Natural selection handout
... Natural resources are limited: Nutrients, water, oxygen, and other natural resources necessary for living organisms are limited in supply at any given time. Changes in populations: The unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to gradual change in a population, with the p ...
... Natural resources are limited: Nutrients, water, oxygen, and other natural resources necessary for living organisms are limited in supply at any given time. Changes in populations: The unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to gradual change in a population, with the p ...
Who Is My Mommy?
... biological traits are passed on to successive generations. • S7L3a Students will explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. • S7L3c Students will recognize that selective breeding can produce plants and animals with desired traits. ...
... biological traits are passed on to successive generations. • S7L3a Students will explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. • S7L3c Students will recognize that selective breeding can produce plants and animals with desired traits. ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
... Assortment= that genes for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes. ...
... Assortment= that genes for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes. ...
What Darwin Never Knew
... Mutations can also be caused by environmental factors, such as radiation and certain chemicals. These factors are called mutagens. ...
... Mutations can also be caused by environmental factors, such as radiation and certain chemicals. These factors are called mutagens. ...
Biology 101 – Quiz 13 – Exercise 14 – Useful Applications of Genetics
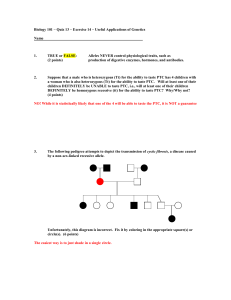
... daughter, Edna, with Noreen, a carrier of the hemophilia trait. What are the chances that Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Since Billy Bob is not a hemophiliac, Edna will receive an X chromosome with the dominant healthy ...
... daughter, Edna, with Noreen, a carrier of the hemophilia trait. What are the chances that Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Since Billy Bob is not a hemophiliac, Edna will receive an X chromosome with the dominant healthy ...
BIO101 Objectives Unit 2 1 Chapter 14 1. Describe the work of
... 3. Outline Morgan’s experiments with Drosophila eye color at Columbia U. that showed the w allele is located on the X chromosome 4. Examine the use of mutant and wildtype allele symbols in Drosophila genetics (genetic nomenclature) 5. Explain why most sex-linked genes are located on the X chromosome ...
... 3. Outline Morgan’s experiments with Drosophila eye color at Columbia U. that showed the w allele is located on the X chromosome 4. Examine the use of mutant and wildtype allele symbols in Drosophila genetics (genetic nomenclature) 5. Explain why most sex-linked genes are located on the X chromosome ...
BILL Entry 6
... BILL Entry #6 1. If 98 out of 200 individuals in a population express the recessive phenotype, what percent of the population would you predict would be heterozygotes? 2. Your original population of 200 was hit by a tidal wave and 100 organisms were wiped out, leaving 36 homozygous recessive out of ...
... BILL Entry #6 1. If 98 out of 200 individuals in a population express the recessive phenotype, what percent of the population would you predict would be heterozygotes? 2. Your original population of 200 was hit by a tidal wave and 100 organisms were wiped out, leaving 36 homozygous recessive out of ...
Population Genetics and the Hardy-Weinberg Equation
... • For every phenotype how many alleles do you have??? ...
... • For every phenotype how many alleles do you have??? ...
Hardy-Weinberg Genetic Equilibrium
... Mutations occur normally but at extremely low rates. Mutations do not cause gene frequencies to change. ...
... Mutations occur normally but at extremely low rates. Mutations do not cause gene frequencies to change. ...
Chapter 17 Review ppt
... A ________ mutation is a change in an organism’s genetic material that does not affect its overall fitness ...
... A ________ mutation is a change in an organism’s genetic material that does not affect its overall fitness ...
Natural Selection
... • Those changes are called adaptations. • Adaptations are inherited, therefore they ...
... • Those changes are called adaptations. • Adaptations are inherited, therefore they ...
Genetic Drift - stephen fleenor
... A population of tropical birds, H. tropicalis, live on an island in the Pacific Ocean. They are unable to fly to the closest island, which is 50 miles away. State one factor limiting their genetic variation, and predict how the genetic variation would change of a subset of the population which were ...
... A population of tropical birds, H. tropicalis, live on an island in the Pacific Ocean. They are unable to fly to the closest island, which is 50 miles away. State one factor limiting their genetic variation, and predict how the genetic variation would change of a subset of the population which were ...
6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles
... • An a______ is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – H___________s describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – H___________s describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. ...
... • An a______ is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – H___________s describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – H___________s describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. ...
Science Hand Out 7 - Literacy Action Network
... QUESTION: What kind of genotypes and phenotypes will result from crosses of dominant red and recessive white flowers? BACKGROUND INFORMATION: A gene is a section of DNA that holds hereditary information. It is a code for traits & characteristics. Genes come in pairs. The two genes in a pair are ...
... QUESTION: What kind of genotypes and phenotypes will result from crosses of dominant red and recessive white flowers? BACKGROUND INFORMATION: A gene is a section of DNA that holds hereditary information. It is a code for traits & characteristics. Genes come in pairs. The two genes in a pair are ...
Genetics
... DNA Fingerprinting is a procedure whereby the genetic information, called DNA, in a person's cells is analyzed and identified. The word fingerprinting is used because, just like a fingerprint, no two person's genetic code is exactly the same. It can be used to: – Determine Family Relationship - DNA ...
... DNA Fingerprinting is a procedure whereby the genetic information, called DNA, in a person's cells is analyzed and identified. The word fingerprinting is used because, just like a fingerprint, no two person's genetic code is exactly the same. It can be used to: – Determine Family Relationship - DNA ...
You Light Up My Life
... Sickle-Cell Anemia • At low oxygen levels, cells with only HbS hemoglobin “sickle” and stick together • This impedes oxygen delivery and blood flow • Over time, it causes damage throughout the body ...
... Sickle-Cell Anemia • At low oxygen levels, cells with only HbS hemoglobin “sickle” and stick together • This impedes oxygen delivery and blood flow • Over time, it causes damage throughout the body ...
The Principle of Segregation
... b. Homozygous- combination of two of the same alleles - TT = Homozygous dominant - tt = Homozygous recessive Probability- the chance that a particular event will occur A. Each trait segregates independently so offspring have a 50/50 chance of inheritance (50% father vs. 50% mother) B. Past outcomes ...
... b. Homozygous- combination of two of the same alleles - TT = Homozygous dominant - tt = Homozygous recessive Probability- the chance that a particular event will occur A. Each trait segregates independently so offspring have a 50/50 chance of inheritance (50% father vs. 50% mother) B. Past outcomes ...
Microevolution - Cloudfront.net
... morph declines if it becomes too common; i.e., parasite/host) ...
... morph declines if it becomes too common; i.e., parasite/host) ...
Genetics Mark Schedule 2010
... characteristic that is harmful is unlikely to become established as it will be selected against due to the individual’s chances of survival and successful reproduction being reduced. • An allele / phenotype / trait / characteristic that is favourable will be selected for and become established in th ...
... characteristic that is harmful is unlikely to become established as it will be selected against due to the individual’s chances of survival and successful reproduction being reduced. • An allele / phenotype / trait / characteristic that is favourable will be selected for and become established in th ...
File
... 2. Which of the following is NOT a pre-zygotic isolating mechanism? C. production of sterile hybrids 3. Behavioral isolating mechanisms may occur when two species have different B. courtship displays ...
... 2. Which of the following is NOT a pre-zygotic isolating mechanism? C. production of sterile hybrids 3. Behavioral isolating mechanisms may occur when two species have different B. courtship displays ...
Population Genetics and Speciation Notes
... 15 individuals in the population (each organism has 2 alleles per trait), thus = 30 alleles for trait - if 6 alleles in this population are of the b variety, & 24 are of the B variety, then frequencies of alleles are: * 6/30 of the genes in the gene pool are b - a frequency of 0.2 * 6/24 of the gene ...
... 15 individuals in the population (each organism has 2 alleles per trait), thus = 30 alleles for trait - if 6 alleles in this population are of the b variety, & 24 are of the B variety, then frequencies of alleles are: * 6/30 of the genes in the gene pool are b - a frequency of 0.2 * 6/24 of the gene ...