Physics - CSUN.edu
... Waves have characteristic properties that do not depend on the type of wave. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. ...
... Waves have characteristic properties that do not depend on the type of wave. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. ...
The Nature of Light
... often called light intensity • Intensity varies inversely with square of distance from light source • Intensity measured with instrument called ...
... often called light intensity • Intensity varies inversely with square of distance from light source • Intensity measured with instrument called ...
Bound-Free Transitions
... derived by Kramers (1923) using classical physics. • A quantum mechanical correction was introduced by Gaunt (1930), known as the Gaunt factor (gbf – not the statistical weight!) ...
... derived by Kramers (1923) using classical physics. • A quantum mechanical correction was introduced by Gaunt (1930), known as the Gaunt factor (gbf – not the statistical weight!) ...
powerpoint - University of Illinois at Urbana
... *Some restrictions apply: There are observable effects due to the special theory of relativity such as the spin-orbit coupling, intersystem crossing, and other scalar relativistic effects. These effects can be substantial in heavy elements. There are also observable quantum electrodynamics effects, ...
... *Some restrictions apply: There are observable effects due to the special theory of relativity such as the spin-orbit coupling, intersystem crossing, and other scalar relativistic effects. These effects can be substantial in heavy elements. There are also observable quantum electrodynamics effects, ...
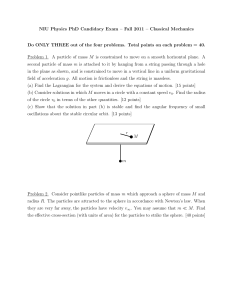
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam – Fall 2011 – Classical
... Problem 3. Consider an infinite number of identical pendulums of mass M in a uniform gravitational field with acceleration g, each hanging by a massless string of length `, and coupled to each other with massless springs of spring constant K as shown. In the equilibrium position, the springs are at ...
... Problem 3. Consider an infinite number of identical pendulums of mass M in a uniform gravitational field with acceleration g, each hanging by a massless string of length `, and coupled to each other with massless springs of spring constant K as shown. In the equilibrium position, the springs are at ...
Quantum Theory of Light, PY4T02 Problem Set 2 Paul Eastham
... (c) (Optional) Confirm directly that Maxwell’s equations reduce to the equations for a set of harmonic oscillators. 2. (a) Consider the single-mode electric field operator Ex = E0 sin(kz)(a + a† ). Calculate the expectation value and variance of the electric field when this mode is in a number state ...
... (c) (Optional) Confirm directly that Maxwell’s equations reduce to the equations for a set of harmonic oscillators. 2. (a) Consider the single-mode electric field operator Ex = E0 sin(kz)(a + a† ). Calculate the expectation value and variance of the electric field when this mode is in a number state ...
Conceptual Physics- Final Examination Review Practice
... _______20. An example of a lever is a hammer. _______21. Any change is speed or velocity is called acceleration. _______22. An object with more mass would be more difficult to stop. _______23. Energy is measured in Joules. _______24. Distance is measured in Watts. _______25. Time is measured in seco ...
... _______20. An example of a lever is a hammer. _______21. Any change is speed or velocity is called acceleration. _______22. An object with more mass would be more difficult to stop. _______23. Energy is measured in Joules. _______24. Distance is measured in Watts. _______25. Time is measured in seco ...
Homework Set #1, Physics 570S, Theoretical Atomic, Molecular, and
... Homework Set #1, Physics 570S, Theoretical Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics Due in class on Friday, Sept.13 Problem 1. A reasonable model potential energy one can use to describe atomic electrons for the lithium atom is given in atomic units by: V(r)= Z(r)/r, where Z(r)= – 1 – 2 exp(– a r) –b ...
... Homework Set #1, Physics 570S, Theoretical Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics Due in class on Friday, Sept.13 Problem 1. A reasonable model potential energy one can use to describe atomic electrons for the lithium atom is given in atomic units by: V(r)= Z(r)/r, where Z(r)= – 1 – 2 exp(– a r) –b ...
Chapter 8 - Lecture 3
... Introduction and Principles Copyright © 2006 by Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula ...
... Introduction and Principles Copyright © 2006 by Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula ...
Quantum Physics and Nuclear Physics
... These observations suggests that the nucleus must have energy levels, similar to atomic energy levels. We say a nucleus that is capable of emitting a gamma (or alpha or beta) particle is unstable. This means it is in an excited state, elevated to a higher nuclear energy level. It can become more sta ...
... These observations suggests that the nucleus must have energy levels, similar to atomic energy levels. We say a nucleus that is capable of emitting a gamma (or alpha or beta) particle is unstable. This means it is in an excited state, elevated to a higher nuclear energy level. It can become more sta ...
... equation [4] is indeed equal to zero. 2. A point charge at (0,yo,0) and a magnetic dipole at (0,-yo,0): Let us assume my volume V is again a sphere oriented at the origin with radius larger than zo so all charges and magnetic dipoles are in volume V. See Fig. 1b below. Note that for all points on th ...
D1 : Introduction to Electromagnetic exploration methods
... (a) Ground-penetrating radar is being used in a area where clay is present with resistivity of 5 Ωm. The radar generates signals at a frequency of 100 MHz (b) Low frequency radio waves from the magnetosphere have a frequency of 0.001 Hz. The crust has a resistivity of 200 Ωm. What depth will the sig ...
... (a) Ground-penetrating radar is being used in a area where clay is present with resistivity of 5 Ωm. The radar generates signals at a frequency of 100 MHz (b) Low frequency radio waves from the magnetosphere have a frequency of 0.001 Hz. The crust has a resistivity of 200 Ωm. What depth will the sig ...
I II III
... Let’s think about our calculations so far. We have an expression for transmission, containing the constants A and F. We need to determine them in order to calculate the transmission. We also wrote down solutions for the wavefunction in region II, but this just introduced two new constants, C and D. ...
... Let’s think about our calculations so far. We have an expression for transmission, containing the constants A and F. We need to determine them in order to calculate the transmission. We also wrote down solutions for the wavefunction in region II, but this just introduced two new constants, C and D. ...
1993 AP Physics B Free-Response
... a. Determine the maximum frequency of the x-rays produced by the tube. b. Determine the maximum momentum of the x-ray photons produced by the tube. An x-ray photon of the maximum energy produced by this tube leaves the tube and collides elastically with an electron at rest. As a result, the electron ...
... a. Determine the maximum frequency of the x-rays produced by the tube. b. Determine the maximum momentum of the x-ray photons produced by the tube. An x-ray photon of the maximum energy produced by this tube leaves the tube and collides elastically with an electron at rest. As a result, the electron ...