Photosynthesis
... What types of organisms perform photosynthesis? What is the major product of the light reaction? What is the major product of the dark reaction? Where does the light reaction occur? Where does the dark reaction occur? What molecule is split in order to release oxygen gas? What is the u ...
... What types of organisms perform photosynthesis? What is the major product of the light reaction? What is the major product of the dark reaction? Where does the light reaction occur? Where does the dark reaction occur? What molecule is split in order to release oxygen gas? What is the u ...
Chapter 6: Adaptations over Time
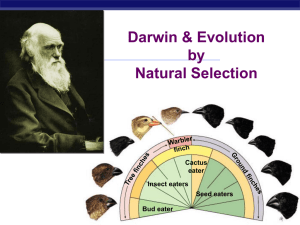
... were similar, except for differences in body size, beak shape, and eating habits, as shown in Figure 3. He also noticed that all the Galápagos finch species were similar to one finch species he had seen on the South American coast. Darwin reasoned that the Galápagos finches must have had to compete ...
... were similar, except for differences in body size, beak shape, and eating habits, as shown in Figure 3. He also noticed that all the Galápagos finch species were similar to one finch species he had seen on the South American coast. Darwin reasoned that the Galápagos finches must have had to compete ...
Vertebrate Origins 2
... probably ‘teeth.’ These are referred to as ‘conodont elements.’ Impressions of complete conodont animals have been ...
... probably ‘teeth.’ These are referred to as ‘conodont elements.’ Impressions of complete conodont animals have been ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics
... B. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. 1.) The layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. 2.) The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. 3.) The temperature inside earth increases as depth increases. C. The Layers of the Earth 1.) Cru ...
... B. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. 1.) The layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. 2.) The deeper down inside Earth, the greater the pressure. 3.) The temperature inside earth increases as depth increases. C. The Layers of the Earth 1.) Cru ...
Water Resources
... Organic compounds, such as petroleum, that contain only hydrogen and carbon • ____________________: Lack carbon-to-carbon bonds Organic compounds include natural gas, petroleum, coal, and gasoline. ...
... Organic compounds, such as petroleum, that contain only hydrogen and carbon • ____________________: Lack carbon-to-carbon bonds Organic compounds include natural gas, petroleum, coal, and gasoline. ...
biology 1406 hcc - HCC Learning Web
... the Form of DNA • Chromosomes contain most of a cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • Each DNA molecule is made up of two long chains of nucleotides arranged in a double helix • DNA is the substance of genes • Genes are the units of inheritance that transmit informatio ...
... the Form of DNA • Chromosomes contain most of a cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • Each DNA molecule is made up of two long chains of nucleotides arranged in a double helix • DNA is the substance of genes • Genes are the units of inheritance that transmit informatio ...
Gateway Biology Review
... sequence of amino acids – Information is translated from language of nucleotides to the language of amino acids – tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes where they are linked together. ...
... sequence of amino acids – Information is translated from language of nucleotides to the language of amino acids – tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes where they are linked together. ...
Gateway - OnMyCalendar
... sequence of amino acids – Information is translated from language of nucleotides to the language of amino acids – tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes where they are linked together. ...
... sequence of amino acids – Information is translated from language of nucleotides to the language of amino acids – tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes where they are linked together. ...
GEOL 100 Survey of Geology
... D. Effectively describe multiple lines of evidence that support the theory of plate tectonics and/or earth structure E. Identify and describe basic properties of minerals and rocks and understand their importance as Earth resources F. Solve quantitative problems associated with plate tectonics and/o ...
... D. Effectively describe multiple lines of evidence that support the theory of plate tectonics and/or earth structure E. Identify and describe basic properties of minerals and rocks and understand their importance as Earth resources F. Solve quantitative problems associated with plate tectonics and/o ...
Unit VIII - Evolution - Lesson Module
... and produces many offspring that are suited to continuing life in the present environment. Asexual reproduction may have a disadvantage in changing conditions because genetically identical offspring respond to the environment in the same way. If a population lacks traits that enable it to survive ...
... and produces many offspring that are suited to continuing life in the present environment. Asexual reproduction may have a disadvantage in changing conditions because genetically identical offspring respond to the environment in the same way. If a population lacks traits that enable it to survive ...
Bio 520 outline -
... 1. digestion – possess a sac, a "dead end" gut, which may be branched in order to reach all parts of the body 2. circulation – materials must reach cells by diffusion. That is why they are flat. 3. excretory – cellular waste products leave through flame cells. 4. bilaterally symmetrical 5. nervous ...
... 1. digestion – possess a sac, a "dead end" gut, which may be branched in order to reach all parts of the body 2. circulation – materials must reach cells by diffusion. That is why they are flat. 3. excretory – cellular waste products leave through flame cells. 4. bilaterally symmetrical 5. nervous ...
ESCI 107 Earth Science STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
... crustal deformation. Students learn about common earth materials that make up the Earth. The impact of weathering, erosion, running water, and glaciers on the earth’s surface and landforms is studied. Additional topics will include, but are not limited to: earthquakes, volcanoes, mass movement, geol ...
... crustal deformation. Students learn about common earth materials that make up the Earth. The impact of weathering, erosion, running water, and glaciers on the earth’s surface and landforms is studied. Additional topics will include, but are not limited to: earthquakes, volcanoes, mass movement, geol ...
Slide 1
... Rocks Formed? • Formed from sediments • Sediments moved by wind, water, ice or gravity • Heavy sediments press down on the layers beneath (compaction) • Dissolved minerals flow between particles and cement them together (cementation) ...
... Rocks Formed? • Formed from sediments • Sediments moved by wind, water, ice or gravity • Heavy sediments press down on the layers beneath (compaction) • Dissolved minerals flow between particles and cement them together (cementation) ...
Unit 1 Evolution Chp 22 Darwinism PPT
... Most fossils are found in sedimentary rocks formed from the sand and mud that settle to the bottom of seas, lakes, and marshes. New layers of sediment cover older ones and compress them into superimposed layers of rock called strata. Later, erosion may scrape or carve through upper (younger) strata ...
... Most fossils are found in sedimentary rocks formed from the sand and mud that settle to the bottom of seas, lakes, and marshes. New layers of sediment cover older ones and compress them into superimposed layers of rock called strata. Later, erosion may scrape or carve through upper (younger) strata ...
File
... b. Earthquakes have pushed the plate as they shake the crust c. The Pacific plate is moving due to changes in the Earth’s mantle d. They are moving across a volcanic hot spot 3. Over the last 250 million years the continents, which were once joined into one large land mass, moved into their current ...
... b. Earthquakes have pushed the plate as they shake the crust c. The Pacific plate is moving due to changes in the Earth’s mantle d. They are moving across a volcanic hot spot 3. Over the last 250 million years the continents, which were once joined into one large land mass, moved into their current ...
Practice Questions (269 KB pdf file)
... All the major groups of land living animals, except the birds, contain species that produce live babies. For animals that mate on land, fertilization within the female is the rule. Retaining fertile eggs within her body long enough for them to hatch there does not require major anatomical or physiol ...
... All the major groups of land living animals, except the birds, contain species that produce live babies. For animals that mate on land, fertilization within the female is the rule. Retaining fertile eggs within her body long enough for them to hatch there does not require major anatomical or physiol ...
What’s Shakin? - Oklahoma Alliance for Geographic
... What could have happened to make these differences? ...
... What could have happened to make these differences? ...
Unit 8: Invertebrates
... Their head is well-developed and has four tentacles and two of them have the eyes. They are herbivores. The tongue (radula) is rasping. They have a single muscular foot to move around. - Bivalves (E.g. Clams, cockles and mussels). They are aquatic. They have a shell with two valves. They don’t have ...
... Their head is well-developed and has four tentacles and two of them have the eyes. They are herbivores. The tongue (radula) is rasping. They have a single muscular foot to move around. - Bivalves (E.g. Clams, cockles and mussels). They are aquatic. They have a shell with two valves. They don’t have ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 1. What is a vent? 2. What happens to magma after it forms in the earth’s mantle? 3. What is a hot spot? Give an example. 4. What type of lava is rich in silica? 5. What type of volcano is formed from alternating layers of lava flow & ash? 6. How does a caldera form? 7. What happens to temperature a ...
... 1. What is a vent? 2. What happens to magma after it forms in the earth’s mantle? 3. What is a hot spot? Give an example. 4. What type of lava is rich in silica? 5. What type of volcano is formed from alternating layers of lava flow & ash? 6. How does a caldera form? 7. What happens to temperature a ...
Script - FOG - City College of San Francisco
... (mostly aluminum silicates). The remainder sits between and is known as the mantle. A similar process happens when we put chocolate and marshmallows in water – the marshmallows are less dense and float on top. The chocolate is more dense and sinks to the bottom. The water sits in the middle. Through ...
... (mostly aluminum silicates). The remainder sits between and is known as the mantle. A similar process happens when we put chocolate and marshmallows in water – the marshmallows are less dense and float on top. The chocolate is more dense and sinks to the bottom. The water sits in the middle. Through ...
Science Grade 7 2015 - HSS-High
... and simple molecules (such as water). This matter is released back into the soil and atmosphere to be reused by producers to make food and to grow. Carbon is essential to life and cycles in many forms within living systems. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enters the leaves of plants and is used in ...
... and simple molecules (such as water). This matter is released back into the soil and atmosphere to be reused by producers to make food and to grow. Carbon is essential to life and cycles in many forms within living systems. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enters the leaves of plants and is used in ...
Chapter 14 Darwin
... Analogous Structures Analogous structures are a contrast to homologous structures. They serve the same function between organisms but are different in internal anatomy. Such as the wings of birds and butterflies. These structures are of no use in classifying organisms or in working out thei ...
... Analogous Structures Analogous structures are a contrast to homologous structures. They serve the same function between organisms but are different in internal anatomy. Such as the wings of birds and butterflies. These structures are of no use in classifying organisms or in working out thei ...
Daphne High School ACOS General Biology Project This sheet must
... you will be completing this project. The science portion of the AHSGE has 90 multiple choice questions. Your completed project will be an effective tool to use as a study guide when preparing to take the AHSGE. If done properly this project will be a concise summery of what you learn throughout the ...
... you will be completing this project. The science portion of the AHSGE has 90 multiple choice questions. Your completed project will be an effective tool to use as a study guide when preparing to take the AHSGE. If done properly this project will be a concise summery of what you learn throughout the ...
Biology Test 2 Study Guide Fungi
... cytoplasm and nuclei. Fruiting bodies: part of the mushroom that is visible; responsible for spore reproduction and releasing it. Their cell walls are made of chitin. They use extracellular digestion by absorbing things; digestion takes place outside cells Types of reproduction? When/how are spores ...
... cytoplasm and nuclei. Fruiting bodies: part of the mushroom that is visible; responsible for spore reproduction and releasing it. Their cell walls are made of chitin. They use extracellular digestion by absorbing things; digestion takes place outside cells Types of reproduction? When/how are spores ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.