Genetics Notes
... • Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. • Probability predicts what will occur, and is not always necessarily what will occur. • Example: if you toss a coin there is a fifty percent chance the coin will land on heads, and fifty percent the coin will land on tails. ...
... • Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. • Probability predicts what will occur, and is not always necessarily what will occur. • Example: if you toss a coin there is a fifty percent chance the coin will land on heads, and fifty percent the coin will land on tails. ...
Genetics Jeopardy
... Punnett Squares - 300 answer Using the key, if you were to cross a true breeding tall plant with a true breeding short plant give the genotypic and phenotypic ratio for the 4 offspring ...
... Punnett Squares - 300 answer Using the key, if you were to cross a true breeding tall plant with a true breeding short plant give the genotypic and phenotypic ratio for the 4 offspring ...
A Laboratory on Population Genetics and Evolution
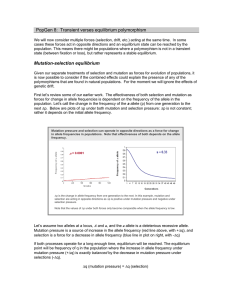
... 2 for observing a table of the allele frequencies from the most recent run. Whenever you observe “(α ≤ .05)” next to a generation number, statistically significant differences exist between the observed allele frequencies and the initial allele frequencies. This is a good criterion for deciding when ...
... 2 for observing a table of the allele frequencies from the most recent run. Whenever you observe “(α ≤ .05)” next to a generation number, statistically significant differences exist between the observed allele frequencies and the initial allele frequencies. This is a good criterion for deciding when ...
E-Halliburton chapter 13
... component) on phenotypic value we see that an individual's estimated breeding value is the product of its phenotypic value and the heritability: A(expected) = h2P where breeding values and phenotypic values are both reckoned as deviations from the population mean. The heritability enters into almost ...
... component) on phenotypic value we see that an individual's estimated breeding value is the product of its phenotypic value and the heritability: A(expected) = h2P where breeding values and phenotypic values are both reckoned as deviations from the population mean. The heritability enters into almost ...
Slide 1
... polymorphisms used in the association model explain the observed linkage or whether other polymorphisms in that region are expected to be of influence QTDT: simple, quick, straigtforward, but not so flexible in terms of models Mx: can be considered less simple, but highly flexible ...
... polymorphisms used in the association model explain the observed linkage or whether other polymorphisms in that region are expected to be of influence QTDT: simple, quick, straigtforward, but not so flexible in terms of models Mx: can be considered less simple, but highly flexible ...
LECTURE 4: PEDIGREE ANALYSIS Reading
... -Requires the chance union of unrelated carriers (heterozygotes). Rare recessive traits are more likely to show up in a pedigree when spouses are related to one another (because relative share alleles due to their common lineage). Many of the classical human genetic studies have been dependent upon ...
... -Requires the chance union of unrelated carriers (heterozygotes). Rare recessive traits are more likely to show up in a pedigree when spouses are related to one another (because relative share alleles due to their common lineage). Many of the classical human genetic studies have been dependent upon ...
Monohybrid Crosses - GaryTurnerScience
... homozygous wire-haired dog with a smooth-haired dog, what will be the phenotype and genotype of the offspring (F1 generation)? 18. What would be the expected offspring if two dogs from the F1 generation were crossed? 19. Use a Punnett square to solve a cross between two parents that both have the ge ...
... homozygous wire-haired dog with a smooth-haired dog, what will be the phenotype and genotype of the offspring (F1 generation)? 18. What would be the expected offspring if two dogs from the F1 generation were crossed? 19. Use a Punnett square to solve a cross between two parents that both have the ge ...
Exam II Notes Mendel
... Incomplete dominance: in this case, the presence of a single allele to code for a particular protein (enzyme) is insufficient to produce the full trait. Ex. In 4 o’clocks and snapdragons, RR = red, rr = white, and Rr = pink! Pleiotropic: when a single gene determines more than one phenotype for an o ...
... Incomplete dominance: in this case, the presence of a single allele to code for a particular protein (enzyme) is insufficient to produce the full trait. Ex. In 4 o’clocks and snapdragons, RR = red, rr = white, and Rr = pink! Pleiotropic: when a single gene determines more than one phenotype for an o ...
b) Phenotypic ratio: 2:2
... Tt b) Phenotypic ratio: 3:1 c) Probability of having a homozygous tall plant: ¼ = .25 = 25% ...
... Tt b) Phenotypic ratio: 3:1 c) Probability of having a homozygous tall plant: ¼ = .25 = 25% ...
Week 8 Lab: SNP Detection, SNP Discussion
... A host shift refers to movement of a parasitic species from one host to a new species of host (in our case, from one species of goldenrod to the other). A host race is a group of organisms (e.g. gall flies) which is found on one type of host (e.g. S. altissima); the term does not go so far as to imp ...
... A host shift refers to movement of a parasitic species from one host to a new species of host (in our case, from one species of goldenrod to the other). A host race is a group of organisms (e.g. gall flies) which is found on one type of host (e.g. S. altissima); the term does not go so far as to imp ...
Warm-up - Tedeschi
... - A dominant trait is one that is seen while a recessive trait is hidden. - An example of a dominant trait is brown eyes and blue eyes are recessive. ...
... - A dominant trait is one that is seen while a recessive trait is hidden. - An example of a dominant trait is brown eyes and blue eyes are recessive. ...
Document
... Mendel then crossed these second generation tall pea plants and ended up with 1 out 4 being small. ...
... Mendel then crossed these second generation tall pea plants and ended up with 1 out 4 being small. ...
Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity
... fatal/lethal. It does not occur until between the ages of ...
... fatal/lethal. It does not occur until between the ages of ...
Tribbles WS - TeacherWeb
... Genetic Patterns in Tribbles Many traits, such as the coats of mammals, are produced by the interaction of many genes. In this activity you will study the genetics of a fictional animal as a model for the genetics of more complex real animals. Tribbles are animals that are familiar to most fans of s ...
... Genetic Patterns in Tribbles Many traits, such as the coats of mammals, are produced by the interaction of many genes. In this activity you will study the genetics of a fictional animal as a model for the genetics of more complex real animals. Tribbles are animals that are familiar to most fans of s ...
Notes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... By actively pollinating one pure plant (a plant that always produced the same characteristics in the offspring) with a different pure plant, he could see how traits were expressed in the offspring of the cross-pollination. Early hypothesis suggested that if you crossed two different traits, the re ...
... By actively pollinating one pure plant (a plant that always produced the same characteristics in the offspring) with a different pure plant, he could see how traits were expressed in the offspring of the cross-pollination. Early hypothesis suggested that if you crossed two different traits, the re ...
Punnet squares lecture rev 1-27
... • and pedigrees are typically traced to determine the probability of passing along an hereditary disease. • Plants are now designed in laboratories to exhibit desired characteristics. • The practical results of Mendel's research has not only changed the way we perceive the world, but also the way we ...
... • and pedigrees are typically traced to determine the probability of passing along an hereditary disease. • Plants are now designed in laboratories to exhibit desired characteristics. • The practical results of Mendel's research has not only changed the way we perceive the world, but also the way we ...
Genetic concepts lab
... Living things contain many genetic characteristics and it is therefore logical to want to design experiments which involve more than one at a time. However, the problem with studying multiple variables is tracing causal factors. In the future, computers may simplify the problem and allow experiments ...
... Living things contain many genetic characteristics and it is therefore logical to want to design experiments which involve more than one at a time. However, the problem with studying multiple variables is tracing causal factors. In the future, computers may simplify the problem and allow experiments ...
Document
... • Narrow-sense heritability can be used to predict changes in the population mean in with individual selection h2 = (M’ - M)/(M* - M) • In general, h2 < H2 . They are equal only when the alleles affecting the trait are additive in their effects = heterozygous phenotype is exactly intermediate betwee ...
... • Narrow-sense heritability can be used to predict changes in the population mean in with individual selection h2 = (M’ - M)/(M* - M) • In general, h2 < H2 . They are equal only when the alleles affecting the trait are additive in their effects = heterozygous phenotype is exactly intermediate betwee ...
Genomic Context and Molecular Evolution
... population are destined for ultimate elimination by selection. A beneficial mutation that arises in a genetic background with one or more mutations will thus also be eliminated, unless its own effect on fitness is large enough to enable it to overcome their deleterious effects (as was tacitly assume ...
... population are destined for ultimate elimination by selection. A beneficial mutation that arises in a genetic background with one or more mutations will thus also be eliminated, unless its own effect on fitness is large enough to enable it to overcome their deleterious effects (as was tacitly assume ...
UNIT V – MENDELIAN GENETICS
... o Vast majority of proteins are enzymes o Abnormal allele → Defective enzyme If the enzyme produced by the normal allele is present in sufficient quantities to catalyze necessary reactions, No noticeable effect on phenotype Defective allele is classified as recessive If the lack of normal enzy ...
... o Vast majority of proteins are enzymes o Abnormal allele → Defective enzyme If the enzyme produced by the normal allele is present in sufficient quantities to catalyze necessary reactions, No noticeable effect on phenotype Defective allele is classified as recessive If the lack of normal enzy ...