Waves and Energy
... spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all forms of radiation. The sequence of colors in visible light can be remembered by the fictitious name Roy G. Biv - Red, Orange, ...
... spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all forms of radiation. The sequence of colors in visible light can be remembered by the fictitious name Roy G. Biv - Red, Orange, ...
From quantum to quantum computer
... A being equipped with unlimited computational power, and given complete knowledge of the positions and momenta of all particles at one instance of time, could use Newton’s equation to predict the future and retrodict the past of the whole ...
... A being equipped with unlimited computational power, and given complete knowledge of the positions and momenta of all particles at one instance of time, could use Newton’s equation to predict the future and retrodict the past of the whole ...
Overview of particle physics
... for nuclear and particle physics research different techniques suitable for different particles and energy regimes most accelerators in large research laboratories use several of these techniques in a chain of accelerators active research going on to develop new accelerating techniques for fut ...
... for nuclear and particle physics research different techniques suitable for different particles and energy regimes most accelerators in large research laboratories use several of these techniques in a chain of accelerators active research going on to develop new accelerating techniques for fut ...
Quantum Number Describes
... or troughs. FrequencyThe number of waves that pass a point each second (the unit is the Hertz, Hz). One complete wave or cycle per. second = 1 Hz. VelocityDistance a peak moves in a unit of time. ...
... or troughs. FrequencyThe number of waves that pass a point each second (the unit is the Hertz, Hz). One complete wave or cycle per. second = 1 Hz. VelocityDistance a peak moves in a unit of time. ...
Structure of Atom
... of classical mechanics & electromagnetic theory. It doesn’t give any idea about distribution of electron around the nucleus and about their energies. It was not able to explain Hydrogen spectrum. ...
... of classical mechanics & electromagnetic theory. It doesn’t give any idea about distribution of electron around the nucleus and about their energies. It was not able to explain Hydrogen spectrum. ...
Atomic Structure
... b. Bohr related his postulate to the classical picture of a hydrogen atom by quantising which quantity? c. Bohr introduced a second postulate to explain how an atom emits radiation. Explain this postulate and show how it can be used to calculate the frequency of the radiation. d. Is the Bohr model u ...
... b. Bohr related his postulate to the classical picture of a hydrogen atom by quantising which quantity? c. Bohr introduced a second postulate to explain how an atom emits radiation. Explain this postulate and show how it can be used to calculate the frequency of the radiation. d. Is the Bohr model u ...
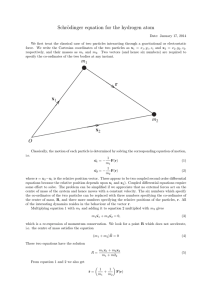
Condensed Plasmoids – The Intermediate State of LENR
... A quantum-mechanical model of this strange state of matter is provided by the author [3], which will in the following be called “condensed plasmoids (CP)”. In contrast to the quantum-mechanical model of the atom, which is based on the spherically symmetric electrostatic potential of the nucleus, the ...
... A quantum-mechanical model of this strange state of matter is provided by the author [3], which will in the following be called “condensed plasmoids (CP)”. In contrast to the quantum-mechanical model of the atom, which is based on the spherically symmetric electrostatic potential of the nucleus, the ...
General Scattering and Resonance – Getting Started
... Probably the most important new phenomena that you will see in this section is an example of a resonance. Although the exact definition of resonance is hard to formulate, the examples you will see here basically occur at "special" energies (or wavelengths or frequencies) where the wave function some ...
... Probably the most important new phenomena that you will see in this section is an example of a resonance. Although the exact definition of resonance is hard to formulate, the examples you will see here basically occur at "special" energies (or wavelengths or frequencies) where the wave function some ...
Chapt7
... related to spatial orientation of orbitals within a given subshell possible values of ml = - l, ..... 0, ....., + l the number of ml values = number of orbitals within a subshell e.g., within a subshell having l = 2, there are 5 orbitals corresponding to the 5 possible values of ml ( - 2, -1, 0, +1, ...
... related to spatial orientation of orbitals within a given subshell possible values of ml = - l, ..... 0, ....., + l the number of ml values = number of orbitals within a subshell e.g., within a subshell having l = 2, there are 5 orbitals corresponding to the 5 possible values of ml ( - 2, -1, 0, +1, ...
9. Charges in motion in a magnetic field
... .1: Equilibrium of forces. A beam of protons is accelerated to a speed of 5 x 106 m/s in a particle accelerator and emergesr horizontally from the accelerator into a uniform magnetic field. What B -field perpendicular to the velocity of the proton would cancel the force of gravity and keep the beam ...
... .1: Equilibrium of forces. A beam of protons is accelerated to a speed of 5 x 106 m/s in a particle accelerator and emergesr horizontally from the accelerator into a uniform magnetic field. What B -field perpendicular to the velocity of the proton would cancel the force of gravity and keep the beam ...
REVIEW OF WAVE MECHANICS
... Independent Schrodinger Equation is itself an eigenvalue equation. Other operators whose eigenvalues we have encountered are the momentum operator ...
... Independent Schrodinger Equation is itself an eigenvalue equation. Other operators whose eigenvalues we have encountered are the momentum operator ...
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... • Photons of just the right wavelength can knock an electron from one energy level to a higher one • To conserve energy, only photons that have the right energy will be absorbed ...
... • Photons of just the right wavelength can knock an electron from one energy level to a higher one • To conserve energy, only photons that have the right energy will be absorbed ...