3 - Cell Structure and Function
... Have their own DNA (mtDNA) and ribosomes – The size of mitochondria (and chloroplasts in plant cells), along with their bacteria-like DNA and ribosomes, supports the theory of endosymbiosis… • Ingested (but not destroyed) aerobic bacteria eventually became mitochondria, and ingested photosynthetic ...
... Have their own DNA (mtDNA) and ribosomes – The size of mitochondria (and chloroplasts in plant cells), along with their bacteria-like DNA and ribosomes, supports the theory of endosymbiosis… • Ingested (but not destroyed) aerobic bacteria eventually became mitochondria, and ingested photosynthetic ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • The ions trigger the cellular response upon entry • This are most common in the nervous system where ligands are neurotransmitters and the ions change the polarity of the cell ...
... • The ions trigger the cellular response upon entry • This are most common in the nervous system where ligands are neurotransmitters and the ions change the polarity of the cell ...
2 SIX KINGDOMS Nelson
... living prokaryotes are far more diverse than anyone had previously suspected. This research led to a new level of classification above kingdoms, known as domains. The domain system better reflects the evolutionary history of life. The three domains are: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria and Eukaryota ...
... living prokaryotes are far more diverse than anyone had previously suspected. This research led to a new level of classification above kingdoms, known as domains. The domain system better reflects the evolutionary history of life. The three domains are: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria and Eukaryota ...
4 4 - Wrdsb
... balls are well—known fungi. iiarmftil fungi incitide those that cause ringworm. Dutch elm disease, and athlete’s foot. l-lowever, there are some unicellular fungi. ...
... balls are well—known fungi. iiarmftil fungi incitide those that cause ringworm. Dutch elm disease, and athlete’s foot. l-lowever, there are some unicellular fungi. ...
Document
... Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ ...
Ch 27 Prokaryotes
... left open at room temperature. This is because bacteria that encounter such an environment A. undergo death by playmoslysis. B. are unable to metabolize the glucose or fructose and thus starve to death. C. undergo death by lysis. D. suffocate once the lid is replaced. E. are unable to swim through t ...
... left open at room temperature. This is because bacteria that encounter such an environment A. undergo death by playmoslysis. B. are unable to metabolize the glucose or fructose and thus starve to death. C. undergo death by lysis. D. suffocate once the lid is replaced. E. are unable to swim through t ...
Homeostasis and Cell Transport
... Plant roots are typically always in a hypotonic environment. This is important to the survival of the organism. Water moves into the roots by osmosis and the cells swell (where is the water stored?) When it fills with water, the cell membrane swells and pushes up against the cell wall; this pressure ...
... Plant roots are typically always in a hypotonic environment. This is important to the survival of the organism. Water moves into the roots by osmosis and the cells swell (where is the water stored?) When it fills with water, the cell membrane swells and pushes up against the cell wall; this pressure ...
Rods vs Cones
... • very sensitive (low threshold) • ~100 rods share same optic nerve fiber to brain • night vision (scotopic vision) ...
... • very sensitive (low threshold) • ~100 rods share same optic nerve fiber to brain • night vision (scotopic vision) ...
Essay 2
... and exclusively freefloating ribosomes (70s, compared to normal eukaryotic 80s), and a plasmid DNA. This illustrates both a contrast of size and function between pro- and eukaryotes, but also of the hazy division between their respective defining properties. Close collaboration between pro- and euka ...
... and exclusively freefloating ribosomes (70s, compared to normal eukaryotic 80s), and a plasmid DNA. This illustrates both a contrast of size and function between pro- and eukaryotes, but also of the hazy division between their respective defining properties. Close collaboration between pro- and euka ...
Essay 2
... The most essential functions of a cell are regulated by a group of highly conserved genes. Over 200 gene families span all three domains of life, mainly involved in DNA transcription, translation and replication. Thus, the basic building blocks of life are common to both pro- and eukaryotic cells. Y ...
... The most essential functions of a cell are regulated by a group of highly conserved genes. Over 200 gene families span all three domains of life, mainly involved in DNA transcription, translation and replication. Thus, the basic building blocks of life are common to both pro- and eukaryotic cells. Y ...
Biology 2005 - Spring Branch ISD
... 1. Describe the general structure of bacteria. 2. Sketch the three shapes of bacteria. Label each. 3. Do bacteria move? Explain. 4. Bacteria may be either autotrophic or heterotrophic in order to acquire energy. Describe how this is accomplished in the following: Chemoheterotrophic bacteria Phot ...
... 1. Describe the general structure of bacteria. 2. Sketch the three shapes of bacteria. Label each. 3. Do bacteria move? Explain. 4. Bacteria may be either autotrophic or heterotrophic in order to acquire energy. Describe how this is accomplished in the following: Chemoheterotrophic bacteria Phot ...
Overheads_Other_Worlds
... The sea never falls much below 2°C Some lakes or seabeds with an exceptionally high salt concentration, this may fall to –5°C or in extreme cases, -12°C ...
... The sea never falls much below 2°C Some lakes or seabeds with an exceptionally high salt concentration, this may fall to –5°C or in extreme cases, -12°C ...
Chapter 7 Cell to Cell Interactions
... connect the cytoplasm of one plant cell to that of another connect actin fibers of one cell to the extracellular matrix of another ...
... connect the cytoplasm of one plant cell to that of another connect actin fibers of one cell to the extracellular matrix of another ...
ACTIVITY: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION, IMPORTANCE OF CELL
... way that will change the weights as they were coming out of the beaker. 5. Analysis: If you have at least three groups of students in class, you can replicate the results 3 times for each treatment (note there are 6 treatments). Data can be plugged into the excel worksheet provided, or students can ...
... way that will change the weights as they were coming out of the beaker. 5. Analysis: If you have at least three groups of students in class, you can replicate the results 3 times for each treatment (note there are 6 treatments). Data can be plugged into the excel worksheet provided, or students can ...
Bacterial Form and Function
... – hollow, hairlike structures of protein larger and more sparse than fimbriae. – allow bacteria to attach to other cells. – sex pilus, - transfer from one bacterial cell to another- conjugation. ...
... – hollow, hairlike structures of protein larger and more sparse than fimbriae. – allow bacteria to attach to other cells. – sex pilus, - transfer from one bacterial cell to another- conjugation. ...
No Slide Title
... Classes of enzyme-linked receptors: 1. Receptor tyrosine kinases - signals (secreted factors, cell-surface-bound molecules) bind extracellular domains - intracellular tyrosine kinase domain ...
... Classes of enzyme-linked receptors: 1. Receptor tyrosine kinases - signals (secreted factors, cell-surface-bound molecules) bind extracellular domains - intracellular tyrosine kinase domain ...
JMU Chemistry and Biochemistry Departmental Seminar Seeking Optimal Antibacterial Products (SOAP or NO SOAP?)
... infections. Random mutations in bacteria that cause structural or metabolic changes enable cells to survive in the presence of an antibiotic. Soaps and detergents kill bacteria by disrupting cell envelopes and destroying the cellular structure. Unfortunately, these molecules cannot be used as dru ...
... infections. Random mutations in bacteria that cause structural or metabolic changes enable cells to survive in the presence of an antibiotic. Soaps and detergents kill bacteria by disrupting cell envelopes and destroying the cellular structure. Unfortunately, these molecules cannot be used as dru ...
THE CELL MEMBRANE Composition The cell membrane is a
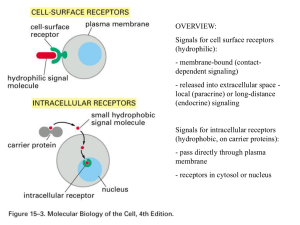
... ● One the signal is inside the cell, the signal is carried by a second messenger. ○ The most common second messenger is cyclic AMP (cAMP). ● Notice that the ligand, the first messenger, never enters the cell. ● Three examples of cell surface receptors are ion channels receptors, Gproteincouple ...
... ● One the signal is inside the cell, the signal is carried by a second messenger. ○ The most common second messenger is cyclic AMP (cAMP). ● Notice that the ligand, the first messenger, never enters the cell. ● Three examples of cell surface receptors are ion channels receptors, Gproteincouple ...
Document
... The theory suggests that some organelles found inside eukaryotes were once free-living prokaryotes. ...
... The theory suggests that some organelles found inside eukaryotes were once free-living prokaryotes. ...
Outline 4.2 (M)
... One of the most important membrane pumps in animal cells is a carrier protein called the sodiumpotassium pump. In a complete cycle, the sodium-potassium pump transports three sodium ions, Na+, out of a cell and two potassium ions, K+, into the cell. The sodium-potassium pump has four steps: 1. Three ...
... One of the most important membrane pumps in animal cells is a carrier protein called the sodiumpotassium pump. In a complete cycle, the sodium-potassium pump transports three sodium ions, Na+, out of a cell and two potassium ions, K+, into the cell. The sodium-potassium pump has four steps: 1. Three ...
Study of the cross-talk between the dopamine D2
... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute the largest family of membrane proteins. A vastly unexplored functional property of GPCRs concerns their propensity to engage in oligomeric assemblies involving two or more GPCRs to form homo- and heterodimers, as well as higher order multimers. Such GP ...
... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute the largest family of membrane proteins. A vastly unexplored functional property of GPCRs concerns their propensity to engage in oligomeric assemblies involving two or more GPCRs to form homo- and heterodimers, as well as higher order multimers. Such GP ...
Chemotaxis

Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.Positive chemotaxis occurs if the movement is toward a higher concentration of the chemical in question; negative chemotaxis if the movement is in the opposite direction. Chemically prompted kinesis (randomly directed or nondirectional) can be called chemokinesis.