14-Research quantum mechanical methods of bioobjects
... than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs. However, the electromagnetic field is not exactly zero just outside the prism. If we bring another prism very close to the first one, experiments show that the electromagnetic wave (light) appears in the second prism The situation is analogo ...
... than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs. However, the electromagnetic field is not exactly zero just outside the prism. If we bring another prism very close to the first one, experiments show that the electromagnetic wave (light) appears in the second prism The situation is analogo ...
The Phase-Resolved Spectra of the Crab Pulsar
... The field lines can be traced by numerical calculations. ...
... The field lines can be traced by numerical calculations. ...
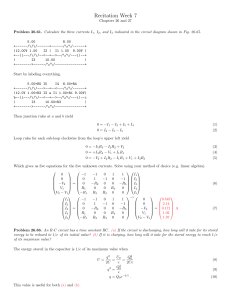
Maak onderstaande opgaven. Vermeld bij opgaven waar gerekend
... the waves is measured 35 km from the source to have an rms value of 0.42 N/C. Determine the average total power radiated by the source. (a) 4.1 × 105 W (c) 3.0 × 106 W (e) 1.7 × 107 W ...
... the waves is measured 35 km from the source to have an rms value of 0.42 N/C. Determine the average total power radiated by the source. (a) 4.1 × 105 W (c) 3.0 × 106 W (e) 1.7 × 107 W ...
Lecture 7
... Planck’s Quantum Theory: Radiation energy is dependent on wavelength Energy is emitted and absorbed in discrete units called quanta Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect Bohr’s description of the hydrogen atom Particle/wave duality of electromagnetic radiation and electrons Heisenberg’s ...
... Planck’s Quantum Theory: Radiation energy is dependent on wavelength Energy is emitted and absorbed in discrete units called quanta Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect Bohr’s description of the hydrogen atom Particle/wave duality of electromagnetic radiation and electrons Heisenberg’s ...
PPT - IIT Kanpur
... e E UP 16 2 me e - electronic charge E - electric field in the light wave - wavelength of the laser me - electronic mass Acceleration 1017 g !!! ...
... e E UP 16 2 me e - electronic charge E - electric field in the light wave - wavelength of the laser me - electronic mass Acceleration 1017 g !!! ...
Final Exam 2004
... where R is the distance between the atoms, n a unit vector in the direction joining the two atoms. For large R, the dipole-dipole interaction can be considered as a small perturbation. Show that the energy of the dipole-dipole interaction of the two atoms in their ground states is zero in the first ...
... where R is the distance between the atoms, n a unit vector in the direction joining the two atoms. For large R, the dipole-dipole interaction can be considered as a small perturbation. Show that the energy of the dipole-dipole interaction of the two atoms in their ground states is zero in the first ...
Diapositive 1 - SLC Home Page
... The maximum electron energy in a photoelectric experiment is 3.4 eV. When the wavelength of the illuminating radiation is increased by 25%, the maximum electron energy drops to 2.6 eV. (a) What is the original wavelength of the illuminating radiation? (b) What is the work function of the emitting su ...
... The maximum electron energy in a photoelectric experiment is 3.4 eV. When the wavelength of the illuminating radiation is increased by 25%, the maximum electron energy drops to 2.6 eV. (a) What is the original wavelength of the illuminating radiation? (b) What is the work function of the emitting su ...
Kinetics of Particles: Newton`s Second Law
... 12.2 NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION If the resultant force acting on a particle is not zero, the particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of the resultant and in the direction of this resultant force. More accurately ...
... 12.2 NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION If the resultant force acting on a particle is not zero, the particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of the resultant and in the direction of this resultant force. More accurately ...
Components of the Atom
... Schrödinger Equation. In the last slide, we gave a rationalization of how, if a particle behaves like a wave and is given by the de Broglie relation, then the wavefunction, , satisfies the wave equation proposed by Erwin Schrödinger. Quantum Mechanics is not “provable”, but is built upon a series ...
... Schrödinger Equation. In the last slide, we gave a rationalization of how, if a particle behaves like a wave and is given by the de Broglie relation, then the wavefunction, , satisfies the wave equation proposed by Erwin Schrödinger. Quantum Mechanics is not “provable”, but is built upon a series ...