* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2_10_14-PBS Day 20
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
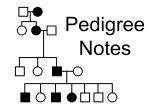
Turn in HW (Do Now and EC) to the front Do Now—2.10.14 Arthur really wants a male child with free earlobes. Kim really wants a female child with attached earlobes. Free earlobes (F) are dominant to attached earlobes (f). Arthur has attached earlobes and Kim is homozygous dominant. Is Arthur or Kim more likely to have the desired child? Turn in HW (Do Now and EC) to the front Do Now—2.10.14 Is Arthur or Kim more likely to have the desired child? Arthur is the only one who can get what he wants. 50% chance of him getting the child he wants. 0% chance of the child Kim wants because they can’t have a female child with attached earlobes. Pedigree F F X 3: Y 50% chance female 50% chance male Ff f Ff X XX XY 100% free earlobes Ff X XX XY 0% attached earlobes f Ff Unit 3: Sickle Cell Disease Test Review and Community Builder 2.10.14 Objectives SWBAT SWBAT review for their unit test. develop a strong sense of community in the classroom. Test Review Homozygous dominant Brown hair Heterozygous Blonde hair Brown hair ww WW or Ww Ss 50% 50% ss S s Ss s ss s Ss 50 ss Test Review W w W WW Ww w Ww 25% 25% ww No, ff is attached earlobes. This couple cannot have a child with attached earlobes because there is a 100% probability of free earlobes (Ff) F F f Ff Ff f Ff Ff Test Review ff Ff Ff F? Ff Ff Ff Ff ff Pedigree 3: ff F? Ff F? F? 4 7 5 ff F? F f F FF Ff f Ff ff 25% chance of child with Probability the child will have sickle cell diseasecystic is ______________________. fibrosis children also had the trait. Generations are drawn underneath the families. Pedigrees are oftengenerations, used to determine mode of parental with the the oldest generation at the top of the pedigree and the oldest individuals within a generation drawn furthest to the left. inheritance (dominant, recessive, etc.) of genetic diseases. If the purpose males of a pedigree is to represent analyze the pattern of inheritance of a particular trait, it is In a pedigree, squares represent and circles customary to shade in the symbol of all individuals females. Horizontal lines connecting a male and female representthat possess this trait. If someone does not have the trait leave the downward person blank. If the person represent is a carrier they have the allele but do not have the trait so mating. Vertical lines extending from a couple they are only half shaded—when a person is heterozygous for a recessive disease. Carriers are not their children. In the pedigree above, the grandparents had two shownThe in ason pedigree. Iftrait. you cannot determine children, a son and aalways daughter. had the One of his four someone’s genotype you but a ‘?’. children also had the trait. Generations are drawn underneath the aa" AA" parental generations, with the oldest generation at the Dominant top of the(A) Autosomal pedigree and the oldest individuals within a generation furthestdominant to the left. -Person can drawn be homozygous or heterozygous to show trait If the purpose of a pedigree is to analyze the pattern of parents inheritance a particular trait, it is -At least one of the mustof have trait -If you that cannot determine allele youdoes but anot ‘?’. have the customary to shade in the of all individuals possess this someone’s trait. If someone Aa"symbolaa" trait leave the person blank. If the person is a carrier they have the allele but do not have the trait so they are only half shaded—when a person is heterozygous for a recessive disease. CarriersAa" are not Aa" Autosomal Recessive (a) always shown in a pedigree. If you cannot determine someone’s genotype you but a ‘?’. Test Review Dd A?" Dd dd Dd dd Aa" aa" Aa" dd A?" Pedigree Practice: Autosomal Dominant (Shaded person can be homozygous dominant or heterozygous) Pedigree Practice: Autosomal Recessive (Shaded person must be homozygous recessive) Write the genotypes of each in of theeach pedigree below assuming a dominant Write the person genotype individual next to the symbol. If antrait. individual is a carrier, then indicate it. Hh hh Hh HH dd Hh Hh hh HH Autosomal Dominant (A) -Person can be homozygous dominant or -At least one of the parents must have t -If you cannot determine someone’s allel dd Autosomal Dominant (A) -Person can be homozygous dominant or h -At least one of the parents must have tr -If you cannot determine someone’s allele Autosomal Recessive (a) -Person must be homozygous recessive to show trait -Parents do not have to have the trait for a child to have it -People can be carriers (have allele but not trait = heterozygous) -If you cannot determine someone’s allele you but a ‘?’. AA" aa" Write the genotypes of each person in the pedigree below assuming a dominant trait. AA" dd dd aa" aa" dd aa" Dd Dd Aa" Pedigree Analysis A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses sym Autosomal Recessive (a) represent relationships. Theseto diagrams make it easier to -Person mustgenetic be homozygous recessive show trait visualize relationships within families, particularly large extended -Parents do not have to have the trait for a child to have it families. are(have oftenallele used but to determine mode of -People can Pedigrees be carriers not trait the = heterozygous) inheritance (dominant, recessive, etc.) of genetic diseases. -If you cannot determine someone’s allele you but a ‘?’. In a pedigree, squares represent males and circles represen females. Horizontal lines connecting a male and female represen Pedigree Practice: Autosomal Dominant (Shaded person can be hom mating. Vertical lines extending downward from a couple repres Write the genotypes of each person in the pedigree below assumin their children. In the pedigree above, the grandparents had two children, a son and a daughter. The son had the trait. One of his fo children also had the trait. Generations are drawn underneath the parental generations, with the oldest generation at the top of the pedigree and the oldest individuals within a generation drawn furth If the purpose of a pedigree is to analyze the pattern of inh customary to shade in the symbol of all individuals that possess thi trait leave the person blank. If the person is a carrier they have th they are only half shaded—when a person is heterozygous for a rec aa" Aa" always Practice: shown in aAutosomal pedigree. If you cannot determine someone’s genh Pedigree Recessive (Shaded person must be Write the genotype of each individual next to the symbol. If an in dd -Person can be homozygous dominant or heterozygous to show trait -At least one of the parents must have trait Pedigree Practice: Autosomal Dominant (Shaded person can be homozygous dominant or heterozygous) -If you cannot determine someone’s allele you but a ‘?’. dd aa" Autosomal Recessive (a) -Person must be homozygous recessive to show trait -Parents do not have to have the trait for a child to have it -People can be carriers (have allele but not trait = heterozygous) -If you cannot determine someone’s allele you but a ‘?’. Aa" AA" Pedigree Practice: Autosomal Dominant (Shaded person can be hom Write the genotypes of each person in the pedigree below assumin Pedigree Practice: Autosomal Recessive (Shaded person must be ho Write the genotype of each individual next to the symbol. If an ind aa" -Person must be homozygous recessive to show trait -Parents do not have to have the trait for a child to have it -PeopleAutosomal can be carriers (have allele Dominant (A) but not trait = heterozygous) -If you cannot determine someone’s allele you but a ‘?’. Test Review XHXh XHY XHXh XHY XHX? XHX? XHX? XHX? XHY XHY XHY XhY XHXh XHY XhY h h H XY XY X Y XHY XHXH XHXH XHY XhY Test Review Meiosis makes gametes, which are the sex cells that make offspring when they are united. Meiosis makes four non identical haploid cells (gametes). Alleles are randomly passed into the gametes during meiosis. Mitosis is two identical diploid somatic (body) cells formed. Homework Study for your test tomorrow! Community Builder Two truths and a lie Think of two things that are true about you but sound like a lie. Then you are going to share with the class the three statements (two truths and a lie), we are going to try and determine what the lie is!!!! Community Builder Write down one nice thing about each person in the class—including yourself. down one constructive thing – something they could change or improve upon. Write