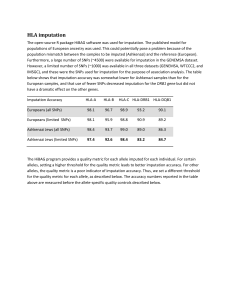
HLA imputation - BioMed Central
... Due to inherent differences between allele frequencies in the Ashkenazi and European populations, certain alleles of certain genes are over-called by imputation in Ashkenazi. These alleles were removed before association analysis was performed. For HLA-A plot below, the height of the colored bars o ...
... Due to inherent differences between allele frequencies in the Ashkenazi and European populations, certain alleles of certain genes are over-called by imputation in Ashkenazi. These alleles were removed before association analysis was performed. For HLA-A plot below, the height of the colored bars o ...
VI. The relationship between genotype and phenotype is rarely simple
... In 1857, Mendel was living in an Augustinian monastery, where he bred garden peas in the abbey garden. He probably chose garden peas as his experimental organisms because: • They were available in many easily distinguishable varieties. • Strict control over mating was possible to ensure the parentag ...
... In 1857, Mendel was living in an Augustinian monastery, where he bred garden peas in the abbey garden. He probably chose garden peas as his experimental organisms because: • They were available in many easily distinguishable varieties. • Strict control over mating was possible to ensure the parentag ...
PATTERNS OF HEREDITY AND HUMAN GENETICS CHapter 12
... • Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked traits. • The alleles for sex-linked traits are written as superscripts of the X or Y chromosomes. • Because the X and Y chromosomes are not homologous, the Y chromosome has no corresponding allele to one on the X chromoso ...
... • Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked traits. • The alleles for sex-linked traits are written as superscripts of the X or Y chromosomes. • Because the X and Y chromosomes are not homologous, the Y chromosome has no corresponding allele to one on the X chromoso ...
3.14 C: Genetic Disorders Quiz PROCTOR VERSION
... to her sons in generation II, and they pass the trait on to their sons in generation III. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that sex-linked, recessive traits are generally passed from mother to son and are mostly observed in males, but does not understand that the ...
... to her sons in generation II, and they pass the trait on to their sons in generation III. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that sex-linked, recessive traits are generally passed from mother to son and are mostly observed in males, but does not understand that the ...
Liberating genetic variance through sex
... result from a constant selective pressure, whether the populations are at equilibrium, changing in response to the selective pressure, or held at a balance between selection and mutation. At first, we would expect that the recombination load would squelch any mutation that increases the frequency of ...
... result from a constant selective pressure, whether the populations are at equilibrium, changing in response to the selective pressure, or held at a balance between selection and mutation. At first, we would expect that the recombination load would squelch any mutation that increases the frequency of ...
appendix 1 – simple nomenclature
... left. It was first shown on page 2; cross the outer two plants) you will get a heterozygote (the middle plant). If we name the gene after the mutation (a is the first letter in “albino” ...
... left. It was first shown on page 2; cross the outer two plants) you will get a heterozygote (the middle plant). If we name the gene after the mutation (a is the first letter in “albino” ...
Population Genetics
... probability of not being passed on; in small populations this probability is significant – Founder effect - A small number of individuals from a large population populate an area. Only the alleles of the few founders are represented in their descendants, not the entire population from which they cam ...
... probability of not being passed on; in small populations this probability is significant – Founder effect - A small number of individuals from a large population populate an area. Only the alleles of the few founders are represented in their descendants, not the entire population from which they cam ...
Gene mapping - Australian Mathematical Sciences Institute
... by the three genotypes (A 1 A 1 ), (A 1 A 2 ) and (A 2 A 2 ).The imporance of this is that evolution through natural selection can occur only if, within the population, there is variation upon which selective forces can act. This obviously depends on the population satisfying conditions some of whic ...
... by the three genotypes (A 1 A 1 ), (A 1 A 2 ) and (A 2 A 2 ).The imporance of this is that evolution through natural selection can occur only if, within the population, there is variation upon which selective forces can act. This obviously depends on the population satisfying conditions some of whic ...
Jeopardy - Cloudfront.net
... dominance. Red is the dominant color, while White is the recessive color. If the offspring Is heterozygous, what color will its petals be? ...
... dominance. Red is the dominant color, while White is the recessive color. If the offspring Is heterozygous, what color will its petals be? ...
Teacher`s Pack
... ÊÊ Use of the chi-squared test to compare the goodness of fit of observed phenotypic ratios with expected ratios. 3.7.2 Populations: ÊÊ A population as a group of organisms of the same species occupying a particular space at a particular time that can potentially interbreed. ÊÊ The concepts of gene ...
... ÊÊ Use of the chi-squared test to compare the goodness of fit of observed phenotypic ratios with expected ratios. 3.7.2 Populations: ÊÊ A population as a group of organisms of the same species occupying a particular space at a particular time that can potentially interbreed. ÊÊ The concepts of gene ...
Population Genetics
... Fixation of an allele: An allele must increase in frequency and ultimately become fixed in the population (all individuals have the same allele). Fitness: of a genotype, a measure of individual’s ability to survive and reproduce (it is rather relative with respect to other individuals). ...
... Fixation of an allele: An allele must increase in frequency and ultimately become fixed in the population (all individuals have the same allele). Fitness: of a genotype, a measure of individual’s ability to survive and reproduce (it is rather relative with respect to other individuals). ...
1 Human Inheritance - Northside Middle School
... alleles. There are four main blood types—A, B, AB, and O. Three alleles control the inheritance of blood types. The allele for blood type A and the allele for blood type B are codominant. The allele for blood type A is written as IA. The allele for blood type B is written IB. The allele for blood ty ...
... alleles. There are four main blood types—A, B, AB, and O. Three alleles control the inheritance of blood types. The allele for blood type A and the allele for blood type B are codominant. The allele for blood type A is written as IA. The allele for blood type B is written IB. The allele for blood ty ...
HARDY WEINBERG PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR DAY 1 1. If 98 out
... (b) Now that you have q, you can solve for p. Remember there are only two alleles in the population, so if you add the frequency of the two alleles, you have accounted for all possibilities and it must equal ...
... (b) Now that you have q, you can solve for p. Remember there are only two alleles in the population, so if you add the frequency of the two alleles, you have accounted for all possibilities and it must equal ...
Sex and Deleterious Mutations
... maximum advantage of recombination occurs for an intermediate value of the deleterious effect of mutations. Furthermore we show that the conditions under which the biggest advantage of sex is achieved are those that produce the fastest fitness decline in the corresponding asexual population and are ...
... maximum advantage of recombination occurs for an intermediate value of the deleterious effect of mutations. Furthermore we show that the conditions under which the biggest advantage of sex is achieved are those that produce the fastest fitness decline in the corresponding asexual population and are ...
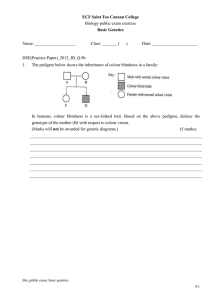
public exam_basic genetics_R1
... Individual 1 possesses straight little fingers, she must be homozygous recessive and pass an allele for straight little fingers to individual 4. Individual 4 possesses bent little fingers, she must have at least one allele for bent ...
... Individual 1 possesses straight little fingers, she must be homozygous recessive and pass an allele for straight little fingers to individual 4. Individual 4 possesses bent little fingers, she must have at least one allele for bent ...
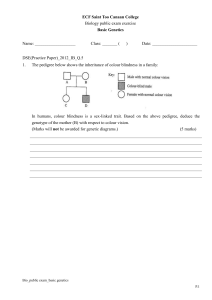
public exam_basic genetics_R1
... Individual 1 possesses straight little fingers, she must be homozygous recessive and pass an allele for straight little fingers to individual 4. Individual 4 possesses bent little fingers, she must have at least one allele for bent ...
... Individual 1 possesses straight little fingers, she must be homozygous recessive and pass an allele for straight little fingers to individual 4. Individual 4 possesses bent little fingers, she must have at least one allele for bent ...
6.2 Mendelian Genetics: When the Role of Genes Is Clear
... – those traits influence by more than one gene ...
... – those traits influence by more than one gene ...
Extensions to Mendel`s Law
... dominant trait Children with heritable PKU can receive a protective diet Genetic predisposition to cardiovascular disease can be influenced by diet and exercise Genetic predisposition to lung cancer is strongly affected by ...
... dominant trait Children with heritable PKU can receive a protective diet Genetic predisposition to cardiovascular disease can be influenced by diet and exercise Genetic predisposition to lung cancer is strongly affected by ...