Lecture 4
... Mendel concluded that the factors for different characteristics are NOT connected. Mendel analyzed each trait for separate inheritance as if the other trait were not present. The 3:1 ratio was seen separately and was in accordance with the Principle of Segregation. The segregation of S and s alleles ...
... Mendel concluded that the factors for different characteristics are NOT connected. Mendel analyzed each trait for separate inheritance as if the other trait were not present. The 3:1 ratio was seen separately and was in accordance with the Principle of Segregation. The segregation of S and s alleles ...
Ineritance Packet inheritancepacket
... Punnett squares will help you predict the chances or probability that a child (or offspring of any organism) will be born with a particular trait IF you know the genetic make-up of the parents. Example Punnet Square: What are the chances that the children of Joe (who is heterozygous for a widow’s pe ...
... Punnett squares will help you predict the chances or probability that a child (or offspring of any organism) will be born with a particular trait IF you know the genetic make-up of the parents. Example Punnet Square: What are the chances that the children of Joe (who is heterozygous for a widow’s pe ...
punnet square practice - Hamilton Local Schools
... SpongeBob and SpongeSuzie had children. What is Spongbob’s genotype? _____________ What is Spongesuzie’s genotype? ___________ What are the chances a child will have a square shape? ________ out of 4 OR _______% What are the chances a child will have a round shape? ________ out of 4 OR _______% ...
... SpongeBob and SpongeSuzie had children. What is Spongbob’s genotype? _____________ What is Spongesuzie’s genotype? ___________ What are the chances a child will have a square shape? ________ out of 4 OR _______% What are the chances a child will have a round shape? ________ out of 4 OR _______% ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems Chromosomes, Karyotyping and Sex
... dominant or recessive, and whether the trait is autosomal or sex-linked. The double line indicates a marriage between two related individuals. Give specific evidence to support your conclusions. Dominant or Recessive? ...
... dominant or recessive, and whether the trait is autosomal or sex-linked. The double line indicates a marriage between two related individuals. Give specific evidence to support your conclusions. Dominant or Recessive? ...
M-Collate2 119..268
... Natural selection is de®ned as the differential reproduction of genetically distinct individuals (genotypes) within a population. Differential reproduction is caused by differences among individuals in such traits as mortality, fertility, fecundity, mating success and the viability of the offspring. ...
... Natural selection is de®ned as the differential reproduction of genetically distinct individuals (genotypes) within a population. Differential reproduction is caused by differences among individuals in such traits as mortality, fertility, fecundity, mating success and the viability of the offspring. ...
TT - Lyndhurst Schools
... mathematical probability of inheriting a specific trait was invented by an early 20th ...
... mathematical probability of inheriting a specific trait was invented by an early 20th ...
Genetics Jeopardy
... Two short-tailed (Manx) cats are bred together. They produce three kittens with long tails, five short tails, and two without any tails. From these results, how do you think tail length in these cats are inherited? Show the genotypes for both the parents and the offspring to support your answer. ...
... Two short-tailed (Manx) cats are bred together. They produce three kittens with long tails, five short tails, and two without any tails. From these results, how do you think tail length in these cats are inherited? Show the genotypes for both the parents and the offspring to support your answer. ...
Document
... Think It Over For most students, their results were slightly different from their predictions. The combined class data should be closer to the expected ratio of one “heads” to one “tails.” Students might infer that the difference is due to chance or that the more coin tosses they make, the closer th ...
... Think It Over For most students, their results were slightly different from their predictions. The combined class data should be closer to the expected ratio of one “heads” to one “tails.” Students might infer that the difference is due to chance or that the more coin tosses they make, the closer th ...
Chapter 1 - Online Open Genetics
... amino acids of a protein can be different if we compare Chapter 2 points out that organisms usually fall into different alleles of a gene and they may behave differentthe classes of being diploid or haploid. Humans and eu- ly – often one protein will “work better” than the other. karyotic genetic sy ...
... amino acids of a protein can be different if we compare Chapter 2 points out that organisms usually fall into different alleles of a gene and they may behave differentthe classes of being diploid or haploid. Humans and eu- ly – often one protein will “work better” than the other. karyotic genetic sy ...
Chapter 1
... 2.12.b – X linked recessive inheritance 2.12.c – I/1 X+Y I/2 XdX+ II/1 XdY II/2 XdX+ II/3 X+X+ III/1 XdX+ III/2 X+Y III/3 a III/4 XdY III/5 X+Y 2.13 – The probability is 0. Fathers give Y chromosomes to their sons 2.14 – In this large family we can see that Duchenne muscular dystrophy affected only ...
... 2.12.b – X linked recessive inheritance 2.12.c – I/1 X+Y I/2 XdX+ II/1 XdY II/2 XdX+ II/3 X+X+ III/1 XdX+ III/2 X+Y III/3 a III/4 XdY III/5 X+Y 2.13 – The probability is 0. Fathers give Y chromosomes to their sons 2.14 – In this large family we can see that Duchenne muscular dystrophy affected only ...
video slide - CARNES AP BIO
... • For example, the four phenotypes of the ABO blood group in humans are determined by three alleles for the enzyme (I) that attaches A or B carbohydrates to red blood cells: IA, IB, and i. • The enzyme encoded by the IA allele adds the A carbohydrate, whereas the enzyme encoded by the IB allele adds ...
... • For example, the four phenotypes of the ABO blood group in humans are determined by three alleles for the enzyme (I) that attaches A or B carbohydrates to red blood cells: IA, IB, and i. • The enzyme encoded by the IA allele adds the A carbohydrate, whereas the enzyme encoded by the IB allele adds ...
Exclusion of a Role of Hearing Loss
... homozygous Cdh23753A (G to A transition at nucleotide 753 in exon 7; this base change causes the in-frame skipping of exon 7) alleles carried by the B6 inbred strain is reported to be associated with the noise-induced hearing loss observed in this strain [18]. Our B6 was a Cdh23753A homozygote genot ...
... homozygous Cdh23753A (G to A transition at nucleotide 753 in exon 7; this base change causes the in-frame skipping of exon 7) alleles carried by the B6 inbred strain is reported to be associated with the noise-induced hearing loss observed in this strain [18]. Our B6 was a Cdh23753A homozygote genot ...
Identifying and Controlling Defective Genes.
... To determine if a disorder has a genetic component, first research its frequency in the breed. Has the disorder been reported previously in your breed? To find out, research veterinary Journals, breed-related publications and breed surveys. Has the disorder been reported in any other breeds, or even ...
... To determine if a disorder has a genetic component, first research its frequency in the breed. Has the disorder been reported previously in your breed? To find out, research veterinary Journals, breed-related publications and breed surveys. Has the disorder been reported in any other breeds, or even ...
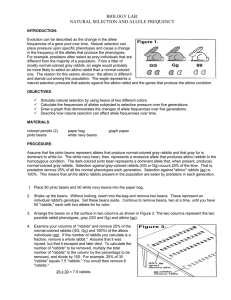
BIOLOGY LAB: NATURAL SELECTION AND ALLELE FREQUENCY
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
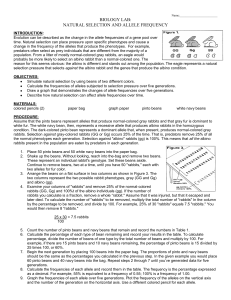
BIOLOGY LAB: NATURAL SELECTION AND ALLELE FREQUENCY
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
Genetics 101 - The Green Isle
... What are the genotypic and phenotypic possibilities for offspring if the parents are TtFf and ttFf? ...
... What are the genotypic and phenotypic possibilities for offspring if the parents are TtFf and ttFf? ...
Basic Genetics - The Institute of Canine Biology
... cannot be distinguished from the homozygous dominant state. This is by no means the only possibility, and in fact as DNA analysis advances, it may become rare. Even without such analysis, however, there are many loci where three phenotypes (appearances) come from two alleles. An example is merle in ...
... cannot be distinguished from the homozygous dominant state. This is by no means the only possibility, and in fact as DNA analysis advances, it may become rare. Even without such analysis, however, there are many loci where three phenotypes (appearances) come from two alleles. An example is merle in ...
Genotyping BoLA-DRB3 alleles in Brazilian Dairy Gir cattle (Bos
... studies, genotyping was carried out using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism of the amplified fragments (PCR-RFLP) for assignment of alleles. This methodology cannot accurately determine differences between all current alleles, and this may have led to the differe ...
... studies, genotyping was carried out using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism of the amplified fragments (PCR-RFLP) for assignment of alleles. This methodology cannot accurately determine differences between all current alleles, and this may have led to the differe ...
Basic Plant and Animal Breeding
... Later cells descending from this parent cell in which the new mutation occurred could show the new mutation, providing it were dominant and could have effects different than observed in other cells in the surrounding tissues. An example is the appearance of brown spot within the otherwise blue eye i ...
... Later cells descending from this parent cell in which the new mutation occurred could show the new mutation, providing it were dominant and could have effects different than observed in other cells in the surrounding tissues. An example is the appearance of brown spot within the otherwise blue eye i ...
Genetic Improvement and Crossbreeding in Meat Goats
... Genetically speaking, we expect individuals of the same breed to share a higher frequency of the same genes than individuals of a different breed. This is what makes the characteristics of animals of the same breed more or less uniform and somewhat predictable generation to generation. Generally it ...
... Genetically speaking, we expect individuals of the same breed to share a higher frequency of the same genes than individuals of a different breed. This is what makes the characteristics of animals of the same breed more or less uniform and somewhat predictable generation to generation. Generally it ...