Chapter 2 - UCF Chemistry
... considers both particle and wave nature of electrons • Heisenberg and Born in 1927 developed the concept of the Uncertainty Principle: It is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position (x,y,z) and momentum (mv) of an electron (or any other small particle). • Consequently, we must speak ...
... considers both particle and wave nature of electrons • Heisenberg and Born in 1927 developed the concept of the Uncertainty Principle: It is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position (x,y,z) and momentum (mv) of an electron (or any other small particle). • Consequently, we must speak ...
PPT
... so the curvature of y is ______ The wavelength is longer. y and dy/dx must be continuous here. ...
... so the curvature of y is ______ The wavelength is longer. y and dy/dx must be continuous here. ...
Chapter 7 - Gordon State College
... • There are five d and seven f-orbitals. • Three of the d-orbitals lie in a plane bisecting the x-, y- and z-axes. • Two of the d-orbitals lie in a plane aligned along the x-, y- and z-axes. • Four of the d-orbitals have four lobes ...
... • There are five d and seven f-orbitals. • Three of the d-orbitals lie in a plane bisecting the x-, y- and z-axes. • Two of the d-orbitals lie in a plane aligned along the x-, y- and z-axes. • Four of the d-orbitals have four lobes ...
The Transactional Interpretation
... • Suppose we want to find out where a ‘particle,’ such an electron, is? • The electron gets created in some state ‘Q’ • It could be in different positions a, b, c • Quantum theory just gives us probabilities for those positions: Prob(a|Q) or Prob(b|Q) or Prob(c|Q)….but no answer for why we only see ...
... • Suppose we want to find out where a ‘particle,’ such an electron, is? • The electron gets created in some state ‘Q’ • It could be in different positions a, b, c • Quantum theory just gives us probabilities for those positions: Prob(a|Q) or Prob(b|Q) or Prob(c|Q)….but no answer for why we only see ...
Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy
... 4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PE s, Q kinetic energy ...
... 4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PE s, Q kinetic energy ...
aaas
... also early in the collision, when it is at its maximum Are the quarks really free or still ...
... also early in the collision, when it is at its maximum Are the quarks really free or still ...
Dear Menon I have used bold italics to express my agreement and
... In a world where Einstein’s relativity is true, space has three dimensions, and there is quantum mechanics, all particles must be either fermions (named after Italian physicist Enrico Fermi) or bosons (named after Indian physicist Satyendra Nath Bose). This statement is a mathematical theorem, not a ...
... In a world where Einstein’s relativity is true, space has three dimensions, and there is quantum mechanics, all particles must be either fermions (named after Italian physicist Enrico Fermi) or bosons (named after Indian physicist Satyendra Nath Bose). This statement is a mathematical theorem, not a ...
Quantum Mechanics: Vibration and Rotation of Molecules
... The associated wavefunctions for the Hamiltonian are products of Gaussians and Hermite Polynomials. The Gaussian is the standard exponential in x 2 while the Hermite polynomials are a recursive set of functions possesing a special type of symmetry. The Hermite polynomials possess either even or odd ...
... The associated wavefunctions for the Hamiltonian are products of Gaussians and Hermite Polynomials. The Gaussian is the standard exponential in x 2 while the Hermite polynomials are a recursive set of functions possesing a special type of symmetry. The Hermite polynomials possess either even or odd ...
Chapter 28 Atoms
... =-3.4 eV – (-13.6 eV) = 10.2 eV B. f = E/h =((10.2 eV)(1.6x10-19 J/eV)) / (6.63x10-34 J/Hz) = 2.46x1015 Hz C. λ= c/f = (3x108 m/s )/(2.46x1015 Hz) = 1.22x10-7m ...
... =-3.4 eV – (-13.6 eV) = 10.2 eV B. f = E/h =((10.2 eV)(1.6x10-19 J/eV)) / (6.63x10-34 J/Hz) = 2.46x1015 Hz C. λ= c/f = (3x108 m/s )/(2.46x1015 Hz) = 1.22x10-7m ...
toolkit - The Open University
... placed at any given point. The electric field at a point P is a vector quantity equal to the electric force per unit charge experienced by a small test charge placed at P. electric force The force experienced by a charged particle or charged body due to an electric field. electrode A conducting plat ...
... placed at any given point. The electric field at a point P is a vector quantity equal to the electric force per unit charge experienced by a small test charge placed at P. electric force The force experienced by a charged particle or charged body due to an electric field. electrode A conducting plat ...
Interference of Waves
... 3. The principle of superposition can be used to explain why pulses are inverted when they reflect from the fixed end of a spring. a. What must the amplitude of a wave always be at the fixed end? b. If you consider the amplitude at the fixed end to be the result of the superposition of the incident ...
... 3. The principle of superposition can be used to explain why pulses are inverted when they reflect from the fixed end of a spring. a. What must the amplitude of a wave always be at the fixed end? b. If you consider the amplitude at the fixed end to be the result of the superposition of the incident ...
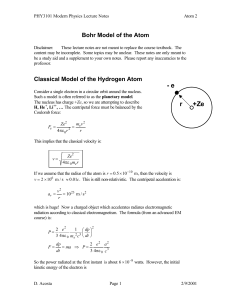
Atom 2 - UF Physics
... In other words, quantization of angular momentum implies that only particular circular orbits are allowed in the atom. The Ground State is the state when n = 1, the lowest level and smallest radius. This derived size of the atom is about what was expected at the time from indirect evidence. ...
... In other words, quantization of angular momentum implies that only particular circular orbits are allowed in the atom. The Ground State is the state when n = 1, the lowest level and smallest radius. This derived size of the atom is about what was expected at the time from indirect evidence. ...