Double Muscle: Genotype and Probability
... 4. Did the number of times you tossed the coin have an impact on the mathematical outcome of your coin toss experiment? *Hint: Think about how often you expect to flip a heads or a tails. If you flip the coin twice, will you get what you expect? As you flip the coin more and more times, do you t ...
... 4. Did the number of times you tossed the coin have an impact on the mathematical outcome of your coin toss experiment? *Hint: Think about how often you expect to flip a heads or a tails. If you flip the coin twice, will you get what you expect? As you flip the coin more and more times, do you t ...
Chapter 23 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... • Mutation rates are low in animals and plants • The average is about one mutation in every 100,000 genes per generation – lower in prokaryotes (but short generations so mutations accumulate quickly) – higher in viruses (and short generations so mutations really accumulate quickly) • RNA ...
... • Mutation rates are low in animals and plants • The average is about one mutation in every 100,000 genes per generation – lower in prokaryotes (but short generations so mutations accumulate quickly) – higher in viruses (and short generations so mutations really accumulate quickly) • RNA ...
Gregor Mendal and Genetics
... phenotypes of the offspring resembled only one of the parent plants with respect to that trait. So, he said to himself, "Greg, there is a factor that makes pea plants tall, and another factor that makes pea plants short. Furthermore Greg ol' boy, when the factors are mixed, the tall factor seems to ...
... phenotypes of the offspring resembled only one of the parent plants with respect to that trait. So, he said to himself, "Greg, there is a factor that makes pea plants tall, and another factor that makes pea plants short. Furthermore Greg ol' boy, when the factors are mixed, the tall factor seems to ...
Heredity Packe
... Objective 12: Describe how blood types are inherited and why they must be considered when doing transfusions (9.12). -It’s important to realize that most genes actually exist in MORE than two allelic forms. An example of this occurs with human blood types. You have two alleles – out of a possible TH ...
... Objective 12: Describe how blood types are inherited and why they must be considered when doing transfusions (9.12). -It’s important to realize that most genes actually exist in MORE than two allelic forms. An example of this occurs with human blood types. You have two alleles – out of a possible TH ...
full text pdf
... (HLA) alleles. The most-common susceptibility haplotypes are DQA1*0301-DQB1*0302 and DQA1*0501-DQB1*0201. Less-common haplotypes such as DQA1*0401-DQBl*0402 and DQA1*0l0lDQB1*0501 are associated with high risk for diabetes; however, large study populations are needed to analyze their effect. The DQA ...
... (HLA) alleles. The most-common susceptibility haplotypes are DQA1*0301-DQB1*0302 and DQA1*0501-DQB1*0201. Less-common haplotypes such as DQA1*0401-DQBl*0402 and DQA1*0l0lDQB1*0501 are associated with high risk for diabetes; however, large study populations are needed to analyze their effect. The DQA ...
LAB 9 – Principles of Genetic Inheritance
... (imagine if you could simply have children identical to yourself, no partner necessary!), it has one extremely significant shortcoming: NO genetic diversity! For some species asexual reproduction works quite well, however for most plants and animals (including humans) this just won’t cut it, genetic ...
... (imagine if you could simply have children identical to yourself, no partner necessary!), it has one extremely significant shortcoming: NO genetic diversity! For some species asexual reproduction works quite well, however for most plants and animals (including humans) this just won’t cut it, genetic ...
Genetic Equilibrium: Human Diversity
... Once again, you will be working in pairs and testing the Hardy-Weinberg Principle by simulating a population using beans, beads, or similar materials. However, with this new experiment, you will be introducing one conditional change—using a small population rather than a large one—in the hopes of si ...
... Once again, you will be working in pairs and testing the Hardy-Weinberg Principle by simulating a population using beans, beads, or similar materials. However, with this new experiment, you will be introducing one conditional change—using a small population rather than a large one—in the hopes of si ...
Understanding Genetics
... C- Zooming out further to see multiple twists of the DNA helix. The cattle genome has approximate 3 billion DNA bases, the same number as found in the human genome. To help store all this information DNA are packaged in chromosomes. These chromosomes can be broken down into 3 categories: autosomes, ...
... C- Zooming out further to see multiple twists of the DNA helix. The cattle genome has approximate 3 billion DNA bases, the same number as found in the human genome. To help store all this information DNA are packaged in chromosomes. These chromosomes can be broken down into 3 categories: autosomes, ...
Peas in a Pod: Expression of Undesirable Genes in Ferrets
... of these ferrets neutered. In some cases, the lineage of seemingly unrelated ferrets with a common disorder can be traced to find a common ancestor. All breeder animals with this ancestor should be neutered. ...
... of these ferrets neutered. In some cases, the lineage of seemingly unrelated ferrets with a common disorder can be traced to find a common ancestor. All breeder animals with this ancestor should be neutered. ...
is the population size of a species relevant to its evolution?
... (1973, 1976, 1992) has shown that if amino acid mutations are slightly deleterious, then protein variation should be insensitive to population size. However, her theory does not easily account for the insensitivity of the rate of protein evolution to N. Cherry (1998), building on the work of Hartl e ...
... (1973, 1976, 1992) has shown that if amino acid mutations are slightly deleterious, then protein variation should be insensitive to population size. However, her theory does not easily account for the insensitivity of the rate of protein evolution to N. Cherry (1998), building on the work of Hartl e ...
LAB 1: Scientific Method/Tools of Scientific Inquiry
... quite convenient (imagine if you could simply have children identical to yourself, no partner necessary!), it has one extremely significant shortcoming: NO genetic diversity! For some species asexual reproduction works quite well, however for most plants and animals (including humans) this just won’ ...
... quite convenient (imagine if you could simply have children identical to yourself, no partner necessary!), it has one extremely significant shortcoming: NO genetic diversity! For some species asexual reproduction works quite well, however for most plants and animals (including humans) this just won’ ...
Genetics PP notes 2015
... An X chromosome paired with a Y chromosome (XY) produces a ___________ Since only a male can produce a gamete bearing a Y chromosome, the __________________determines the _________of the child Note: the X chromosome contains additional genetic information that the Y chromosome does not have, therefo ...
... An X chromosome paired with a Y chromosome (XY) produces a ___________ Since only a male can produce a gamete bearing a Y chromosome, the __________________determines the _________of the child Note: the X chromosome contains additional genetic information that the Y chromosome does not have, therefo ...
Chapter 8 Evolution at multiple loci: linkage and
... Assumption 1 (mode of reproduction does not affect number of offspring she can produce) is violated in species where males helps females (humans, birds, many mammals, some fish). However, not likely a general explanation because in most species male does not help. ...
... Assumption 1 (mode of reproduction does not affect number of offspring she can produce) is violated in species where males helps females (humans, birds, many mammals, some fish). However, not likely a general explanation because in most species male does not help. ...
I-1 to I-7
... 1) Straightforward-but-tedious way: Consider all possible matings. 2) Easier way – use intuition : random mating = random union of haploid gametes. – if intuition is correct, then: frequencies of A and a among the gametes produced = frequencies in mating adults: p and q = 1– p . As with the haploid ...
... 1) Straightforward-but-tedious way: Consider all possible matings. 2) Easier way – use intuition : random mating = random union of haploid gametes. – if intuition is correct, then: frequencies of A and a among the gametes produced = frequencies in mating adults: p and q = 1– p . As with the haploid ...
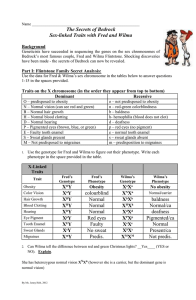
Part I: Flintstone Family Secret Analysis
... Is Fred lying when he tells Wilma that he thinks her hair is a gorgeous shade of red? ___Yes__ (YES or NO). Explain. Her genotype contains two recessive alleles that expresses baldness therefore he may like her wig colour but she would not have a hair colour to express if she is bald ...
... Is Fred lying when he tells Wilma that he thinks her hair is a gorgeous shade of red? ___Yes__ (YES or NO). Explain. Her genotype contains two recessive alleles that expresses baldness therefore he may like her wig colour but she would not have a hair colour to express if she is bald ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... selection at this stage would affect which genes get passed on • Once an individual is done reproducing, selection becomes less effective… this becomes even more true after individuals are done caring for offspring • What happens to individuals after reproduction and childcare will not affect allele ...
... selection at this stage would affect which genes get passed on • Once an individual is done reproducing, selection becomes less effective… this becomes even more true after individuals are done caring for offspring • What happens to individuals after reproduction and childcare will not affect allele ...
Key area 2: Plant and animal breeding by manipulation of heredity
... This is due to the accumulation of homozygous recessive alleles which can be deleterious (harmful). This appears as a decline in vigour, size, fertility and yield of the plant or animal. ...
... This is due to the accumulation of homozygous recessive alleles which can be deleterious (harmful). This appears as a decline in vigour, size, fertility and yield of the plant or animal. ...
Genetics Project: Design a Species
... Describe and draw an example of each of the traits on the list, showing all genotypes and phenotypes for each. This is your key. (see smiley face sample) Some reminders: a. Single Allele / Complete Dominance: one allele is dominant and masks the recessive allele. Only 2 possible phenotypes Show TWO ...
... Describe and draw an example of each of the traits on the list, showing all genotypes and phenotypes for each. This is your key. (see smiley face sample) Some reminders: a. Single Allele / Complete Dominance: one allele is dominant and masks the recessive allele. Only 2 possible phenotypes Show TWO ...
Genetics Tutorial
... The gene for flower color has two varieties: purple and white. These alternative forms of a gene are called alleles. The purple flower has two alleles that determine it's flower color. One allele came from each parent. We use capital letters to abbreviate the two dominant alleles (PP). The white flo ...
... The gene for flower color has two varieties: purple and white. These alternative forms of a gene are called alleles. The purple flower has two alleles that determine it's flower color. One allele came from each parent. We use capital letters to abbreviate the two dominant alleles (PP). The white flo ...