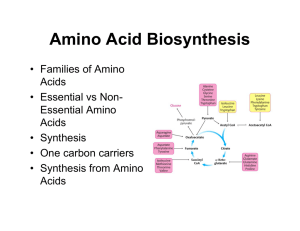
Amino Acid Synthesis
... – Glutamine dehydrogenase: reversible reaction already observed • Glutamate can serve as nitrogen source for AA in transamination ...
... – Glutamine dehydrogenase: reversible reaction already observed • Glutamate can serve as nitrogen source for AA in transamination ...
Amino acids, introduction
... Cysteine Aspartic acid (Aspartate) Glutamic acid (Glutamate) Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Methionine Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine ©CMBI 2001 ...
... Cysteine Aspartic acid (Aspartate) Glutamic acid (Glutamate) Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Methionine Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine ©CMBI 2001 ...
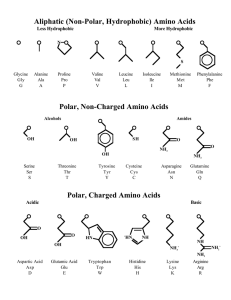
Physical properties of amino acids: Chemical properties of amino
... N2= measure of free NH2 group in protein or peptide. 6-Oxidative deamination (Removal of NH2) H ...
... N2= measure of free NH2 group in protein or peptide. 6-Oxidative deamination (Removal of NH2) H ...
Amino Acids - University of Houston
... pK1 2.2 while pK2 9.4, pKR for R group pK’s In the physiological pH range, both NH2 and COOH are completely ionized They can act as either an acid or a base ...
... pK1 2.2 while pK2 9.4, pKR for R group pK’s In the physiological pH range, both NH2 and COOH are completely ionized They can act as either an acid or a base ...
Protein Similarities II
... The "lighter" amino acids aren't necessary to the electron-carrying function; at least, they don't have to be precisely the same for the protein to work. This isn't at all unlikely. For instance, there is an alpha helix going up the left side of the image above. It probably has to be an alpha helix ...
... The "lighter" amino acids aren't necessary to the electron-carrying function; at least, they don't have to be precisely the same for the protein to work. This isn't at all unlikely. For instance, there is an alpha helix going up the left side of the image above. It probably has to be an alpha helix ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... • To know the general pKa’s of amino acids: their carboxyls, aminos, the R-group weak acids. ...
... • To know the general pKa’s of amino acids: their carboxyls, aminos, the R-group weak acids. ...
24.8 Fates of the Carbon Atoms from Amino Acids
... General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
Amino Acids slides
... 2. What is the ratio of conjugate base/acid of glutamate at pH 4.5? 3. What is the total charge of lysine at pH 7? ...
... 2. What is the ratio of conjugate base/acid of glutamate at pH 4.5? 3. What is the total charge of lysine at pH 7? ...
A - Alanine (Ala)
... An Amino Acid Code. To the left is shown twenty amino acids with their one and three-letter abbreviations. 1. Choose a partner at another table and write a short message to that partner using only the letters included in the single letter abbreviations for amino acids (no B, J, O, U, X, or Z). Write ...
... An Amino Acid Code. To the left is shown twenty amino acids with their one and three-letter abbreviations. 1. Choose a partner at another table and write a short message to that partner using only the letters included in the single letter abbreviations for amino acids (no B, J, O, U, X, or Z). Write ...
2.21 Amino Acids.docx
... 2.21 Amino Acids Similar to carbohydrates, proteins contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). However, unlike carbohydrates (and lipids) proteins also contain nitrogen (N). Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids. This name amino acid signifies that each contains an amino (N ...
... 2.21 Amino Acids Similar to carbohydrates, proteins contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). However, unlike carbohydrates (and lipids) proteins also contain nitrogen (N). Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids. This name amino acid signifies that each contains an amino (N ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... Review Problems For week 9. We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. ...
... Review Problems For week 9. We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. ...
Amino acid
Amino acids (/əˈmiːnoʊ, ˈæmənoʊ, əˈmaɪnoʊ/) are biologically important organic compounds containing amine (-NH2) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional groups, usually along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, though other elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known and can be classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations as alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids; other categories relate to polarity, pH level, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acids comprise the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human muscles, cells and other tissues. Outside proteins, amino acids perform critical roles in processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.In biochemistry, amino acids having both the amine and the carboxylic acid groups attached to the first (alpha-) carbon atom have particular importance. They are known as 2-, alpha-, or α-amino acids (generic formula H2NCHRCOOH in most cases, where R is an organic substituent known as a ""side-chain""); often the term ""amino acid"" is used to refer specifically to these. They include the 22 proteinogenic (""protein-building"") amino acids, which combine into peptide chains (""polypeptides"") to form the building-blocks of a vast array of proteins. These are all L-stereoisomers (""left-handed"" isomers), although a few D-amino acids (""right-handed"") occur in bacterial envelopes and some antibiotics. Twenty of the proteinogenic amino acids are encoded directly by triplet codons in the genetic code and are known as ""standard"" amino acids. The other three (""non-standard"" or ""non-canonical"") are selenocysteine (present in many noneukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA), pyrrolysine (found only in some archea and one bacterium) and N-formylmethionine (which is often the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts). Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons; for example, selenocysteine is encoded by stop codon and SECIS element. Codon–tRNA combinations not found in nature can also be used to ""expand"" the genetic code and create novel proteins known as alloproteins incorporating non-proteinogenic amino acids.Many important proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids also play critical non-protein roles within the body. For example, in the human brain, glutamate (standard glutamic acid) and gamma-amino-butyric acid (""GABA"", non-standard gamma-amino acid) are, respectively, the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters; hydroxyproline (a major component of the connective tissue collagen) is synthesised from proline; the standard amino acid glycine is used to synthesise porphyrins used in red blood cells; and the non-standard carnitine is used in lipid transport.Nine proteinogenic amino acids are called ""essential"" for humans because they cannot be created from other compounds by the human body and, so, must be taken in as food. Others may be conditionally essential for certain ages or medical conditions. Essential amino acids may also differ between species.Because of their biological significance, amino acids are important in nutrition and are commonly used in nutritional supplements, fertilizers, and food technology. Industrial uses include the production of drugs, biodegradable plastics, and chiral catalysts.















![Before Activity[TIGER] After Activity[DARUMA](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013178957_1-6dbed7883d701eb814f0eadede7a0279-300x300.png)