OCHeM.com ©1999 Thomas Poon Amino Acids, Peptides, and
... Be able to predict the structure of any amino acid based on its pKa values and the pH of the surrounding solution. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the major form of an amino acid at any pH. In general, if the pKa < pH a protic functional group will be “more acidic than th ...
... Be able to predict the structure of any amino acid based on its pKa values and the pH of the surrounding solution. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the major form of an amino acid at any pH. In general, if the pKa < pH a protic functional group will be “more acidic than th ...
Amino Acids - Newcastle University
... Amino acids are often referred to as ‘the building blocks of life’. This is because they combine in different sequences to form proteins, which are fundamental to all living organisms. There are 21 amino acids, 9 of which are called ‘essential’ because they cannot be naturally found in the body. Thi ...
... Amino acids are often referred to as ‘the building blocks of life’. This is because they combine in different sequences to form proteins, which are fundamental to all living organisms. There are 21 amino acids, 9 of which are called ‘essential’ because they cannot be naturally found in the body. Thi ...
All amino acids participate in these reactions at some
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
Amino Acids Worksheet and Problem Set
... What does the R group determine for an amino acid and why is it important? Which are the aliphatic amino acids? (Group 1) Which are the Group 2 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 3 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 4 amino acids and why? Chapter 3.3: Draw the normal structure of a gener ...
... What does the R group determine for an amino acid and why is it important? Which are the aliphatic amino acids? (Group 1) Which are the Group 2 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 3 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 4 amino acids and why? Chapter 3.3: Draw the normal structure of a gener ...
Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]
... Proteins are naturally-occurring biopolymers comprised of amino acids. ...
... Proteins are naturally-occurring biopolymers comprised of amino acids. ...
homework 3 assigned
... Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corresponding amino acids. You may omit error c ...
... Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corresponding amino acids. You may omit error c ...
Pulsatílla praténsis
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
Amino acid Metabolism 2
... 5. T/F It is possible for an amino acid to be both ketogenic and glucogenic. ...
... 5. T/F It is possible for an amino acid to be both ketogenic and glucogenic. ...
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... The stereochemical reference for amino acids is the Fischer projection of L-serine Proteins are derived exclusively from L-amino acids ...
... The stereochemical reference for amino acids is the Fischer projection of L-serine Proteins are derived exclusively from L-amino acids ...
Notes Guide Part 2
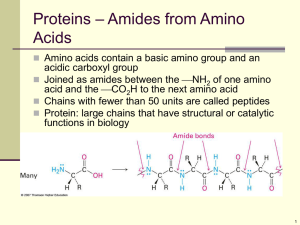
... Protein- Amino acids join by _________________________________ rxn to form dipeptides and polypeptides. ...
... Protein- Amino acids join by _________________________________ rxn to form dipeptides and polypeptides. ...
amino acid letter codes
... 2. POLAR: When the British gave Hong Kong to China, a lot of political polarization was produced by the Communists, or: HK RED H his K lys E glu (5th letter, 5 carbons) ...
... 2. POLAR: When the British gave Hong Kong to China, a lot of political polarization was produced by the Communists, or: HK RED H his K lys E glu (5th letter, 5 carbons) ...
Origin of L-Theanine in the formula LTO3
... Secondly, we say that our L-Theanine is from a plant origin, because we are talking amino acids here. Indeed, L-Theanine and L-Glutamic are amino acids. L-Glutamic acid is one of the 20 amino acids constitutive of proteins of living matter. The amino acids are molecules containing an acid function. ...
... Secondly, we say that our L-Theanine is from a plant origin, because we are talking amino acids here. Indeed, L-Theanine and L-Glutamic are amino acids. L-Glutamic acid is one of the 20 amino acids constitutive of proteins of living matter. The amino acids are molecules containing an acid function. ...
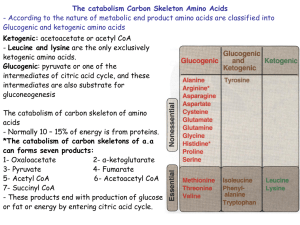
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Amino acid
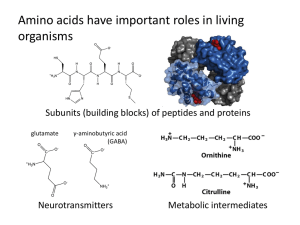
Amino acids (/əˈmiːnoʊ, ˈæmənoʊ, əˈmaɪnoʊ/) are biologically important organic compounds containing amine (-NH2) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional groups, usually along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, though other elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known and can be classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations as alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids; other categories relate to polarity, pH level, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acids comprise the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human muscles, cells and other tissues. Outside proteins, amino acids perform critical roles in processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.In biochemistry, amino acids having both the amine and the carboxylic acid groups attached to the first (alpha-) carbon atom have particular importance. They are known as 2-, alpha-, or α-amino acids (generic formula H2NCHRCOOH in most cases, where R is an organic substituent known as a ""side-chain""); often the term ""amino acid"" is used to refer specifically to these. They include the 22 proteinogenic (""protein-building"") amino acids, which combine into peptide chains (""polypeptides"") to form the building-blocks of a vast array of proteins. These are all L-stereoisomers (""left-handed"" isomers), although a few D-amino acids (""right-handed"") occur in bacterial envelopes and some antibiotics. Twenty of the proteinogenic amino acids are encoded directly by triplet codons in the genetic code and are known as ""standard"" amino acids. The other three (""non-standard"" or ""non-canonical"") are selenocysteine (present in many noneukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA), pyrrolysine (found only in some archea and one bacterium) and N-formylmethionine (which is often the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts). Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons; for example, selenocysteine is encoded by stop codon and SECIS element. Codon–tRNA combinations not found in nature can also be used to ""expand"" the genetic code and create novel proteins known as alloproteins incorporating non-proteinogenic amino acids.Many important proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids also play critical non-protein roles within the body. For example, in the human brain, glutamate (standard glutamic acid) and gamma-amino-butyric acid (""GABA"", non-standard gamma-amino acid) are, respectively, the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters; hydroxyproline (a major component of the connective tissue collagen) is synthesised from proline; the standard amino acid glycine is used to synthesise porphyrins used in red blood cells; and the non-standard carnitine is used in lipid transport.Nine proteinogenic amino acids are called ""essential"" for humans because they cannot be created from other compounds by the human body and, so, must be taken in as food. Others may be conditionally essential for certain ages or medical conditions. Essential amino acids may also differ between species.Because of their biological significance, amino acids are important in nutrition and are commonly used in nutritional supplements, fertilizers, and food technology. Industrial uses include the production of drugs, biodegradable plastics, and chiral catalysts.







![Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001231379_1-1c71e58dd2b4a4d156753bc870eff68b-300x300.png)