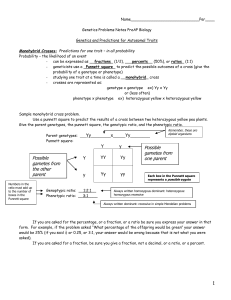
Solving Genetics Problems I: Monohybrid Crosses
... Step Five: Figure out the Phenotype ratio for your predicted babies. ...
... Step Five: Figure out the Phenotype ratio for your predicted babies. ...
Mendel brought an experimental and quantitative approach to
... • Each character (but one) is controlled by a single gene. • Each gene has only two alleles, one of which is completely dominant to the other. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • Each character (but one) is controlled by a single gene. • Each gene has only two alleles, one of which is completely dominant to the other. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Psychiatry Pharmacogenetics Expanded Panel
... or at least one copy of the CYP2C19*17 allele. Individuals with homozygous CYP2C19*1 (wildtype) alleles have an extensive metabolizer phenotype (EM). Approximately 74% of Caucasians have an EM phenotype, compared to 66% of Africans and 38% of Chinese. For CYP2C19, the prevalence of poor metabolizers ...
... or at least one copy of the CYP2C19*17 allele. Individuals with homozygous CYP2C19*1 (wildtype) alleles have an extensive metabolizer phenotype (EM). Approximately 74% of Caucasians have an EM phenotype, compared to 66% of Africans and 38% of Chinese. For CYP2C19, the prevalence of poor metabolizers ...
Segregation and the Evolution of Sex Under Overdominant Selection
... range of biologically reasonable parameters in a partially sexual population that inbreeds to some extent. This result is due to genetic associations between the modifier locus and the fitness locus that are formed upon introduction of the rare modifier allele, causing double heterozygotes and doubl ...
... range of biologically reasonable parameters in a partially sexual population that inbreeds to some extent. This result is due to genetic associations between the modifier locus and the fitness locus that are formed upon introduction of the rare modifier allele, causing double heterozygotes and doubl ...
Genetics Problems Notes
... Blood Type Baby Mystery--“Using Genetics to Help Solve Mysteries” Adapted from a worksheet by Merrill Publishing Co., 1991 (Homework due _____________) Geneticists are often called upon to solve mysteries using some of the tools you have become familiar with in this chapter. Using genetic clues, giv ...
... Blood Type Baby Mystery--“Using Genetics to Help Solve Mysteries” Adapted from a worksheet by Merrill Publishing Co., 1991 (Homework due _____________) Geneticists are often called upon to solve mysteries using some of the tools you have become familiar with in this chapter. Using genetic clues, giv ...
Early frameshift alleles of zebrafish tbx5a that fail to
... complex (RNP)-mediated mutagenesis using our established sgRNA[tbx5ccA] that targets the first coding exon (Fig. 1A)11. This sgRNA targets the coding sequence in the first coding exon downstream of the conserved translation initiation codon 12. We targeted the first exon to introduce frameshift and ...
... complex (RNP)-mediated mutagenesis using our established sgRNA[tbx5ccA] that targets the first coding exon (Fig. 1A)11. This sgRNA targets the coding sequence in the first coding exon downstream of the conserved translation initiation codon 12. We targeted the first exon to introduce frameshift and ...
Chapter 12 Patterns of Inheritance
... of two traits, without blending When Mendel crossed white-flowered and purple-flowered plants, the hybrid offspring he obtained did not have flowers of inter- mediate color, as the hypothesis of blending inheritance would predict. Instead, in every case the flower color of the offspring resembled t ...
... of two traits, without blending When Mendel crossed white-flowered and purple-flowered plants, the hybrid offspring he obtained did not have flowers of inter- mediate color, as the hypothesis of blending inheritance would predict. Instead, in every case the flower color of the offspring resembled t ...
PopGen 6: Brief Introduction to Evolution by Natural Selection
... natural selection on an allele within a population, it will be useful to review the logical argument for natural selection. Natural selection will operate on any system in which there is (i) variation among individuals, (ii) individual are able to make copies of themselves, and (iii) this variation ...
... natural selection on an allele within a population, it will be useful to review the logical argument for natural selection. Natural selection will operate on any system in which there is (i) variation among individuals, (ii) individual are able to make copies of themselves, and (iii) this variation ...
Genetics
... 2C. There is no possibility that any of their children could not have freckles. Mom has two big F genes, which means she will always give her children a F. Therefore all of the children will have freckles. You need two little f’s for non-freckles. ...
... 2C. There is no possibility that any of their children could not have freckles. Mom has two big F genes, which means she will always give her children a F. Therefore all of the children will have freckles. You need two little f’s for non-freckles. ...
Pedigree Chart Qu
... Explain one piece of evidence from the diagram which proves that the allele for Tay-Sachs disease is recessive. Explain one piece of evidence from the diagram which proves that the allele for Tay-Sachs disease is not on the X chromosome. In a human population, one in every 1000 children born had Tay ...
... Explain one piece of evidence from the diagram which proves that the allele for Tay-Sachs disease is recessive. Explain one piece of evidence from the diagram which proves that the allele for Tay-Sachs disease is not on the X chromosome. In a human population, one in every 1000 children born had Tay ...
Additional File 2
... mapped on the null distribution represents the probability that it is a false positive. From each null distribution, the z-scores corresponding to the probabilities at 0.005, 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 were extracted by the quantile function of R using its default parameters. Simulations and analyses are im ...
... mapped on the null distribution represents the probability that it is a false positive. From each null distribution, the z-scores corresponding to the probabilities at 0.005, 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 were extracted by the quantile function of R using its default parameters. Simulations and analyses are im ...
Notes - GitHub Pages
... with an occasional recessive allele (r) showing up that is usually deleterious. Natural selection operates mostly as purifying selection, removing recessive alleles that are deleterious. This was the view in the early 1900s that emerged from classical genetics, when the only way that “genotypes” cou ...
... with an occasional recessive allele (r) showing up that is usually deleterious. Natural selection operates mostly as purifying selection, removing recessive alleles that are deleterious. This was the view in the early 1900s that emerged from classical genetics, when the only way that “genotypes” cou ...
F - UBC Zoology
... One of the most enduring questions in evolutionary biology is why sexual reproduction has evolved and maintained itself in so many species (BELL 1982; MICHOD and LEVIN 1988). Numerous studies have proposed models to identify the conditions most favorable to the evolution and maintenance of sex and g ...
... One of the most enduring questions in evolutionary biology is why sexual reproduction has evolved and maintained itself in so many species (BELL 1982; MICHOD and LEVIN 1988). Numerous studies have proposed models to identify the conditions most favorable to the evolution and maintenance of sex and g ...
Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics What You’ll Learn
... recessive genotypes among their children would be 1:2:1. Of those genotypes possible for the members of generation II, only the homozygous recessive genotype will express the trait, which is the case for II-3. You can’t tell the genotypes of II-4 and II-5, but they have a normal phenotype. If you lo ...
... recessive genotypes among their children would be 1:2:1. Of those genotypes possible for the members of generation II, only the homozygous recessive genotype will express the trait, which is the case for II-3. You can’t tell the genotypes of II-4 and II-5, but they have a normal phenotype. If you lo ...
DOC
... reappeared: about 50% of the offspring were tall, and 50% were dwarf plants. When Mendel crossed the F1 generation peas with themselves, he found that the second generation had about 75% tall and 25% dwarf plants. On the basis of his experiments, Mendel hypothesized that traits, such as tallness, ar ...
... reappeared: about 50% of the offspring were tall, and 50% were dwarf plants. When Mendel crossed the F1 generation peas with themselves, he found that the second generation had about 75% tall and 25% dwarf plants. On the basis of his experiments, Mendel hypothesized that traits, such as tallness, ar ...
Mendel`s Pea Plants
... reasons: 1) they have easily identifiable traits, 2) they grow quickly, and 3) they can self-pollinate or be crosspollinated. Self-pollination means that only one flower is involved; the flower’s pollen lands on its own reproductive organs. Cross-pollination is done by hand, by moving pollen from on ...
... reasons: 1) they have easily identifiable traits, 2) they grow quickly, and 3) they can self-pollinate or be crosspollinated. Self-pollination means that only one flower is involved; the flower’s pollen lands on its own reproductive organs. Cross-pollination is done by hand, by moving pollen from on ...