CE SG back matter - Washington Middle School
... c rust: The earth’s outer layer; the coolest and least dense layer of the earth. See also core; mantle. cumulonimbus cloud: An exceptionally dense, tall cloud that is often accompanied by heavy rain, lightning, thunder, and sometimes hail. The top is often shaped like an anvil. It is also known as a ...
... c rust: The earth’s outer layer; the coolest and least dense layer of the earth. See also core; mantle. cumulonimbus cloud: An exceptionally dense, tall cloud that is often accompanied by heavy rain, lightning, thunder, and sometimes hail. The top is often shaped like an anvil. It is also known as a ...
C21 Earth Sciences - British Geological Survey
... cycles and ecosystems which, in turn, can alter ocean–atmosphere interactions Ice sheet dynamics, particularly in relation to substrate and subglacial hydrology, directly impacts on sea level change. Human activities, such as forest clearance, agriculture, settlement affect erosion regimes, land ...
... cycles and ecosystems which, in turn, can alter ocean–atmosphere interactions Ice sheet dynamics, particularly in relation to substrate and subglacial hydrology, directly impacts on sea level change. Human activities, such as forest clearance, agriculture, settlement affect erosion regimes, land ...
EARTH SCIENCE SOL REVIEW
... Sunspots—dark, cool area that occur in pairs. Solar flares and sunspot activity are increased every 11 years. Produces disruptions in electrical service on earth. Corona—largest layer that is only visible during a solar eclipse Photosphere—produces light ...
... Sunspots—dark, cool area that occur in pairs. Solar flares and sunspot activity are increased every 11 years. Produces disruptions in electrical service on earth. Corona—largest layer that is only visible during a solar eclipse Photosphere—produces light ...
The Milky Way - Department of Physics
... a belt of high-energy particles around Earth: Van Allen belts ...
... a belt of high-energy particles around Earth: Van Allen belts ...
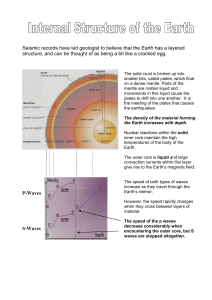
Internal Structure of the Earth File
... on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. Nuclear reactions within the solid inner ...
... on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. Nuclear reactions within the solid inner ...
Intro2-3
... The energy of colliding plates creates new landforms. When two ocean plates collide, they may form deep valleys on the ocean’s floor. When ocean plates collide with continental plates, mountain ranges are formed. Mountains are also created when two continental plates collide. When plates separate, u ...
... The energy of colliding plates creates new landforms. When two ocean plates collide, they may form deep valleys on the ocean’s floor. When ocean plates collide with continental plates, mountain ranges are formed. Mountains are also created when two continental plates collide. When plates separate, u ...
Structures of the Earth
... • Which best summarizes the COMPOSITION of the Earth’s Core? • A) It contains a solid outer region surrounding a liquid iron core. • B) It contains a liquid outer region surrounding a solid iron core. • C) It contains a semi-liquid rock outer region surrounding a liquid core. • D) It contains a basa ...
... • Which best summarizes the COMPOSITION of the Earth’s Core? • A) It contains a solid outer region surrounding a liquid iron core. • B) It contains a liquid outer region surrounding a solid iron core. • C) It contains a semi-liquid rock outer region surrounding a liquid core. • D) It contains a basa ...
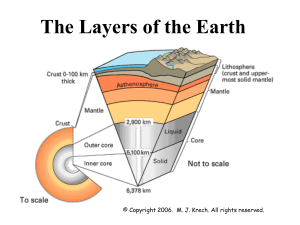
Layers of the Earth
... This layer of the earth lies between the mantle and the solid inner core. It is the only liquid layer, a sea of mostly iron and nickel ...
... This layer of the earth lies between the mantle and the solid inner core. It is the only liquid layer, a sea of mostly iron and nickel ...
6th - inside earth study guide1
... 5. Where can a compass be used for navigation & why? On land & at sea because the magnetic field of earth is so large it can be used by a compass anywhere 6. The tectonic plates are part of this Earth layer Lithosphere 7. On average, the Earth’s lithospheric plates move about how far each year? A fe ...
... 5. Where can a compass be used for navigation & why? On land & at sea because the magnetic field of earth is so large it can be used by a compass anywhere 6. The tectonic plates are part of this Earth layer Lithosphere 7. On average, the Earth’s lithospheric plates move about how far each year? A fe ...
Inside Earth Test Study Guide
... 5. Where can a compass be used for navigation & why? On land & at sea because the magnetic field of earth is so large it can be used by a compass anywhere 6. The tectonic plates are part of this Earth layer Lithosphere 7. On average, the Earth’s lithospheric plates move about how far each year? A fe ...
... 5. Where can a compass be used for navigation & why? On land & at sea because the magnetic field of earth is so large it can be used by a compass anywhere 6. The tectonic plates are part of this Earth layer Lithosphere 7. On average, the Earth’s lithospheric plates move about how far each year? A fe ...
Lecture Exam 1
... The Earth’s continents are today as they have been for the last 3.5 billion years of Earth’s history. 3____ Catastrophism is the idea that a. Earth’s landscapes have been shaped by sudden worldwide disasters b. Earth’s landscapes have been shaped suddenly by unknown forces not in operation today c. ...
... The Earth’s continents are today as they have been for the last 3.5 billion years of Earth’s history. 3____ Catastrophism is the idea that a. Earth’s landscapes have been shaped by sudden worldwide disasters b. Earth’s landscapes have been shaped suddenly by unknown forces not in operation today c. ...
Part A: Modeling Shadow Zones The structure of the Earth consists
... shockwaves from earthquakes travel through the planet, physicists have been able to work out its likely structure. Right at the heart of the Earth is a solid inner core, two thirds of the size of the Moon and composed primarily of iron. At a hellish 5,700°C, this iron is as hot as the Sun’s surface, ...
... shockwaves from earthquakes travel through the planet, physicists have been able to work out its likely structure. Right at the heart of the Earth is a solid inner core, two thirds of the size of the Moon and composed primarily of iron. At a hellish 5,700°C, this iron is as hot as the Sun’s surface, ...
Earths Layered Structure
... Meteorites formed from the same materials at the same time as the terrestrial planets. Some of them are rocky and some are metallic EQ waves were found to reflect, bounce off “something” solid in the center ...
... Meteorites formed from the same materials at the same time as the terrestrial planets. Some of them are rocky and some are metallic EQ waves were found to reflect, bounce off “something” solid in the center ...
Earth’s Layers
... The crust is composed of two rocks. The continental crust is mostly granite. The oceanic crust is basalt. Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
... The crust is composed of two rocks. The continental crust is mostly granite. The oceanic crust is basalt. Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
Layers of the Earth
... crust under oceans, and ___________________________ crust is the crust under the continents The crust can range from ____________ thick (oceanic) to _____________ thick (continental) Plate Tectonics _________________________________________ is where we find the plates. The crust is attached to the p ...
... crust under oceans, and ___________________________ crust is the crust under the continents The crust can range from ____________ thick (oceanic) to _____________ thick (continental) Plate Tectonics _________________________________________ is where we find the plates. The crust is attached to the p ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... © Copyright 2004 - 2005. M. J. Krech. All rights reserved. Reproduction for educational purposes is encouraged. ...
... © Copyright 2004 - 2005. M. J. Krech. All rights reserved. Reproduction for educational purposes is encouraged. ...
File - earth science online
... • Travels through liquids as well as solids • In all materials, P waves travel faster than do S waves – S waves • Cannot travel through liquids Seismic Waves (cont.) Seismic waves – Seismic waves refract (bend) as they pass from one material to another – P & S wave shadow zones – http://www.youtube. ...
... • Travels through liquids as well as solids • In all materials, P waves travel faster than do S waves – S waves • Cannot travel through liquids Seismic Waves (cont.) Seismic waves – Seismic waves refract (bend) as they pass from one material to another – P & S wave shadow zones – http://www.youtube. ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes Page
... what about areas such as Hawaii, and Yellowstone National Park, where volcanic activity occurs in the middle of a tectonic plate, not associated with either of these boundaries? These areas are called “Hot Spots”. ...
... what about areas such as Hawaii, and Yellowstone National Park, where volcanic activity occurs in the middle of a tectonic plate, not associated with either of these boundaries? These areas are called “Hot Spots”. ...
- Maheshtala College
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
Homework #4 - Leslie Looney
... 1. It absorbs the solar wind as it streams into Earth, thereby protecting life from these dangerous ionizing radiations. n 2. It absorbs much of the dangerous solar ultraviolet light. j k l m j 3. It acts as a disinfectant, killing dangerous viruses and bacteria that drift in all the time from k l m ...
... 1. It absorbs the solar wind as it streams into Earth, thereby protecting life from these dangerous ionizing radiations. n 2. It absorbs much of the dangerous solar ultraviolet light. j k l m j 3. It acts as a disinfectant, killing dangerous viruses and bacteria that drift in all the time from k l m ...
PDF sample
... the inner parts of the Earth. Furthermore, some, perhaps significant amounts of water originated from outside the Earth and were aquaired via impacts of comets and meteorites even after the planet formation. As the Earth cooled, water vapor condensed at the bottom of craters and valleys, which led t ...
... the inner parts of the Earth. Furthermore, some, perhaps significant amounts of water originated from outside the Earth and were aquaired via impacts of comets and meteorites even after the planet formation. As the Earth cooled, water vapor condensed at the bottom of craters and valleys, which led t ...
3.1.1 - Biosphere
... 25 kilometers and then gradually increases up to the upper boundary of the layer. The amount of water vapor in the stratosphere is very low, so it is not an important factor in the temperature regulation of the layer. Instead, it is ozone (O3) that causes the observed temperature inversion. The thir ...
... 25 kilometers and then gradually increases up to the upper boundary of the layer. The amount of water vapor in the stratosphere is very low, so it is not an important factor in the temperature regulation of the layer. Instead, it is ozone (O3) that causes the observed temperature inversion. The thir ...