From Elemental Carbon to the Formation and Radiation Stability of
... C60 was detected for the first time in space in 2010 in the circumstellar medium (in certain protoplanetary nebulae) but also in the interstellar medium (for example in reflection nebulae). Actually C60 is the largest molecule known in the space. C60 once ejected in the interstellar medium can conde ...
... C60 was detected for the first time in space in 2010 in the circumstellar medium (in certain protoplanetary nebulae) but also in the interstellar medium (for example in reflection nebulae). Actually C60 is the largest molecule known in the space. C60 once ejected in the interstellar medium can conde ...
Chemotropism of Achlya ambisexualis to Methionine
... activity in A. ambisexualis. Among individual amino acids only L-methionine induced a tropic response (Table 1a). The reorientation of hyphal tips (Fig. 1d) in response to changed positions of methionine-containing donor blocks is consistent with the conclusion that this compound is chemotropically ...
... activity in A. ambisexualis. Among individual amino acids only L-methionine induced a tropic response (Table 1a). The reorientation of hyphal tips (Fig. 1d) in response to changed positions of methionine-containing donor blocks is consistent with the conclusion that this compound is chemotropically ...
Special aspects of renal metabolism
... Transamination: the funneling of amino groups into Glutemate ...
... Transamination: the funneling of amino groups into Glutemate ...
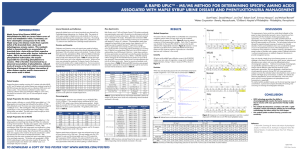
a rapid uplc™ - ms/ms method for determining specific
... can provide this separation but takes up to an hour per sample for analysis and the detection system lacks the sensitivity of mass spectrometric approaches. We have developed a rapid (less than 6minute) separation protocol utilizing UPLC with mass spectrometric analysis to monitor the individual iso ...
... can provide this separation but takes up to an hour per sample for analysis and the detection system lacks the sensitivity of mass spectrometric approaches. We have developed a rapid (less than 6minute) separation protocol utilizing UPLC with mass spectrometric analysis to monitor the individual iso ...
Amino Acids - Portal UniMAP
... The amino and carboxylic groups of amino acids readily ionized At physiological pH (7) - carboxyl group of an amino acid is unprotonated. conjugate base form (-COO-) - amino group of an amino acid is protonated. in its conjugate acid form (+NH3) Thus, each amino acid can behave as an acid or base re ...
... The amino and carboxylic groups of amino acids readily ionized At physiological pH (7) - carboxyl group of an amino acid is unprotonated. conjugate base form (-COO-) - amino group of an amino acid is protonated. in its conjugate acid form (+NH3) Thus, each amino acid can behave as an acid or base re ...
Pharos university Faculty of Allied Medical SCIENCE Biochemistry 1
... The basic structure of an amino-acid molecule consists of a carbon atom bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a fourth group that differs from one amino acid to another and often is referred to as the-R group or the side chain. ...
... The basic structure of an amino-acid molecule consists of a carbon atom bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a fourth group that differs from one amino acid to another and often is referred to as the-R group or the side chain. ...
essential amino acids
... Ala or A CH3CH(NH2)CO2H Asn or N H2NCOCH2CH(NH2)CO2H Cys or C HSCH2CH(NH2)CO2H Gln or Q H2NCOCH2CH2CH(NH2)CO2H Gly or G CH2(NH2)CO2H Ile or I CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(NH2)CO2H Leu or L (CH3)2CHCH2CH(NH2)CO2H Met or M CH3SCH2CH2CH(NH2)CO2H Phe or F C6H5CH2CH(NH2)CO2H Pro or P N CO2H H © E.V. Blackburn, 2008 ...
... Ala or A CH3CH(NH2)CO2H Asn or N H2NCOCH2CH(NH2)CO2H Cys or C HSCH2CH(NH2)CO2H Gln or Q H2NCOCH2CH2CH(NH2)CO2H Gly or G CH2(NH2)CO2H Ile or I CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(NH2)CO2H Leu or L (CH3)2CHCH2CH(NH2)CO2H Met or M CH3SCH2CH2CH(NH2)CO2H Phe or F C6H5CH2CH(NH2)CO2H Pro or P N CO2H H © E.V. Blackburn, 2008 ...
General Amino Acid Metabolism
... another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called aminotransferases. Most of the amino acids undergo these reaction except lysine and threonine The main reaction of amino Acid : A. Transamination: the tunneling of amino groups to glutamate i. Transamination is the exchange of t ...
... another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called aminotransferases. Most of the amino acids undergo these reaction except lysine and threonine The main reaction of amino Acid : A. Transamination: the tunneling of amino groups to glutamate i. Transamination is the exchange of t ...
Separation of Low Levels of Isoleucine from Leucine Using
... and quantitative composition of amino acids and mixtures of amino acids. The requirements for allowed impurities are also defined. Manufacturers of amino acids are legally bound to prove that their amino acids meet these specifications before they can distribute their products in Europe. Leucine (Le ...
... and quantitative composition of amino acids and mixtures of amino acids. The requirements for allowed impurities are also defined. Manufacturers of amino acids are legally bound to prove that their amino acids meet these specifications before they can distribute their products in Europe. Leucine (Le ...
Fundementals I
... Two cysteine side-chains react to form Cystine. Two disulfide bonds oxidized to join and form from cysteine and cysteine to form cystine. Oxidation in biochemistry usually means taking away a hydrogen atom. (take away proton and it’s associated electron) Have left: 2 protons and 2 electrons. Have ta ...
... Two cysteine side-chains react to form Cystine. Two disulfide bonds oxidized to join and form from cysteine and cysteine to form cystine. Oxidation in biochemistry usually means taking away a hydrogen atom. (take away proton and it’s associated electron) Have left: 2 protons and 2 electrons. Have ta ...
Amino acids used in Animal Nutrition
... Since there are only 20 amino acids, several will repeat! A protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains ...
... Since there are only 20 amino acids, several will repeat! A protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains ...
Lecture 17: Nitrogen metabolism
... acids. Those that cannot be synthesized have to come from diet/food. ...
... acids. Those that cannot be synthesized have to come from diet/food. ...
4. AMINO ACIDS
... • R-COOH and R-NH3+ are the protonated, or acidic partners. In these the R-COO- and R-NH2 are the conjugate bases (proton acceptors) of the corresponding acids. • Although both R-COOH and R-NH3+ are weak acids, R-COOH is a far stronger acid than is RNH3+. • At the pH of blood plasma or the intracel ...
... • R-COOH and R-NH3+ are the protonated, or acidic partners. In these the R-COO- and R-NH2 are the conjugate bases (proton acceptors) of the corresponding acids. • Although both R-COOH and R-NH3+ are weak acids, R-COOH is a far stronger acid than is RNH3+. • At the pH of blood plasma or the intracel ...
Amino acid
Amino acids (/əˈmiːnoʊ, ˈæmənoʊ, əˈmaɪnoʊ/) are biologically important organic compounds containing amine (-NH2) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional groups, usually along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, though other elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known and can be classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations as alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids; other categories relate to polarity, pH level, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acids comprise the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human muscles, cells and other tissues. Outside proteins, amino acids perform critical roles in processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.In biochemistry, amino acids having both the amine and the carboxylic acid groups attached to the first (alpha-) carbon atom have particular importance. They are known as 2-, alpha-, or α-amino acids (generic formula H2NCHRCOOH in most cases, where R is an organic substituent known as a ""side-chain""); often the term ""amino acid"" is used to refer specifically to these. They include the 22 proteinogenic (""protein-building"") amino acids, which combine into peptide chains (""polypeptides"") to form the building-blocks of a vast array of proteins. These are all L-stereoisomers (""left-handed"" isomers), although a few D-amino acids (""right-handed"") occur in bacterial envelopes and some antibiotics. Twenty of the proteinogenic amino acids are encoded directly by triplet codons in the genetic code and are known as ""standard"" amino acids. The other three (""non-standard"" or ""non-canonical"") are selenocysteine (present in many noneukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA), pyrrolysine (found only in some archea and one bacterium) and N-formylmethionine (which is often the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts). Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons; for example, selenocysteine is encoded by stop codon and SECIS element. Codon–tRNA combinations not found in nature can also be used to ""expand"" the genetic code and create novel proteins known as alloproteins incorporating non-proteinogenic amino acids.Many important proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids also play critical non-protein roles within the body. For example, in the human brain, glutamate (standard glutamic acid) and gamma-amino-butyric acid (""GABA"", non-standard gamma-amino acid) are, respectively, the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters; hydroxyproline (a major component of the connective tissue collagen) is synthesised from proline; the standard amino acid glycine is used to synthesise porphyrins used in red blood cells; and the non-standard carnitine is used in lipid transport.Nine proteinogenic amino acids are called ""essential"" for humans because they cannot be created from other compounds by the human body and, so, must be taken in as food. Others may be conditionally essential for certain ages or medical conditions. Essential amino acids may also differ between species.Because of their biological significance, amino acids are important in nutrition and are commonly used in nutritional supplements, fertilizers, and food technology. Industrial uses include the production of drugs, biodegradable plastics, and chiral catalysts.