The TNF and TNFR superfamilies
... cytokines and drive naïve T cells to differentiate into TH1 cells. Pathogens are also captured in multiple ways, including phagocytosis, endocytosis or via TLRs themselves. Captured pathogens are then processed and presented to T cells as major histocompatibility complex–antigen. This up-regulation ...
... cytokines and drive naïve T cells to differentiate into TH1 cells. Pathogens are also captured in multiple ways, including phagocytosis, endocytosis or via TLRs themselves. Captured pathogens are then processed and presented to T cells as major histocompatibility complex–antigen. This up-regulation ...
MELOS LIFE SEARCH PROPOSAL: SEARCH FOR MICROBES ON
... life. The “cell” should be surrounded by an impermeable membrane to define “self” and “non-self” and to distinguish inside from outside. The presence of this defining characteristic will be tested detecting the boundaries using a combination of membrane permeable and impermeable pigments. The second ...
... life. The “cell” should be surrounded by an impermeable membrane to define “self” and “non-self” and to distinguish inside from outside. The presence of this defining characteristic will be tested detecting the boundaries using a combination of membrane permeable and impermeable pigments. The second ...
Endosymbiosis Theory From prokaryotes to eukaryotes
... The DNA of mitochondria and chloroplasts is different from that of the eukaryotic cell in which they are found. As Margulis predicted, both types of organelle include DNA that is like that of prokaryotes – it is circular, not linear. The DNA of these organelles evolves independently – and at a diffe ...
... The DNA of mitochondria and chloroplasts is different from that of the eukaryotic cell in which they are found. As Margulis predicted, both types of organelle include DNA that is like that of prokaryotes – it is circular, not linear. The DNA of these organelles evolves independently – and at a diffe ...
1. The production of the genetically engineered “golden rice”... developing nations, especially in South-East Asia, because:
... B. All habitable places on Earth are already filled to capacity. C. There is much less visible light reaching Earth now than when life first originated. D. There is not enough lightening to provide an energy source. E. The oxidizing atmosphere of today’s Earth is not conducive to spontaneous formati ...
... B. All habitable places on Earth are already filled to capacity. C. There is much less visible light reaching Earth now than when life first originated. D. There is not enough lightening to provide an energy source. E. The oxidizing atmosphere of today’s Earth is not conducive to spontaneous formati ...
Chap 3 Cell Structure and Function Spring 2015
... • The smallest free-living microbe—the bacterium Mycoplasma—is nonmotile. Why is it alive, even though it cannot move? ...
... • The smallest free-living microbe—the bacterium Mycoplasma—is nonmotile. Why is it alive, even though it cannot move? ...
Name - Wsfcs
... 9.What is the function for most bacteria and how is this helpful to them? 10. Name several food products made with the help of bacteria. 11. Give an example of a photosynthetic bacterium. Most bacterial species are either spherical, called cocci (sing. coccus, from Greek kókkos, grain, and seed) or ...
... 9.What is the function for most bacteria and how is this helpful to them? 10. Name several food products made with the help of bacteria. 11. Give an example of a photosynthetic bacterium. Most bacterial species are either spherical, called cocci (sing. coccus, from Greek kókkos, grain, and seed) or ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... eukaryotic. All living organisms fall into one of three domains: Eukarya, Bacteria, or Archaea. All animals, fungi, protists, and algae are in the Eukarya domain because they have eukaryotic cells. Bacteria and Archae species are single prokaryotic cells. 2 Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus inside a m ...
... eukaryotic. All living organisms fall into one of three domains: Eukarya, Bacteria, or Archaea. All animals, fungi, protists, and algae are in the Eukarya domain because they have eukaryotic cells. Bacteria and Archae species are single prokaryotic cells. 2 Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus inside a m ...
chemical mediators of inflammation
... CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION 2 GROUPS 1.MEDIATORS RELEASED BY CELLS 2.MEDIATORS DERIVED FROM PLASMA. ...
... CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION 2 GROUPS 1.MEDIATORS RELEASED BY CELLS 2.MEDIATORS DERIVED FROM PLASMA. ...
b. Bacteria
... 19. Which is a way bacteria can cause symptoms of disease? a. They can invade parts of the body, multiplying in body tissues. b. They can poison the body with chemicals the produce and release. c. They can poison the body with chemicals that are part of the bacteria ...
... 19. Which is a way bacteria can cause symptoms of disease? a. They can invade parts of the body, multiplying in body tissues. b. They can poison the body with chemicals the produce and release. c. They can poison the body with chemicals that are part of the bacteria ...
cell theory
... Red blood cells lack a nucleus allowing more room for molecules of hemoglobin, the molecule that transports oxygen in the blood Muscle cells are tubular and specialized to contract Nerve cells have very long extensions that facilitate the transmission of impulses ...
... Red blood cells lack a nucleus allowing more room for molecules of hemoglobin, the molecule that transports oxygen in the blood Muscle cells are tubular and specialized to contract Nerve cells have very long extensions that facilitate the transmission of impulses ...
03 Endocrine and Cell Communication Hormonal Communication PPT
... • The same hormone may have different effects on target cells that have – Different receptors for the hormone – Different signal transduction pathways ...
... • The same hormone may have different effects on target cells that have – Different receptors for the hormone – Different signal transduction pathways ...
Document
... * Notice the shape of the Mitochondria. Does it remind you of any cells we have discussed before? Scientists believe that mitochondria were once rod shaped Prokaryotic Bacteria that were engulfed by other bacteria. The inner bacteria provided energy and the outer cell provided protection. This was a ...
... * Notice the shape of the Mitochondria. Does it remind you of any cells we have discussed before? Scientists believe that mitochondria were once rod shaped Prokaryotic Bacteria that were engulfed by other bacteria. The inner bacteria provided energy and the outer cell provided protection. This was a ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... hypersensitivity reactions & describe in details about type I hypersensitivity reaction. ...
... hypersensitivity reactions & describe in details about type I hypersensitivity reaction. ...
A Head
... reference to cell wall, nucleus (if any), cytoplasm, cell membrane, vacuoles, cell shape, cell size. (6 marks) ...
... reference to cell wall, nucleus (if any), cytoplasm, cell membrane, vacuoles, cell shape, cell size. (6 marks) ...
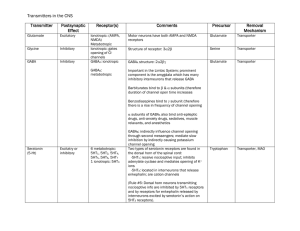
Transmitters in the CNS - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... sriatum, one group with D1 receptors and another with D2 receptors Important in the ascending arousal system Activation of nAChRs via ascending arousal system is an essential step in maintaining our level of consciousness and alertness Atropine blocks muscarinic receptors in the brainstem and cerebr ...
... sriatum, one group with D1 receptors and another with D2 receptors Important in the ascending arousal system Activation of nAChRs via ascending arousal system is an essential step in maintaining our level of consciousness and alertness Atropine blocks muscarinic receptors in the brainstem and cerebr ...
Bacterial physiology
... is used (broken down) by degradation or decomposition, into smaller pieces. • Anabolism: Anabolism is just the opposite of catabolism. In this portion of metabolism, the cell consumes energy to produce larger molecules via smaller ones. ATP is the currency of the cell. When the cell needs to use ene ...
... is used (broken down) by degradation or decomposition, into smaller pieces. • Anabolism: Anabolism is just the opposite of catabolism. In this portion of metabolism, the cell consumes energy to produce larger molecules via smaller ones. ATP is the currency of the cell. When the cell needs to use ene ...
2nd lecture Cell Biology Classification of cells: Prokaryotic cells
... 2) Indeed, bacteria can be considered as a typically prokaryotic cell, which contain essentially no organelles not even a nucleus to hold its DNA. 3) Most prokaryotes range between 1 µm to 10 µm, but they can vary in size from 0.2 µm to 750 µm. 4) They belong to two taxonomic domains, which are the ...
... 2) Indeed, bacteria can be considered as a typically prokaryotic cell, which contain essentially no organelles not even a nucleus to hold its DNA. 3) Most prokaryotes range between 1 µm to 10 µm, but they can vary in size from 0.2 µm to 750 µm. 4) They belong to two taxonomic domains, which are the ...
Essential Medical Microbiology
... pathogens include transmissibility, adherence to host cells, invasion of host cells and tissues, toxigenicity, and ability to evade the host's immune system. Disease occurs if the bacteria or immunologic reactions to their presence cause sufficient harm to the person. Transmission of Infection ...
... pathogens include transmissibility, adherence to host cells, invasion of host cells and tissues, toxigenicity, and ability to evade the host's immune system. Disease occurs if the bacteria or immunologic reactions to their presence cause sufficient harm to the person. Transmission of Infection ...
ENGAGE - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... 1600s. He observed a piece of cork under a microscope and noticed the arrangement of little boxes all in a row. He called these boxes cells because they reminded him of the rooms that monks would stay in. Hooke started observing other things under the microscope and soon discovered that all living t ...
... 1600s. He observed a piece of cork under a microscope and noticed the arrangement of little boxes all in a row. He called these boxes cells because they reminded him of the rooms that monks would stay in. Hooke started observing other things under the microscope and soon discovered that all living t ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... I. Determine if pure cultures of bacteria cause disease symptoms when introduced to a healthy host. II. Determine if disease symptoms correlate with presence of a suspected pathogen. III. Isolate the suspected pathogen and grow it in pure culture, free of other possible pathogens. IV. Attempt to iso ...
... I. Determine if pure cultures of bacteria cause disease symptoms when introduced to a healthy host. II. Determine if disease symptoms correlate with presence of a suspected pathogen. III. Isolate the suspected pathogen and grow it in pure culture, free of other possible pathogens. IV. Attempt to iso ...
Cell Communication PPT
... Signal initiated by conformational change of receptor protein When receptors are membrane proteins, the transduction stage is usually a multistep ...
... Signal initiated by conformational change of receptor protein When receptors are membrane proteins, the transduction stage is usually a multistep ...
Micro Life Revision Powerpoint
... • Why are human cells unharmed by antibiotics? An antibiotic is a poison that works to destroy bacterial cells while leaving human cells unharmed. Antibiotics destroy the cell wall of bacteria. As viruses have no cell wall, they have no effect on viruses. ...
... • Why are human cells unharmed by antibiotics? An antibiotic is a poison that works to destroy bacterial cells while leaving human cells unharmed. Antibiotics destroy the cell wall of bacteria. As viruses have no cell wall, they have no effect on viruses. ...
Chemotaxis

Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.Positive chemotaxis occurs if the movement is toward a higher concentration of the chemical in question; negative chemotaxis if the movement is in the opposite direction. Chemically prompted kinesis (randomly directed or nondirectional) can be called chemokinesis.