Example 11-3.
... 11.3 The Periodic and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM Important: the force in SHM is not constant, so the acceleration is not constant, so you can’t use the equations of kinematics. An object rotating in a circle (which is has a frequency and a period) is mathematically analogous to the SHM of a vibrating ...
... 11.3 The Periodic and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM Important: the force in SHM is not constant, so the acceleration is not constant, so you can’t use the equations of kinematics. An object rotating in a circle (which is has a frequency and a period) is mathematically analogous to the SHM of a vibrating ...
GRE-thermo
... A car of rest length 5 meters passes through a garage of rest length 4 meters. Due to the relativistic Lorentz contraction, the car is only 3 meters long in the garage's rest frame. There are doors on both ends of the garage, which open automatically when the front of the car reaches them and close ...
... A car of rest length 5 meters passes through a garage of rest length 4 meters. Due to the relativistic Lorentz contraction, the car is only 3 meters long in the garage's rest frame. There are doors on both ends of the garage, which open automatically when the front of the car reaches them and close ...
Solutions to the 2014 Physics Exam paper
... 18a The magnetic flux through the loop is constantly changing (1). As the loop rotates, the amount of magnetic flux through the loop increases from zero to a maximum, when the loop is face on to the field then decreases back to zero, when it is flat in the field. With further rotation the magnetic ...
... 18a The magnetic flux through the loop is constantly changing (1). As the loop rotates, the amount of magnetic flux through the loop increases from zero to a maximum, when the loop is face on to the field then decreases back to zero, when it is flat in the field. With further rotation the magnetic ...
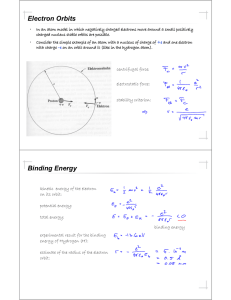
Electron Orbits
... Comment of Franck on their Experiment "It might interest you to know that when we made the experiments that we did not know Bohr's theory. We had neither read nor heard about it. We had not read it because we were negligent to read the literature well enough -- and you know how that happens. On the ...
... Comment of Franck on their Experiment "It might interest you to know that when we made the experiments that we did not know Bohr's theory. We had neither read nor heard about it. We had not read it because we were negligent to read the literature well enough -- and you know how that happens. On the ...
\chapter{Introduction}
... So where does our intuitive definition of the vacuum break down?\\ When taking into account the study of quantum mechanics, first of all the notion of a particle is blurred out, and we are to think about a wave-particle dualism. States are represented by wave vectors $|\psi\rangle$ so our volume $V$ ...
... So where does our intuitive definition of the vacuum break down?\\ When taking into account the study of quantum mechanics, first of all the notion of a particle is blurred out, and we are to think about a wave-particle dualism. States are represented by wave vectors $|\psi\rangle$ so our volume $V$ ...
Exercises - Word
... expect (Exercise 1)? What happens if you reduce the initial kinetic energy of the ion by a factor of 100? A factor of 10,000? (c) What is the kinetic energy of the ion at the end of its trajectory? How does it compare to its initial energy? ...
... expect (Exercise 1)? What happens if you reduce the initial kinetic energy of the ion by a factor of 100? A factor of 10,000? (c) What is the kinetic energy of the ion at the end of its trajectory? How does it compare to its initial energy? ...
Final
... Q (1) Consider the BCS ground state wavefunction |ΨBCS i = k (uk + vk c†k↑ c†−k↓ )|0i. (i) Calculate hΨBCS |ΨBCS i. [3 mks] (ii) Calculate hΨBCS |c−k↓ ck↑ |ΨBCS i, and express it in terms of the gap and the 1-particle energy. [4 mks] (iii) Calculate hΨBCS |bk↑ |ΨBCS i. [3 mks] (2) Show that the Lond ...
... Q (1) Consider the BCS ground state wavefunction |ΨBCS i = k (uk + vk c†k↑ c†−k↓ )|0i. (i) Calculate hΨBCS |ΨBCS i. [3 mks] (ii) Calculate hΨBCS |c−k↓ ck↑ |ΨBCS i, and express it in terms of the gap and the 1-particle energy. [4 mks] (iii) Calculate hΨBCS |bk↑ |ΨBCS i. [3 mks] (2) Show that the Lond ...
- Philsci
... The laws of physics were not handed down from above. Neither are they rules somehow built into the structure of the universe. They are ingredients of the models that physicists invent to describe observations. Rather than being restrictions on the behavior of matter, the laws of physics are restrict ...
... The laws of physics were not handed down from above. Neither are they rules somehow built into the structure of the universe. They are ingredients of the models that physicists invent to describe observations. Rather than being restrictions on the behavior of matter, the laws of physics are restrict ...
File
... Study heat and it relationship to work. Paved the way for the theory of the conservation of energy ...
... Study heat and it relationship to work. Paved the way for the theory of the conservation of energy ...
XII 2012-13 - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Ichhanath Surat
... There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one marks each., questions 9 to18 carry two marks each, questions19 to 27 carry three marks each and questions 28 to 30 carry five marks each. ...
... There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one marks each., questions 9 to18 carry two marks each, questions19 to 27 carry three marks each and questions 28 to 30 carry five marks each. ...
Balmer Series
... Universe is made of hydrogen. Emission or absorption processes in the hydrogen atom give rise to several line series, which are sequences of lines corresponding to electron transitions, each ending or beginning with the same atomic state in hydrogen. Thus, for example, the Balmer Series involves tra ...
... Universe is made of hydrogen. Emission or absorption processes in the hydrogen atom give rise to several line series, which are sequences of lines corresponding to electron transitions, each ending or beginning with the same atomic state in hydrogen. Thus, for example, the Balmer Series involves tra ...
matter unified - Swedish Association for New Physics
... The gravity process is explained in terms of an inflow process of matter from vacuum space into particles. The rate of this inflow is the Hubnle constant and the driving force is the thermal background radiation in space. The G-constant is in this way derived ...
... The gravity process is explained in terms of an inflow process of matter from vacuum space into particles. The rate of this inflow is the Hubnle constant and the driving force is the thermal background radiation in space. The G-constant is in this way derived ...
The nucleus
... Nuclear e/m moments (Krane §3.5) Electric multipole moments: - 0th or monopole moment: the electric field varies as r-2 (L=0) - 1st or dipole moment: the electric field varies as r-3 (L=1) - 2nd or quadrupole moment: the electric field varies as r-4 (L=2), etc. where L is the order of the moment We ...
... Nuclear e/m moments (Krane §3.5) Electric multipole moments: - 0th or monopole moment: the electric field varies as r-2 (L=0) - 1st or dipole moment: the electric field varies as r-3 (L=1) - 2nd or quadrupole moment: the electric field varies as r-4 (L=2), etc. where L is the order of the moment We ...